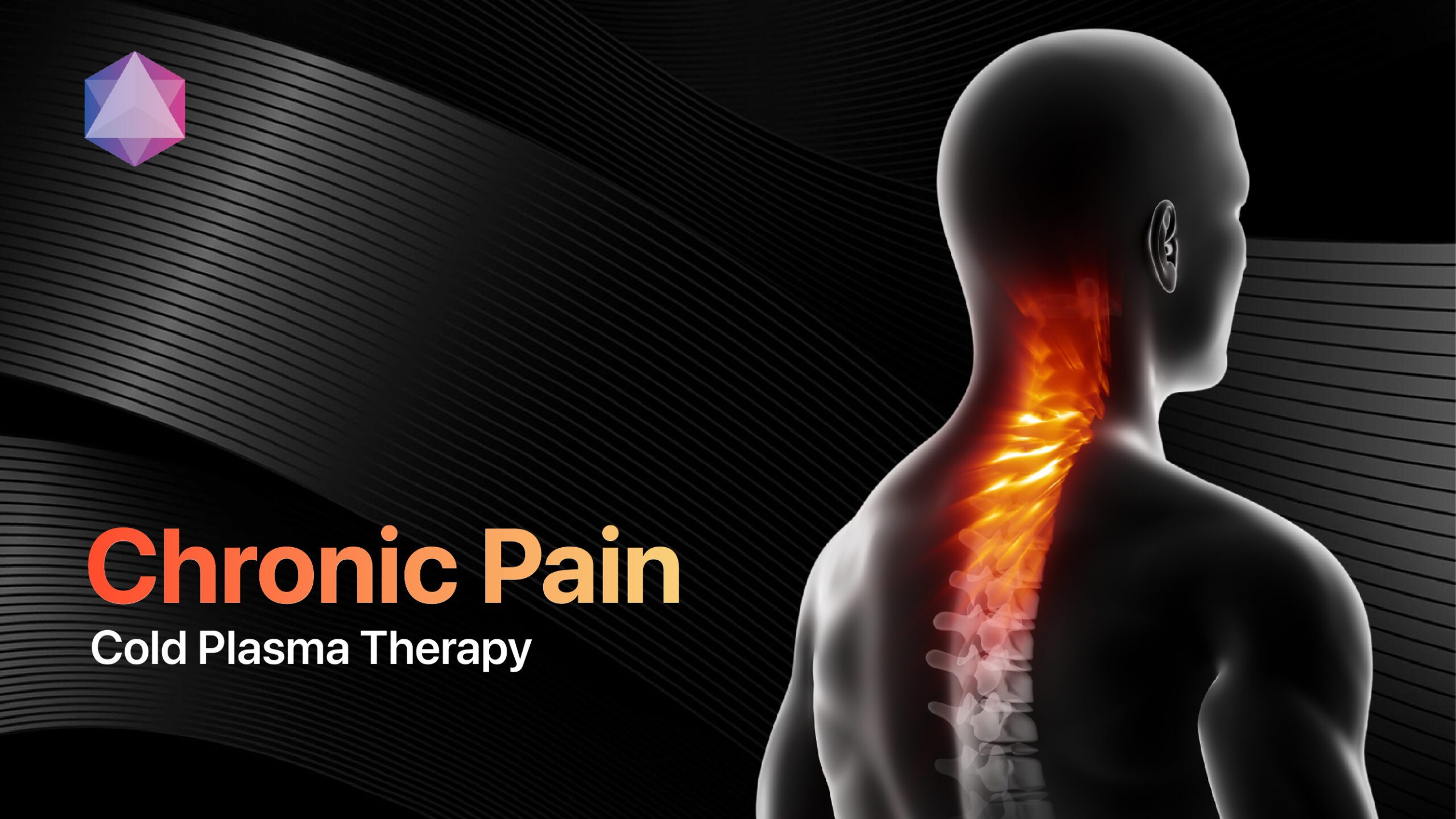
Chronic pain affects an estimated 20.9% of U.S. adults (51.6 million people), according to the CDC, representing one of the most common reasons people seek medical care[2]. This debilitating condition is defined as pain that persists for more than three months, continuing beyond normal healing time from injury or illness[4][21][26]. Unlike acute pain that serves a protective purpose, chronic pain disrupts daily life, affecting work, relationships, and mental health.
Modern treatment approaches combine medications, therapies, and innovative technologies like cold plasma to provide comprehensive pain management and improved quality of life.
