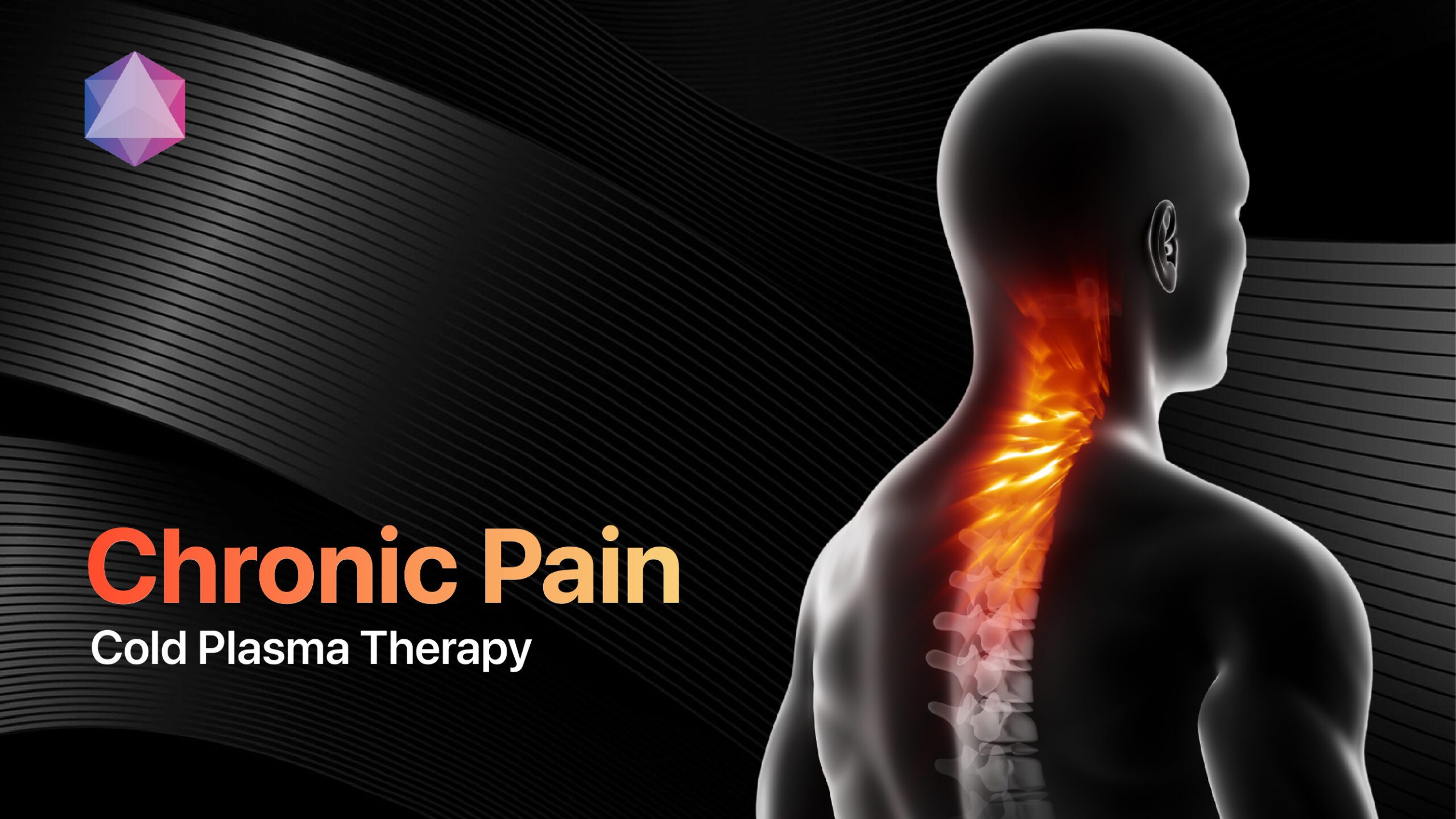
Neuropathic pain affects approximately 5% of the global population, representing one of the most challenging chronic pain conditions for both patients and healthcare providers to manage effectively[1]. This complex disorder arises from damage or dysfunction of the somatosensory nervous system, causing abnormal pain sensations that can be debilitating and resistant to conventional treatments. Unlike typical pain that serves as a protective warning, neuropathic pain persists long after the initial injury, creating a cycle of suffering that dramatically impacts quality of life and daily functioning.
Recent advances in medical technology have introduced groundbreaking treatment options that address the underlying mechanisms of neuropathic pain while providing sustained relief. The Mirari Cold Plasma System, developed by General Vibronics and commercialized by Mirari Doctor, represents a revolutionary breakthrough in non-invasive pain management, utilizing nitric oxide-based plasma therapy to modulate neural pathways and promote nerve regeneration without the risks associated with pharmaceutical interventions.
Understanding Neuropathic Pain: Mechanisms and Clinical Manifestations
What makes neuropathic pain different from other pain conditions?
Neuropathic pain occurs when the nervous system itself becomes damaged or dysfunctional, leading to abnormal pain processing and transmission[2]. Unlike nociceptive pain that results from tissue damage, neuropathic pain stems from malfunctioning nerve fibers that send incorrect signals to pain centers in the brain.
The condition manifests through several characteristic symptoms that distinguish it from other pain types:
Primary Symptoms:
- Burning, shooting, or electric shock-like sensations
- Allodynia (pain from normally non-painful stimuli)
- Hyperalgesia (increased sensitivity to painful stimuli)
- Spontaneous pain occurring without triggers
- Numbness and tingling in affected areas
Secondary Manifestations:
- Sleep disturbances and fatigue
- Depression and anxiety
- Reduced quality of life
- Functional impairment in daily activities
- Social isolation due to chronic discomfort[1]
Common causes and risk factors
Neuropathic pain can result from various underlying conditions affecting both central and peripheral nervous systems:
Central Nervous System Causes:
- Stroke and brain injuries
- Spinal cord injuries
- Multiple sclerosis
- Syringomyelia
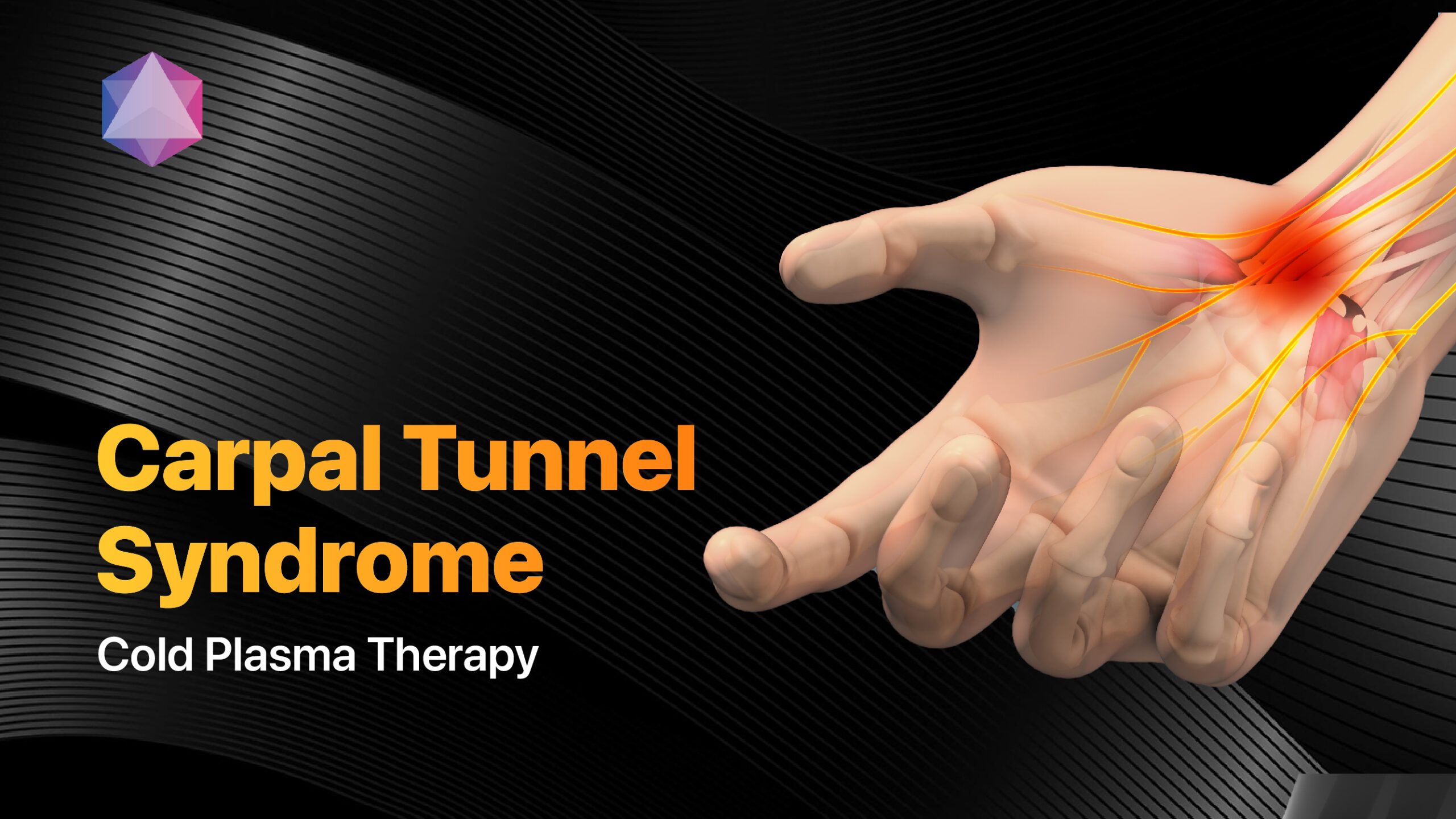
- Trigeminal neuralgia[4]