Understanding Chronic Pain: Beyond Basic Definitions
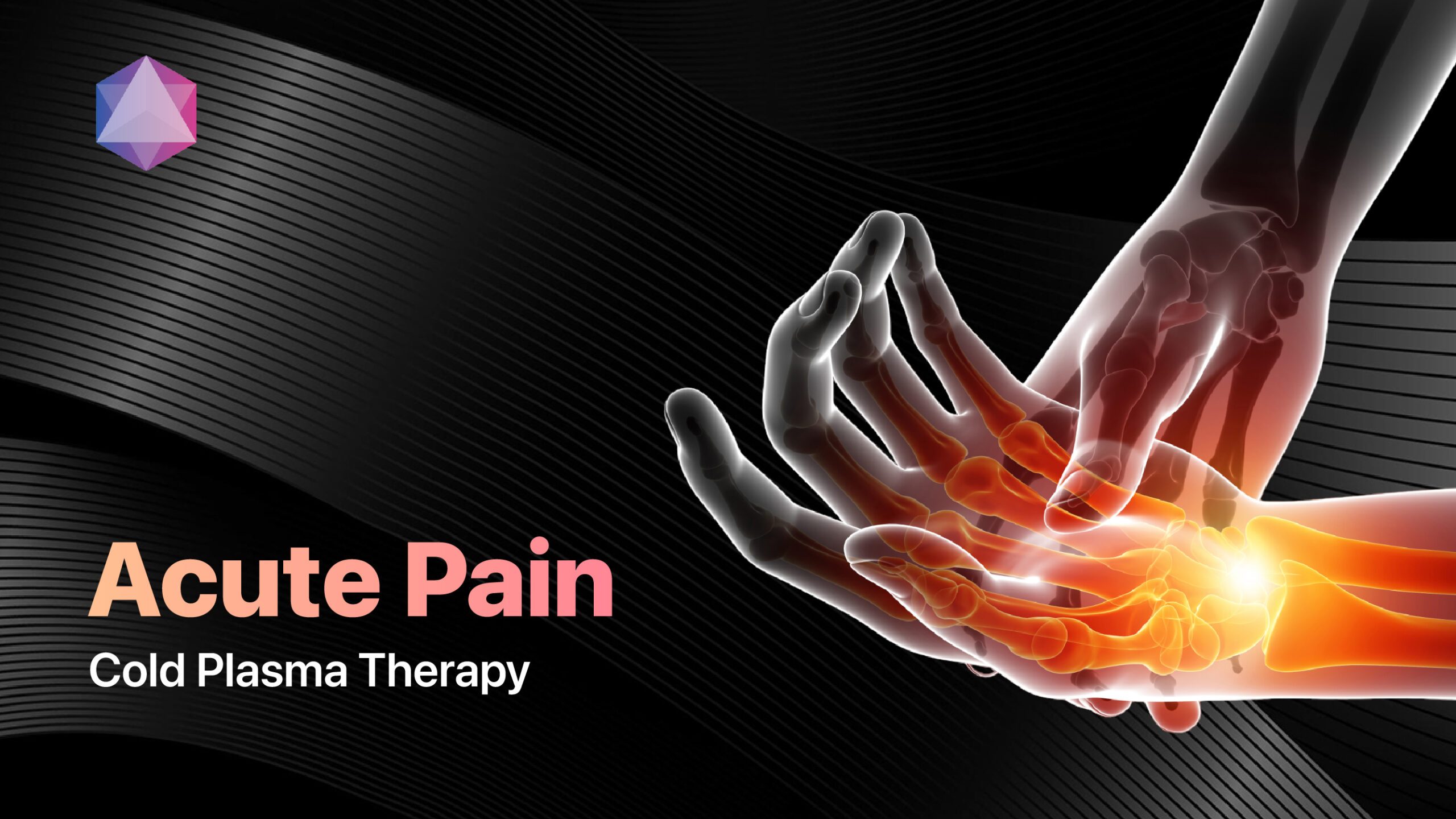
What Distinguishes Chronic Pain from Acute Pain?
Chronic pain fundamentally differs from acute pain in duration, purpose, and physiological mechanisms[2]. While acute pain alerts us to injury and typically resolves as tissues heal, chronic pain persists without serving any protective function.
The condition involves complex changes in the nervous system where pain pathways become hypersensitive. Nerves may fire more readily, and the brain might misinterpret other signals as pain[11].
Key distinguishing features include:
- Duration exceeding 3-6 months
- Pain that outlasts normal tissue healing
- Often disproportionate to visible injury
- Accompanied by psychological and social impacts
- May exist without identifiable cause[5]
The Global Impact of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain affects more people than diabetes, cancer, and heart disease combined[5]. Prevalence varies significantly across countries, ranging from 8% to 55.2% of populations, with industrialized nations showing higher rates.
The economic burden is staggering—estimated at $560-635 billion annually in the United States alone, including healthcare costs, lost productivity, and disability payments[5].
Comprehensive Symptom Profile of Chronic Pain
Primary Physical Symptoms
Chronic pain manifests through diverse physical sensations that significantly impact daily functioning:
Pain Characteristics
- Aching: Deep, constant discomfort
- Burning: Sharp, hot sensations