Peripheral Nervous System Causes:
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Post-herpetic neuralgia
- Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy
- Nerve compression syndromes
- Post-traumatic nerve injuries
- HIV-related neuropathy[4]
Risk Factors:
- Advanced age
- Diabetes mellitus
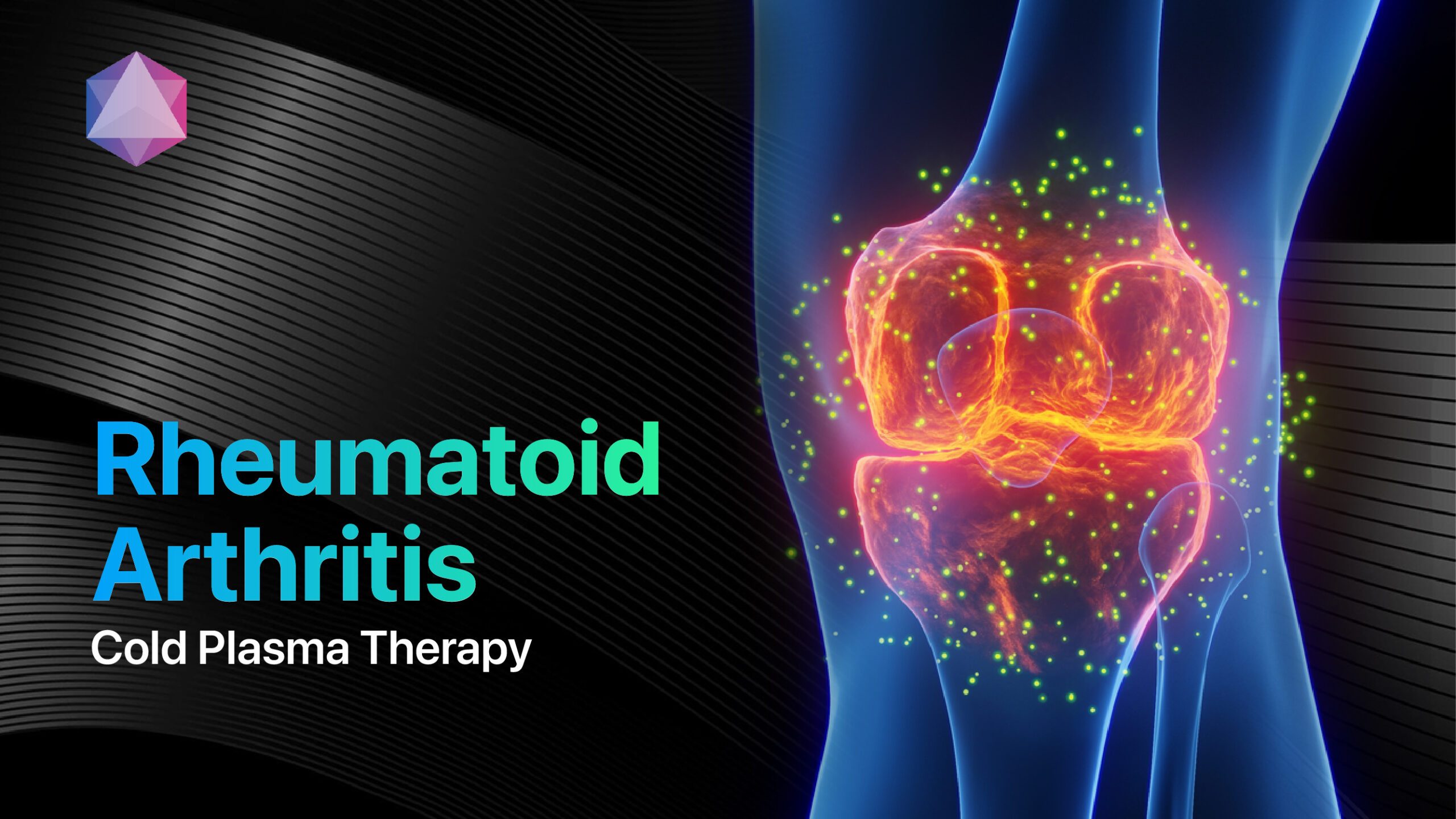
- Autoimmune disorders
- Viral infections
- Cancer treatments
- Surgical procedures
- Genetic predisposition
Pathophysiology of neuropathic pain development
The development of neuropathic pain involves complex changes in nerve structure and function. Damaged nerve fibers undergo several pathological processes:
Peripheral Sensitization:
- Increased sodium channel expression
- Altered ion channel function
- Spontaneous nerve firing
- Reduced firing thresholds
- Enhanced neurotransmitter release
Central Sensitization:
- Spinal cord hyperexcitability
- Loss of inhibitory control
- Glial cell activation
- Inflammatory cascade initiation
- Altered pain processing pathways[1]
These mechanisms create a self-perpetuating cycle where pain signals become amplified and distorted, leading to the characteristic symptoms of neuropathic pain.
Current Treatment Landscape and Limitations
Traditional approaches to neuropathic pain management
Conventional neuropathic pain treatment follows established guidelines that prioritize specific medication classes based on clinical evidence[6]. However, these approaches often provide only modest improvements and may cause significant side effects.
First-Line Treatments:
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Alpha-2-delta ligands (gabapentin, pregabalin)
- Topical lidocaine for localized pain
Second-Line Options:
- Capsaicin patches
- Topical capsaicin cream
- Lidocaine plasters
- Tramadol for specific conditions
Third-Line Interventions:
- Botulinum toxin type A