- Shooting: Electric-like jolts
- Throbbing: Pulsating rhythmic pain
- Stabbing: Sharp, piercing sensations[2][19]
Associated Physical Symptoms
- Fatigue: Persistent exhaustion beyond normal tiredness
- Sleep disturbances: Difficulty falling or staying asleep
- Muscle stiffness: Reduced flexibility and range of motion
- Swelling: Inflammation in affected areas
- Sensitivity: Heightened response to touch, temperature, or pressure[15]
Secondary Complications
Chronic pain frequently triggers cascading health problems:
- Depression and anxiety: Affecting up to 85% of chronic pain patients
- Cognitive dysfunction: Memory problems, concentration difficulties
- Social withdrawal: Isolation from family and friends
- Sleep disorders: Insomnia, restless sleep patterns
- Reduced physical fitness: Deconditioning from activity avoidance[2]
| Symptom Category | Specific Manifestations | Impact Severity | Treatment Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Pain | Aching, burning, shooting sensations[19] | Severe | Primary focus |
| Psychological | Depression, anxiety, mood changes[2] | High | Critical component |
| Sleep-Related | Insomnia, unrefreshing sleep[15] | High | Essential for recovery |
| Cognitive | Memory issues, concentration problems[4] | Moderate-High | Often overlooked |
Root Causes and Risk Factors
Primary Etiological Categories
Chronic pain develops through multiple pathways, often involving complex interactions between physical, psychological, and environmental factors[5]:
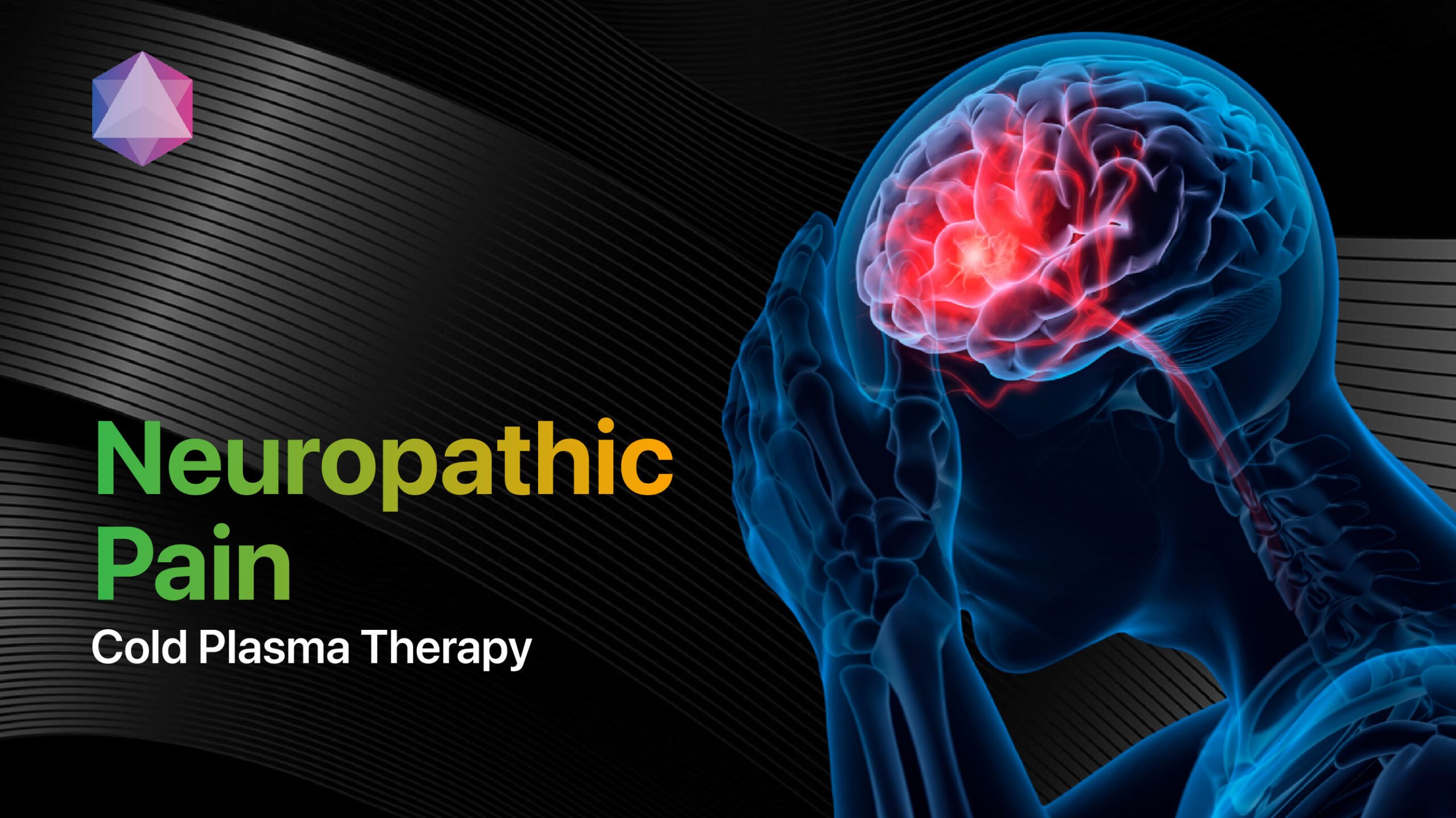