- Opioids (with caution)
- Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS)
- Spinal cord stimulation[6]
Challenges with conventional treatments
Neuropathic pain management faces significant obstacles with traditional approaches:
Limited Efficacy:
- Only 30-50% of patients achieve meaningful pain reduction
- Treatment effects are often modest
- Many patients remain inadequately treated
- High rates of treatment discontinuation
Side Effect Burden:
- Sedation and cognitive impairment
- Weight gain and metabolic changes
- Cardiovascular risks
- Gastrointestinal complications
- Drug interactions and contraindications[11]
Treatment Resistance:
- Some patients show no response to multiple medications
- Tolerance development over time
- Complex dosing requirements
- Need for combination therapies
Emerging therapeutic approaches
Recent research has identified promising new targets for neuropathic pain treatment:
Novel Mechanisms:
- HCN channel modulators
- AAK1 inhibitors
- Selective sodium channel blockers
- TRPV1 antagonists
- Nerve growth factor inhibitors
Advanced Medications:
- Mirogabalin besylate (15-30 mg daily)
- VX-548 (100 mg initial, 50 mg maintenance)
- Dextromethorphan (90 mg daily)
- Selective receptor modulators[11]
Personalized Medicine:
- Genetic testing for treatment selection
- Biomarker-guided therapy
- Patient stratification methods
- Sensory profiling approaches
Revolutionary Cold Plasma Technology for Neuropathic Pain
How cold plasma transforms neuropathic pain treatment
Cold plasma technology represents a paradigm shift in neuropathic pain management, offering patients a non-invasive, drug-free alternative that addresses underlying nerve dysfunction. The Mirari Cold Plasma System utilizes controlled ionized gas at room temperature to generate therapeutic molecules that modulate pain pathways and promote nerve regeneration[7].
Unlike traditional treatments that focus on symptom suppression, cold plasma therapy targets the fundamental mechanisms of neuropathic pain through multiple therapeutic pathways:
Neural Pathway Modulation:
- Direct effects on ion channel function
- Normalization of nerve firing patterns
- Reduction of spontaneous neural activity
- Enhanced inhibitory control mechanisms
Tissue Regeneration:
- Promotion of nerve fiber regrowth
- Schwann cell proliferation
- Myelin sheath repair
- Improved nerve conduction velocity[13]
Scientific mechanisms behind cold plasma therapy
The therapeutic effects of cold plasma in neuropathic pain treatment stem from controlled generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) that interact with damaged nerve tissues:
Nitric Oxide Production: Cold plasma significantly increases endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression, leading to enhanced NO production that directly affects neural signaling pathways. This mechanism provides both immediate pain relief and long-term nerve healing benefits[7].
Anti-inflammatory Effects: The controlled generation of reactive species reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines while enhancing anti-inflammatory mediators. This balanced approach promotes healing without the side effects associated with pharmaceutical anti-inflammatory treatments.
Cellular Repair Mechanisms: Cold plasma stimulates cellular metabolism and promotes the production of growth factors essential for nerve regeneration. These processes directly address the underlying pathology of neuropathic pain[13].
Mirari Cold Plasma System: Advanced neuropathic pain treatment
The Mirari Cold Plasma System represents the most advanced portable cold plasma technology available for neuropathic pain treatment. Available through Mirari Doctor, this innovative device has demonstrated exceptional results in clinical applications for various neurological conditions[8].
Healthcare providers report significant improvements in patient outcomes when using the Mirari system for neuropathic pain management. The device’s user-friendly design and comprehensive safety features make it suitable for various clinical settings, from specialized pain clinics to general medical practices.
Key Advantages:
- Nitric oxide-based plasma generation for enhanced safety
- Precise control over treatment parameters
- Non-thermal operation eliminating burn risks
- Portable design for flexible clinical use
- FDA-cleared technology for medical applications
Technical Specifications and Clinical Applications
Advanced features of cold plasma systems
| Parameter | Specification | Clinical Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Room temperature (20-25°C) | Eliminates thermal damage risk |
| Treatment Duration | 15-20 minutes per session | Optimal therapeutic exposure |
| Power Output | Adjustable 2-4W | Customizable treatment intensity |
| Plasma Generation | Nitric oxide-based system | Enhanced neural pathway modulation |
| Safety Features | Automatic monitoring systems | Real-time patient protection |
| Portability | Handheld design | Flexible clinical deployment |
The Mirari Cold Plasma System incorporates sophisticated engineering designed to optimize therapeutic outcomes while ensuring patient safety. The device’s ability to deliver precise, controlled doses of therapeutic plasma makes it particularly effective for neuropathic pain management across diverse patient populations[18].