Neuropathic Pain
Results from direct nerve damage or dysfunction affecting:
- Peripheral nerves: Diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia
- Central nervous system: Post-stroke pain, spinal cord injuries
- Mixed mechanisms: Complex regional pain syndrome[11]
Nociceptive Pain
Arises from tissue damage or inflammation:
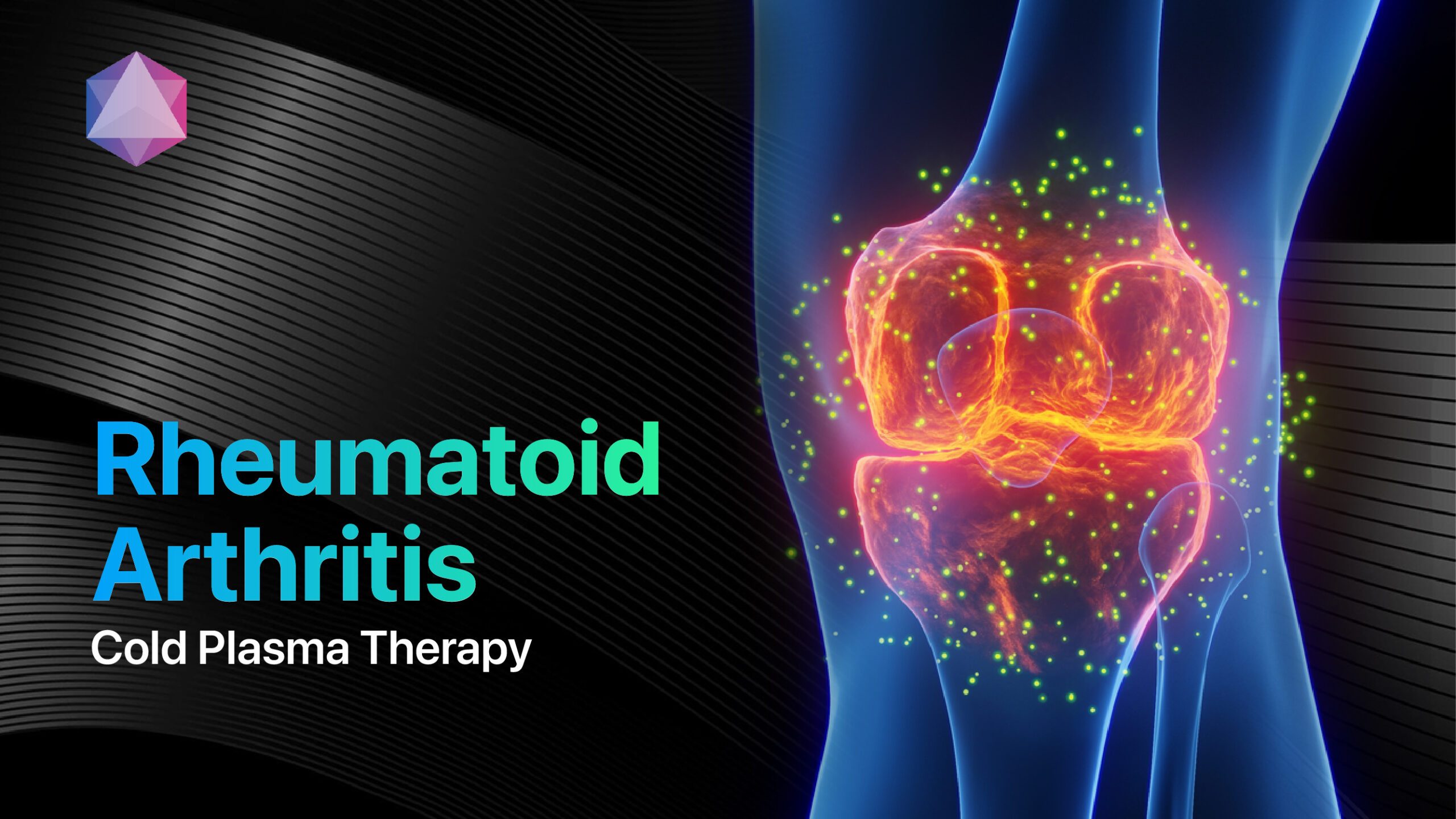
- Musculoskeletal conditions: Arthritis, back pain, fibromyalgia
- Inflammatory diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease
- Cancer-related pain: Tumor pressure, treatment effects[7]
Nociplastic Pain
Involves altered pain processing without clear tissue damage:
- Central sensitization: Amplified pain signals
- Fibromyalgia: Widespread pain sensitivity
- Irritable bowel syndrome: Visceral hypersensitivity[4]
Contributing Risk Factors
Chronic pain development involves multiple predisposing factors:
- Age: Higher prevalence in older adults
- Gender: Women experience chronic pain more frequently
- Genetics: Familial clustering suggests hereditary components
- Previous injuries: History of trauma or surgery
- Psychological factors: Depression, anxiety, stress
- Lifestyle factors: Obesity, smoking, sedentary behavior[2][7]
Revolutionary Treatment Approaches
Multimodal Pain Management Philosophy
Chronic pain treatment requires comprehensive approaches combining multiple therapeutic modalities[8]. Single-intervention strategies rarely provide adequate relief for complex chronic conditions.
Evidence-based treatment components include:
- Pharmacological interventions: Medications targeting different pain pathways
- Non-pharmacological therapies: Physical, psychological, and complementary treatments
- Lifestyle modifications: Exercise, stress management, sleep hygiene
- Innovative technologies: Advanced pain management devices[6][12]
Pharmaceutical Management Strategies
First-Line Medications
- Acetaminophen: Safe initial option for mild-moderate pain
- NSAIDs: Anti-inflammatory effects for tissue-based pain
- Topical agents: Localized treatment with reduced systemic effects[24]
Specialized Medications
- Anticonvulsants: Gabapentin and pregabalin for neuropathic pain
- Antidepressants: Tricyclics, SNRIs for pain modulation
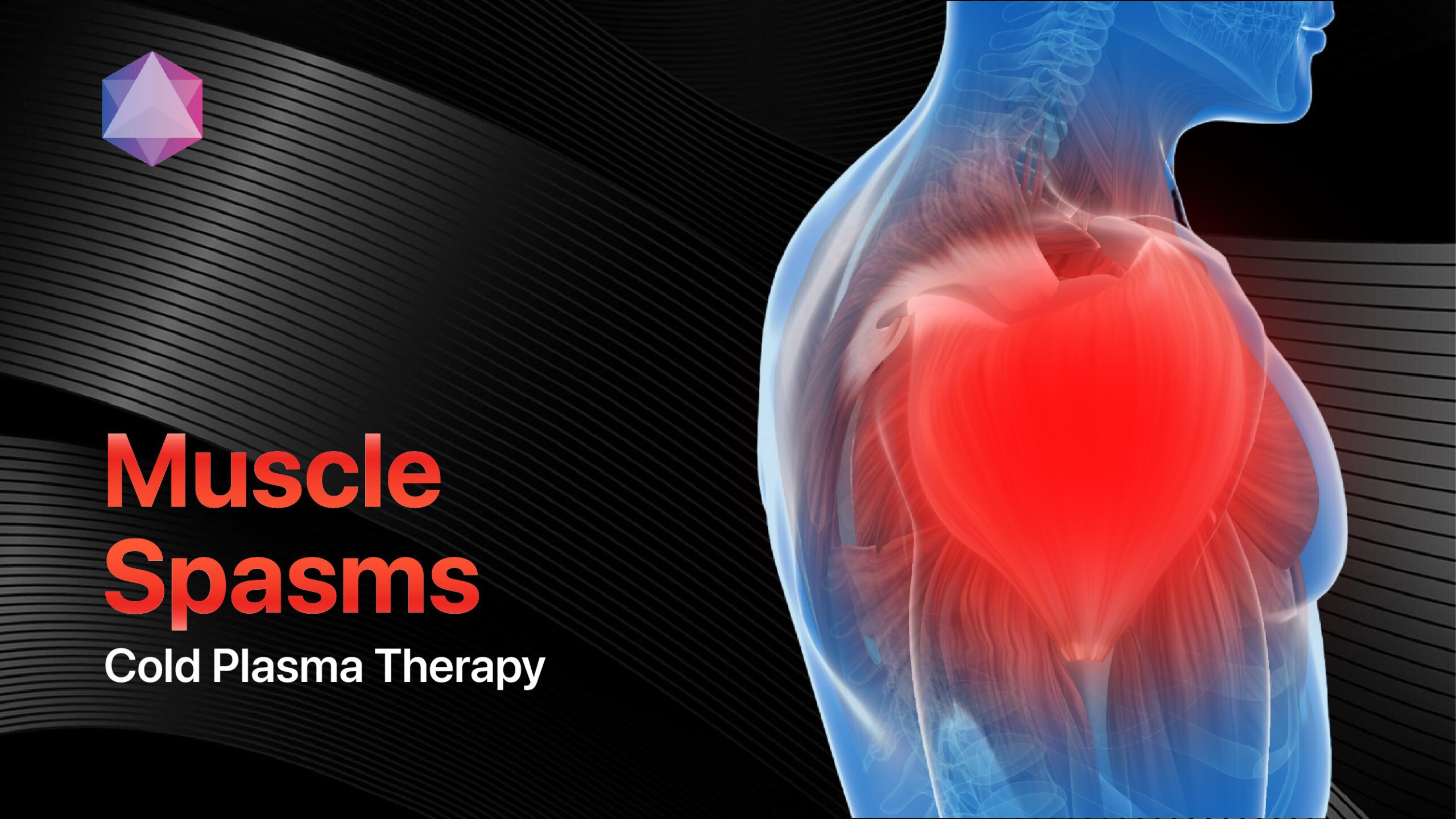
- Muscle relaxants: For spasm-related chronic pain[2]
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in chronic pain management through:
- Therapeutic exercise: Strength, flexibility, and endurance training
- Manual therapy: Hands-on techniques for mobility improvement
- Modalities: Heat, cold, electrical stimulation
- Movement education: Proper body mechanics and posture[12]
Psychological Therapies
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) demonstrates significant effectiveness for chronic pain by:
- Reframing pain perceptions: Changing thought patterns about pain
- Coping strategy development: Practical pain management techniques
- Stress reduction: Relaxation and mindfulness training
- Activity pacing: Balancing rest and activity[12]
Breakthrough Cold Plasma Technology