Clinical benefits and treatment outcomes
Evidence-based protocols for cold plasma therapy in neuropathic pain management demonstrate significant advantages over traditional approaches:
| Application Area | Treatment Protocol | Expected Outcomes | Timeline for Relief |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetic Neuropathy | 20 minutes, 3x weekly | 40-60% pain reduction | 2-4 weeks |
| Post-Herpetic Neuralgia | 15 minutes, daily | Reduced burning sensation | 1-3 weeks |
| Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathy | 20 minutes, 2x weekly | Improved sensation | 3-6 weeks |
| Trigeminal Neuralgia | 15 minutes, 3x weekly | Decreased shooting pain | 2-5 weeks |
| Peripheral Nerve Injuries | 20 minutes, daily | Enhanced nerve function | 4-8 weeks |
| Complex Regional Pain Syndrome | 15 minutes, 2x daily | Reduced allodynia | 1-4 weeks |
The versatility of cold plasma therapy allows for customized treatment approaches based on individual patient needs and specific neuropathic pain conditions. Healthcare providers can adjust treatment parameters to optimize outcomes while maintaining safety standards[7].
Safety Profile and Clinical Evidence
Comprehensive safety data for neuropathic pain treatment
Cold plasma therapy demonstrates excellent safety profiles for neuropathic pain treatment when administered according to established protocols. Clinical studies report minimal adverse effects, with most patients experiencing only slight tingling sensations during therapy[17].
Safety Advantages:
- Non-thermal operation eliminates burn risks
- No systemic side effects unlike oral medications
- Minimal contraindications for most patients
- Excellent tolerance across age groups
- Compatible with other treatment modalities
Reported Side Effects:
- Mild skin irritation (temporary)
- Slight tingling sensation during treatment
- Minimal discomfort at treatment site
- Rare instances of skin sensitivity
- No serious adverse events in clinical studies
The adverse effects such as pain, burning sensation, and itching were mild and significantly reduced after treatment, making cold plasma therapy a well-tolerated option for patients with neuropathic pain[17].
Patient selection and treatment protocols
Neuropathic pain patients benefit from individualized treatment protocols based on pain characteristics, underlying causes, and patient factors:
Ideal Candidates:
- Patients with confirmed neuropathic pain diagnosis
- Those seeking non-pharmacological alternatives
- Individuals with medication sensitivities
- Patients with treatment-resistant conditions
- Those experiencing medication side effects
Treatment Considerations:
- Pain location and distribution
- Underlying neurological conditions
- Patient age and overall health
- Concurrent medications
- Treatment goals and expectations
Contraindications:
- Implanted electronic devices (pacemakers, defibrillators)
- Active infections at treatment sites
- Pregnancy (precautionary)
- Severe bleeding disorders
- Certain skin conditions
Comparative Analysis with Traditional Treatments
How does cold plasma compare to conventional neuropathic pain therapies?
Cold plasma therapy offers distinct advantages over traditional neuropathic pain management approaches, particularly regarding safety, efficacy, and patient satisfaction:
Efficacy Comparison:
- Cold plasma: 40-60% pain reduction in clinical studies
- Traditional medications: 30-50% response rates
- Cold plasma: Sustained improvements over time
- Medications: Often require dose escalation
Safety Profile:
- Cold plasma: Minimal local side effects
- TCAs: Sedation, weight gain, cardiac risks
- Anticonvulsants: Dizziness, cognitive impairment
- Opioids: Addiction potential, respiratory depression[6]
Patient Acceptance:
- Cold plasma: High satisfaction rates
- Medications: Frequent discontinuation due to side effects
- Cold plasma: No drug interactions
- Medications: Complex interaction profiles
Integration with multimodal pain management
The incorporation of cold plasma therapy into comprehensive neuropathic pain management protocols represents best practice in modern healthcare:
Synergistic Effects:
- Enhanced medication efficacy
- Reduced drug requirements
- Improved functional outcomes
- Better quality of life measures
Combined Approaches:
- Cold plasma with physical therapy
- Integration with psychological support
- Combination with topical treatments
- Adjunct to interventional procedures[8]
Cost-Effectiveness:
- Reduced medication costs
- Fewer healthcare visits
- Improved work productivity
- Enhanced quality of life
Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Modifications
Comprehensive neuropathic pain prevention approaches
Effective neuropathic pain prevention requires addressing modifiable risk factors and implementing protective strategies:
Diabetes Management:
- Optimal blood glucose control
- Regular monitoring and adjustment
- Lifestyle modifications
- Preventive foot care
- Early intervention for complications
Infection Prevention:
- Vaccination against shingles
- Prompt treatment of viral infections
- Immune system support
- Wound care and hygiene
- Regular health screenings
Medication Safety:
- Careful monitoring of neurotoxic drugs
- Dose optimization strategies
- Alternative medication selection
- Regular neurological assessments
- Patient education on warning signs
Lifestyle factors and neuropathic pain risk
Nutritional Support:
- B-vitamin supplementation
- Antioxidant-rich diet
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Adequate protein intake
- Limiting alcohol consumption
Physical Activity:
- Regular exercise programs
- Balance and coordination training
- Strength maintenance
- Flexibility exercises
- Activity modification as needed
Stress Management:
- Relaxation techniques
- Mindfulness practices
- Adequate sleep hygiene
- Social support systems
- Professional counseling when needed
Patient-Focused Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly can I expect relief from cold plasma treatment for my neuropathic pain?