Cold plasma therapy represents a revolutionary advancement in chronic pain treatment. The Mirari Cold Plasma System, developed by General Vibronics and commercialized through miraridoctor.com, offers innovative pain relief through nitric oxide-based technology[10].
Clinical mechanisms include:
- Neural pathway modulation: Altering pain signal transmission
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Reducing tissue inflammation
- Improved circulation: Enhancing oxygen and nutrient delivery
- Tissue regeneration: Promoting healing at cellular level[10]
Research demonstrates that cold plasma can reduce pain intensity scores by 30–50% in various chronic conditions, with particularly strong effects for superficial tissue pain[10].
| Treatment Modality | Primary Mechanism | Success Rate | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Plasma Therapy | Neural modulation, anti-inflammatory[10] | 30-50% pain reduction | Superficial chronic pain, fibromyalgia |
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy | Psychological pain processing[12] | 25-40% improvement | All chronic pain types |
| Physical Therapy | Functional improvement, strength[12] | 20-35% pain reduction | Musculoskeletal conditions |
| Multimodal Approach | Combined mechanisms[6] | Up to 60% improvement | Complex chronic pain syndromes |
Specialized Treatment for Different Chronic Pain Types
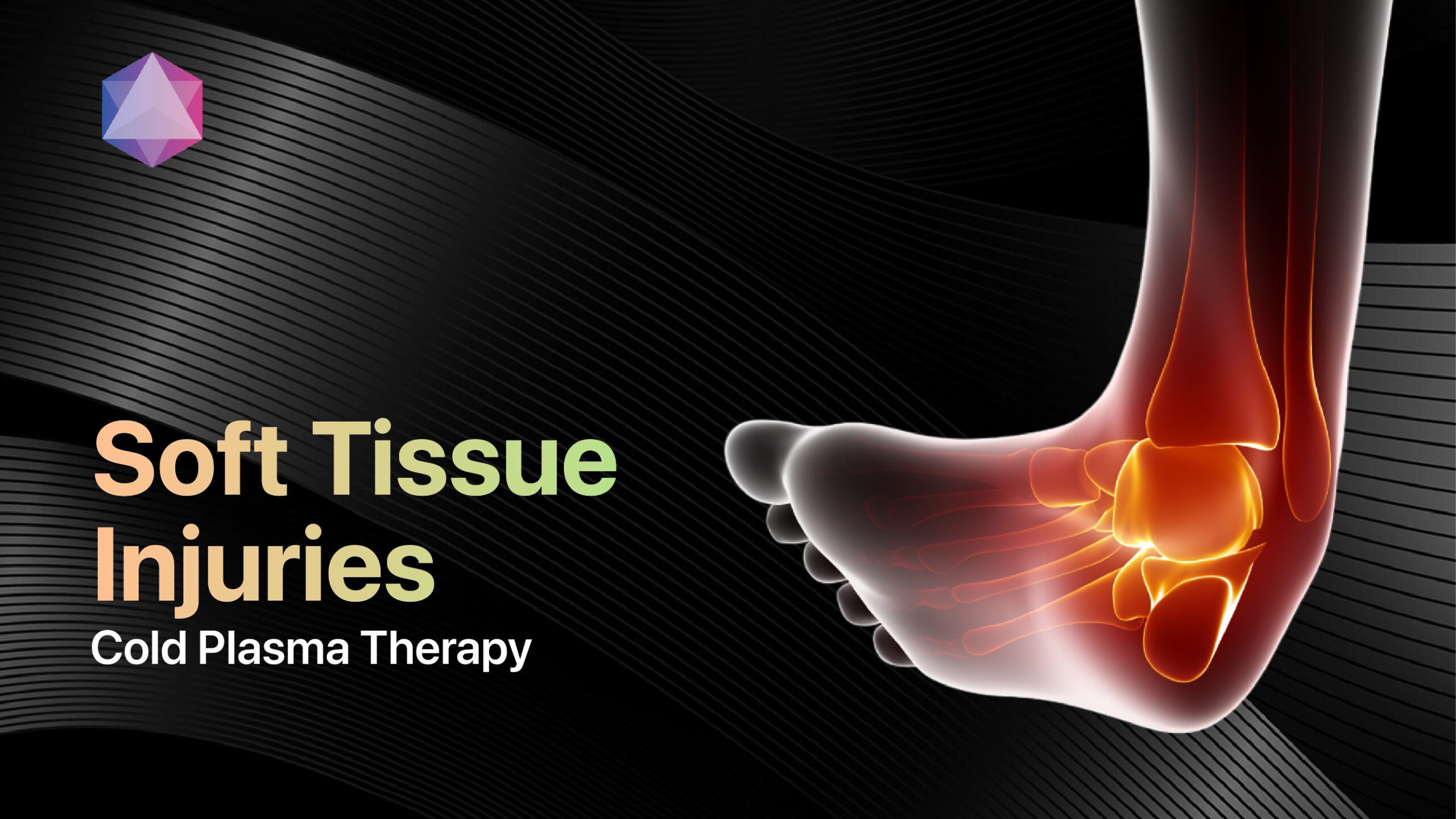
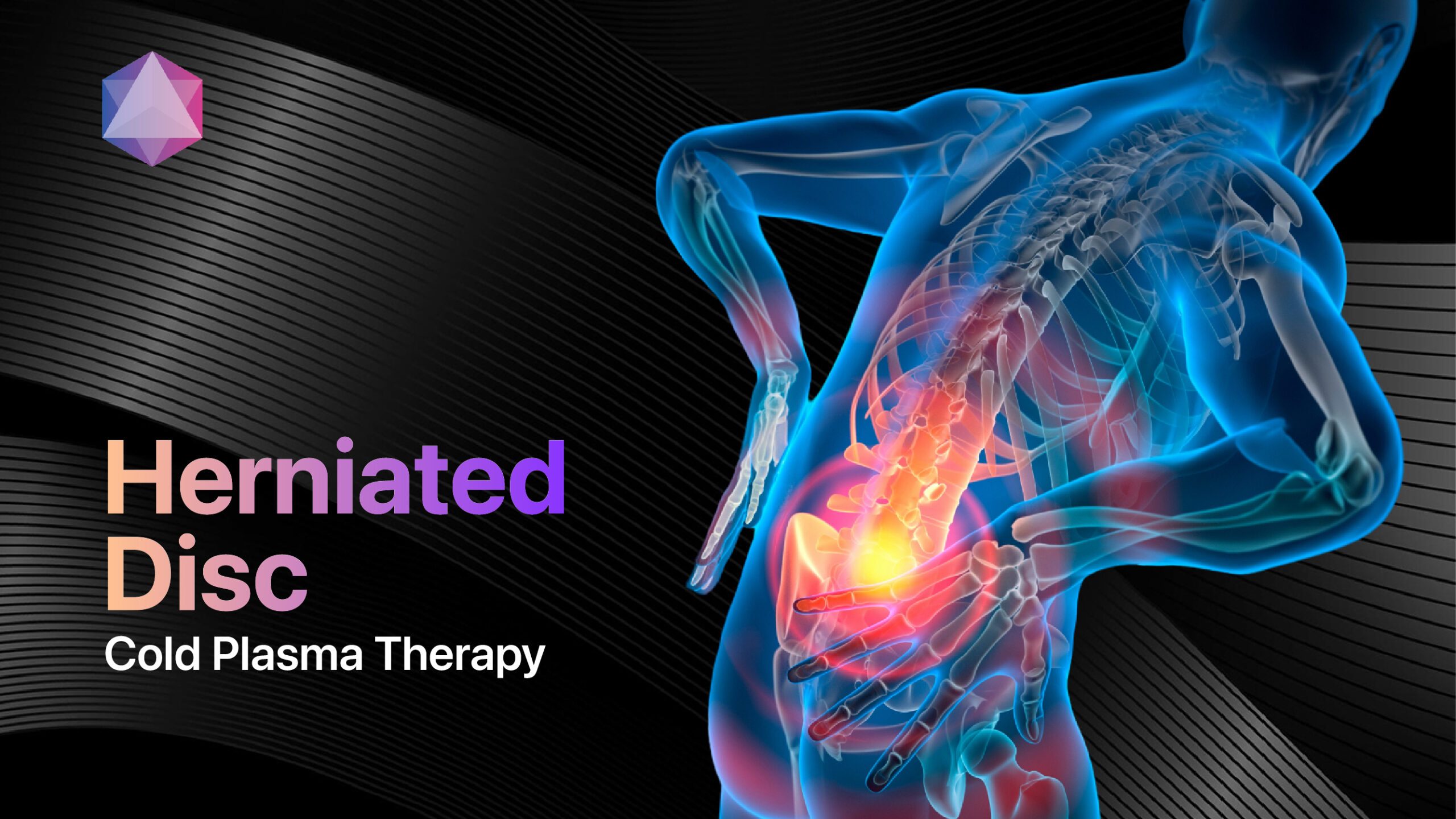
Musculoskeletal Chronic Pain
Back and neck pain represent the most common chronic pain conditions, affecting millions globally[11].
Effective management includes:
- Exercise therapy: Specific strengthening and mobility programs
- Spinal manipulation: Manual therapy techniques
- Injection therapies: Targeted pain relief procedures
- Ergonomic modifications: Workplace and lifestyle adjustments[18]
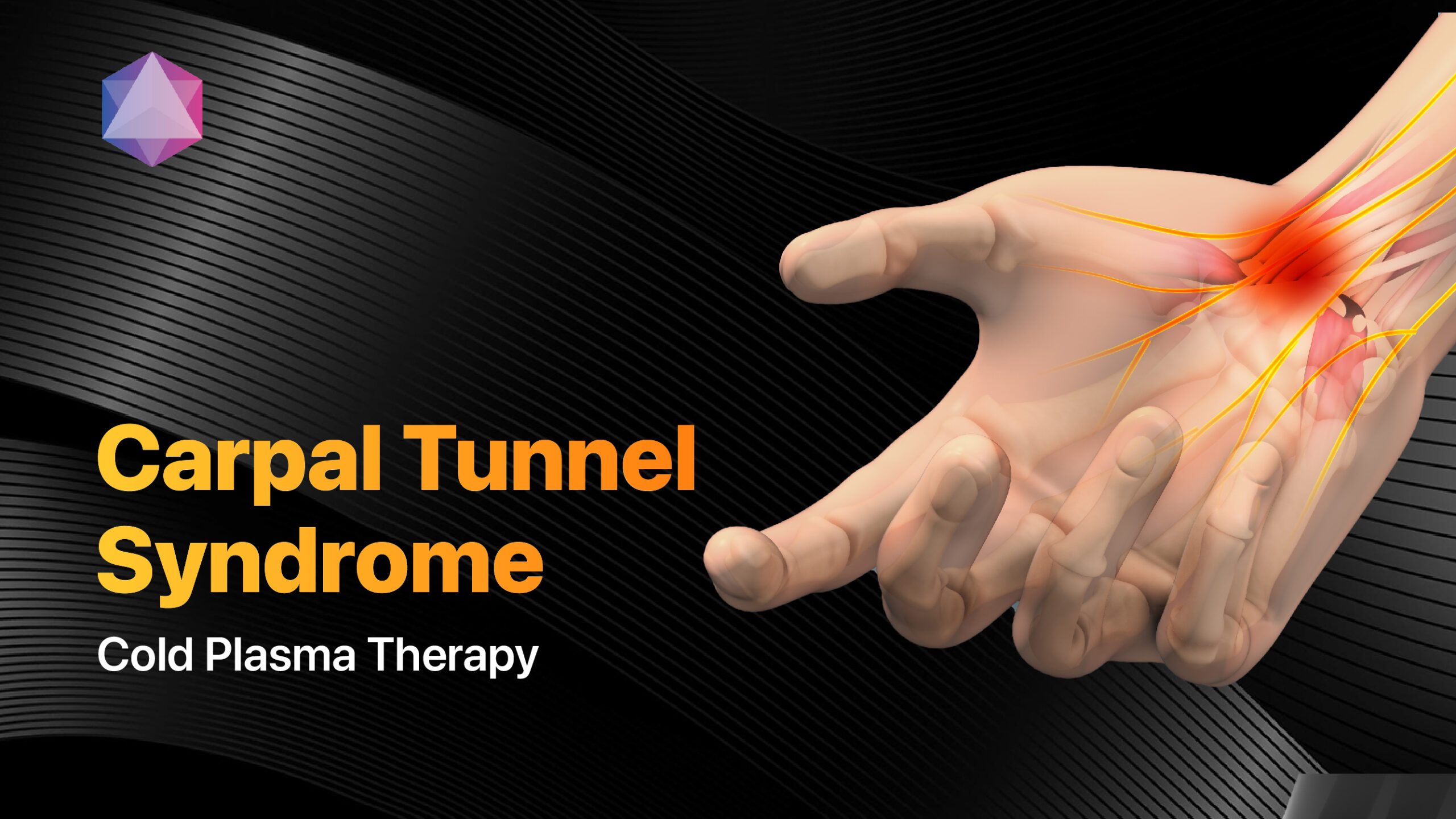
Neuropathic Chronic Pain
Neuropathic pain from conditions like diabetic neuropathy or post-herpetic neuralgia requires specialized approaches:
- Anticonvulsant medications: First-line pharmaceutical treatment
- Topical treatments: Lidocaine patches, capsaicin creams
- Nerve blocks: Targeted injection procedures
- Advanced technologies: Spinal cord stimulation, cold plasma therapy[25]
Fibromyalgia and Widespread Pain
Fibromyalgia affects approximately 2-4% of the population, predominantly women[11].
Comprehensive management involves:
- FDA-approved medications: Pregabalin, duloxetine, milnacipran
- Exercise programs: Low-impact aerobic and strength training
- Sleep management: Addressing sleep disturbances
- Stress reduction: Mindfulness and relaxation techniques[18]
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Evidence-Based Alternative Treatments
Acupuncture shows proven effectiveness for several chronic pain conditions:
- Back pain: Strong evidence for pain reduction
- Migraines: Effective for headache prevention
- Osteoarthritis: Modest benefits for knee pain
- Cancer-related pain: Supportive therapy benefits[18]
Mind-Body Approaches
Mindfulness-based interventions demonstrate significant benefits for chronic pain:
- Meditation: Reduces pain intensity and improves coping
- Yoga: Combines physical movement with mindfulness
- Tai Chi: Gentle movement therapy for pain management
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Systematic tension release[18]
Lifestyle Management and Self-Care
Exercise as Medicine
Regular physical activity proves essential for chronic pain management despite initial discomfort[6].
Benefits include:
- Endorphin release: Natural pain relief chemicals
- Improved strength: Supporting affected body parts
- Better sleep: Enhanced rest quality
- Mood improvement: Reduced depression and anxiety
- Increased function: Better daily activity performance[12]
Sleep Optimization
Quality sleep directly impacts chronic pain intensity and coping ability:
- Sleep hygiene: Regular bedtime routines and environment
- Pain-sleep cycle: Breaking the cycle of pain disrupting sleep
- Sleep disorders: Addressing underlying conditions
- Medication timing: Optimizing pain relief for rest[2]
Stress Management
Chronic stress increases the perception of pain and decreases the effectiveness of treatments.
- Relaxation techniques: Deep breathing, meditation
- Cognitive strategies: Positive thinking patterns
- Social support: Family, friends, support groups
- Professional counseling: Addressing psychological factors[6]
Long-term Prognosis and Management
Realistic Outcome Expectations
Current chronic pain treatments typically reduce pain scores by about 30% while significantly improving quality of life[2]. Complete pain elimination is rarely achievable, but meaningful improvement in function and well-being is realistic.