Most patients with neuropathic pain begin experiencing symptom improvement within 2-4 weeks of starting cold plasma therapy. Clinical studies demonstrate that patients typically notice reduced burning sensations and improved nerve function within the first few treatment sessions[13]. The technology’s ability to modulate pain signaling pathways means that many patients report immediate comfort during treatment, with progressive improvement in overall symptoms over subsequent weeks. For conditions like diabetic neuropathy, patients often experience 40-60% pain reduction within the first month of treatment. Individual response times vary based on the underlying cause, severity of nerve damage, and overall health status, but most patients report meaningful improvement within the first few weeks of consistent treatment.
Can cold plasma therapy be used safely alongside my current neuropathic pain medications?
Yes, cold plasma therapy can be safely combined with most neuropathic pain medications, as it works through different mechanisms than pharmaceutical treatments. The localized nature of cold plasma means it doesn’t interfere with systemic medications such as gabapentin, pregabalin, or tricyclic antidepressants[7]. Many patients find they can reduce their medication requirements when cold plasma is included in their treatment plan, which is particularly beneficial given the side effects associated with many neuropathic pain medications. However, patients should always inform their healthcare provider about all medications they’re taking before beginning treatment. The integration of cold plasma with existing neuropathic pain management protocols often produces superior outcomes compared to single-treatment approaches, allowing for optimized symptom control with reduced medication dependence.
What should I expect during a cold plasma treatment session for neuropathic pain?
During a cold plasma treatment session for neuropathic pain, patients experience a comfortable, non-invasive procedure lasting 15-20 minutes. The healthcare provider positions the Mirari Cold Plasma device over the affected nerve distribution areas, moving the applicator systematically to ensure complete coverage[8]. Patients may feel mild warmth or tingling sensations, but the treatment remains painless and well-tolerated. Many patients report immediate relief from burning or shooting pain during the session itself. The treatment environment is similar to other outpatient procedures, with no special preparation required. Treatment frequency depends on the specific neuropathic condition and symptom severity, with typical protocols involving 2-3 sessions per week initially, followed by maintenance treatments as needed based on individual response patterns.
Are there any side effects or risks associated with cold plasma therapy for neuropathic pain?
Cold plasma therapy demonstrates excellent safety profiles for neuropathic pain treatment when administered according to established protocols. The most common side effects are mild and temporary, including slight skin irritation that resolves quickly after treatment[17]. The technology operates at room temperature, eliminating thermal burn risks while providing effective therapeutic benefits. Clinical studies report that adverse effects such as pain, burning sensation, and itching are mild and significantly reduced after treatment. The non-invasive nature of cold plasma therapy makes it suitable for patients who may not tolerate pharmaceutical interventions due to allergies or medication sensitivities. Healthcare providers should conduct thorough evaluations for patients with implanted electronic devices, active infections at treatment sites, or certain skin conditions, as these may represent contraindications to treatment.
How does the Mirari Cold Plasma System compare to other neuropathic pain treatments?