Success factors include:
- Early intervention: Preventing pain chronification
- Comprehensive treatment: Addressing multiple factors
- Patient engagement: Active participation in management
- Realistic expectations: Focusing on functional improvement[8]
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Chronic pain research continues advancing with promising developments:
- Precision medicine: Personalized treatment based on genetics
- Advanced neurostimulation: Improved device technologies
- Regenerative medicine: Stem cell and tissue therapies
- Digital therapeutics: App-based treatment programs[2]
The Mirari Doctor platform exemplifies technological advancement, utilizing cold atmospheric plasma to provide novel therapeutic options for challenging chronic pain conditions[10].
FAQ: Essential Questions About Chronic Pain
What exactly is chronic pain, and how is it different from regular pain?
Chronic pain is pain that persists for more than 3–6 months and continues beyond normal tissue healing time[2][26]. Unlike acute pain that serves as a protective warning system, chronic pain serves no useful purpose and involves changes in the nervous system that make pain pathways hypersensitive[11]. It often exists without visible injury and affects daily functioning significantly.
What are the most common causes of chronic pain?
Common chronic pain causes include arthritis, back problems, fibromyalgia, nerve damage, and previous injuries that don’t heal properly[7][11]. Risk factors include age, gender (more common in women), genetics, obesity, depression, and lifestyle factors[2]. Sometimes chronic pain develops without an identifiable cause, involving complex nervous system changes.
What are the most effective treatments for chronic pain?
Most effective chronic pain treatment involves multimodal approaches combining medications, physical therapy, psychological support, and lifestyle changes[8][12]. Current treatments typically reduce pain scores by about 30% while significantly improving quality of life[2]. Innovative therapies like cold plasma show 30-50% pain reduction in appropriate conditions[10].
Can chronic pain be cured, or does it ever go away?
There’s currently no cure for chronic pain, but it can be effectively managed[2]. The goal is managing symptoms and improving function rather than complete elimination. Some patients experience significant improvement or even remission with proper treatment, while others learn to manage their condition effectively. Early intervention prevents pain from becoming more entrenched[8].
How does chronic pain affect mental health and daily life?
Chronic pain significantly impacts mental health, increasing the risk of depression, anxiety, and social isolation[2]. It affects sleep, work performance, relationships, and overall quality of life. About 25% of chronic pain patients develop chronic pain syndrome with additional psychological symptoms[4]. Comprehensive treatment addressing both physical and psychological aspects proves most effective[12].
Chronic pain represents a complex medical condition affecting millions globally. While challenging, comprehensive management approaches combining traditional therapies with innovative treatments like cold plasma technology offer hope for improved outcomes. Understanding the condition empowers patients to work effectively with healthcare providers in developing personalized treatment strategies that focus on functional improvement and enhanced quality of life.
References
- NCBI Bookshelf. (2025). Chronic Pain – StatPearls. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553030/
- Cleveland Clinic. (2024). Chronic Pain: What It Is, Symptoms, Treatment & Management. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4798-chronic-pain
- ScienceDirect. (2025). Chronic Pain – an overview. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/chronic-pain
- WebMD. (2024). Chronic Pain Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/chronic-pain-syndrome-overview
- Wikipedia. (2002). Chronic pain. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chronic_pain
- Health Direct Australia. (2025). Options for managing chronic pain. Available at: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/options-for-managing-chronic-pain
- WebMD. (2024). What Causes Chronic Pain? Available at: https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/cause-chronic-pain
- Mayo Clinic Health System. (2023). Tips for managing chronic pain. Available at: https://www.mayoclinichealthsystem.org/hometown-health/speaking-of-health/8-tips-for-managing-chronic-pain
- Mayo Clinic. (2022). Complex regional pain syndrome – Symptoms & causes. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/crps-complex-regional-pain-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20371151
- Mirari Doctor. (2025). Cold Plasma in Pain Relief: Revolutionary Non-Invasive Treatment. Available at: https://miraridoctor.com/cold-plasma-in-pain-relief/
- Health Direct Australia. (2025). Chronic pain – about, causes and management. Available at: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/chronic-pain
- NCBI Bookshelf. (2009). Chronic Pain Management. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92054/
- Healthline. (2011). Causes of Chronic Pain. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/chronic-pain
- NSW Pain Management Network. (2016). Chronic Pain. Available at: https://aci.health.nsw.gov.au/chronic-pain
- Stanford Healthcare. (2025). Chronic Pain Symptoms. Available at: https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-conditions/brain-and-nerves/chronic-pain/symptoms.html
- PubMed. (2022). Efficacy of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Therapy on Chronic Wounds. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36262869/
- US Pain Foundation. (2024). Chronic pain overview: Everything you need to know. Available at: https://uspainfoundation.org/pain/
- UCLA Health. (2024). 5 alternative treatments for chronic pain. Available at: https://www.uclahealth.org/news/article/5-alternative-treatments-chronic-pain
- MyMichigan Health. (2022). How To Tell If Your Pain is Chronic Pain. Available at: https://www.mymichigan.org/about/news/healthdoseblog/how-to-tell-if-your-pain-is-chronic-pain/
- Vietnam Medical Journal. (2023). Investigating Adverse Effects of Cold Plasma. Available at: https://tapchiyhocvietnam.vn/index.php/vmj/article/download/5055/4625/9322
- International Association for the Study of Pain. (2024). Chronic Pain. Available at: https://www.iasp-pain.org/resources/topics/chronic-pain/
- The BMJ. (2023). Chronic pain: definitions and diagnosis. Available at: https://www.bmj.com/content/381/bmj-2023-076036
- Mayo Clinic Press. (2024). Chronic Pain Definition: How It Works. Available at: https://mcpress.mayoclinic.org/opioids/how-chronic-pain-works/
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Chronic pain: Medication decisions. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/back-pain/in-depth/chronic-pain-medication-decisions/art-20360371
- PMC. (2024). Cold Atmospheric Plasma Is a Promising Alternative Treatment. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11006453/
- PubMed. (2019). Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: the IASP Classification. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30586067/
Related articles
Made in USA