The Mirari Cold Plasma System, developed by General Vibronics and available through Mirari Doctor, offers several distinct advantages for neuropathic pain treatment compared to traditional approaches. Unlike medications that may cause sedation, weight gain, or cognitive impairment, the Mirari system provides localized treatment without systemic side effects[18]. The device’s nitric oxide-based technology provides enhanced neural pathway modulation through direct effects on nerve function, offering both immediate symptom relief and long-term nerve regeneration benefits. Healthcare providers report that patients using the Mirari system experience comprehensive improvement in neuropathic pain symptoms, including reduced burning sensations, improved sensation, and enhanced quality of life. The system’s ability to provide both immediate symptom relief and promote actual nerve healing makes it a valuable addition to comprehensive neuropathic pain management protocols, often allowing patients to reduce their reliance on medications while achieving better overall outcomes.
Medical Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with qualified healthcare providers before beginning any new treatment for neuropathic pain or other medical conditions.
References
- PMC. (2019). The neuropathic pain: An overview of the current treatment and future therapeutic approaches. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6431761/
- Cleveland Clinic. (2025). Neuropathic Pain (Nerve Pain): What It Is, Causes & Symptoms. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15833-neuropathic-pain
- ScienceDirect. (2025). Neuropathic Pain – an overview. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/pharmacology-toxicology-and-pharmaceutical-science/neuropathic-pain
- Physiopedia. (2025). Neuropathic Pain. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Neuropathic_Pain?lang=en
- Wikipedia. (2025). Neuropathic pain. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuropathic_pain
- University of the Witwatersrand. (2025). Treating Neuropathic Pain: A Review of Pharmacotherapy and Non-Invasive Neuromodulation. https://www.wits.ac.za/news/sources/health-news/2025/treating-neuropathic-pain-a-review-of-pharmacotherapy-and-non-invasive-neuromodulation.html
- Mirari Doctor. (2025). Cold Plasma in Pain Relief: Revolutionary Non-Invasive Treatment. https://miraridoctor.com/cold-plasma-in-pain-relief/
- Mirari Doctor. (2025). Mirari Cold Plasma for Chronic Pain: A Comprehensive Guide. https://miraridoctor.com/cold-plasma-for-chronic-pain/
- GlobalData. (2025). Neuropathic Pain (Neuralgia) Clinical Trial Analysis by Phase, Trial Status, End Point, Sponsor Type and Region, 2025 Update. https://www.globaldata.com/store/report/neuropathic-pain-clinical-trials-analysis/
- Physiological Reviews. (2025). Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/physrev.00045.2019
- Global RPh. (2025). Exploring New Drugs For Neuropathic Pain. https://globalrph.com/2025/01/exploring-new-drugs-for-neuropathic-pain-latest-treatment-options-video/
- PubMed. (2024). A combined treatment for self-traumatic chronic skin lesions. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39133400/
- Mirari Doctor. (2025). Neuropathic Pain Relief: The Power of Cold Plasma Therapy. https://miraridoctor.com/neuropathic-pain/
- Yahoo Finance. (2025). Neuropathic Pain (Neuralgia) Global Clinical Trials Market Review. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/neuropathic-pain-neuralgia-global-clinical-150900265.html
- ScienceDirect. (2025). Neuropathic Pain – an overview. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/neuropathic-pain
- DVC Stem. (2025). Latest Treatments for Neuropathy: Exploration & Study. https://www.dvcstem.com/post/what-is-the-latest-treatment-for-neuropathy
- Vietnam Medical Journal. (2025). Investigating Adverse Effects of Cold Plasma Therapy. https://tapchiyhocvietnam.vn/index.php/vmj/article/download/5055/4625/9322
- Mirari Doctor. (2025). Mirari Cold Plasma vs Other Plasma Technologies. https://miraridoctor.com/mirari-cold-plasma-vs-other-plasma-technologies/
- Globe Newswire. (2025). Neuropathic Pain (Neuralgia) Global Clinical Trials Market Review 2025. https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/05/23/3087586/28124/en/Neuropathic-Pain-Neuralgia-Global-Clinical-Trials-Market-Review-2025-Explore-Trial-Numbers-Enrollment-Data-Prominent-Drugs-and-Regional-Insights.html
- Physiopedia. (2025). Neuropathic Pain. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Neuropathic_Pain
Related articles
Made in USA