You May Be Interested In:
What is acute chest pain? It affects millions experiencing sudden, severe discomfort requiring immediate medical evaluation[4][21]. Acute chest pain is a new-onset or sudden change in pattern, intensity, or duration that may signal life-threatening conditions like a heart attack, pulmonary embolism, or aortic dissection[35][2]. This emergency symptom originates from structures in the thoracic cavity and requires rapid assessment to prevent death[34]. What is acute chest pain? It includes sudden severe chest pain, pressure, tightness, burning sensations, and pain radiating to arms, neck, jaw, or back[8][23]. Why do I have acute chest pain? It varies from heart attacks to muscle strains—proper evaluation determines the cause and urgency.
Immediate medical attention saves lives when acute chest pain strikes.
Understanding Acute Chest Pain Definition
Primary Characteristics of Acute Chest Pain
Acute chest pain represents new-onset chest discomfort or significant changes in existing patterns[35]. This sudden symptom serves as a warning sign for diseases with imminent death risk[34].
Key defining features:
- Sudden onset without previous pattern
- Severe intensity preventing normal activities
- Duration from minutes to hours
- Associated symptoms like sweating, nausea, shortness of breath[8][21]
Clinical significance lies in its emergency nature—most patients require hospitalization for evaluation of acute coronary syndrome[34].
Location and Quality Patterns
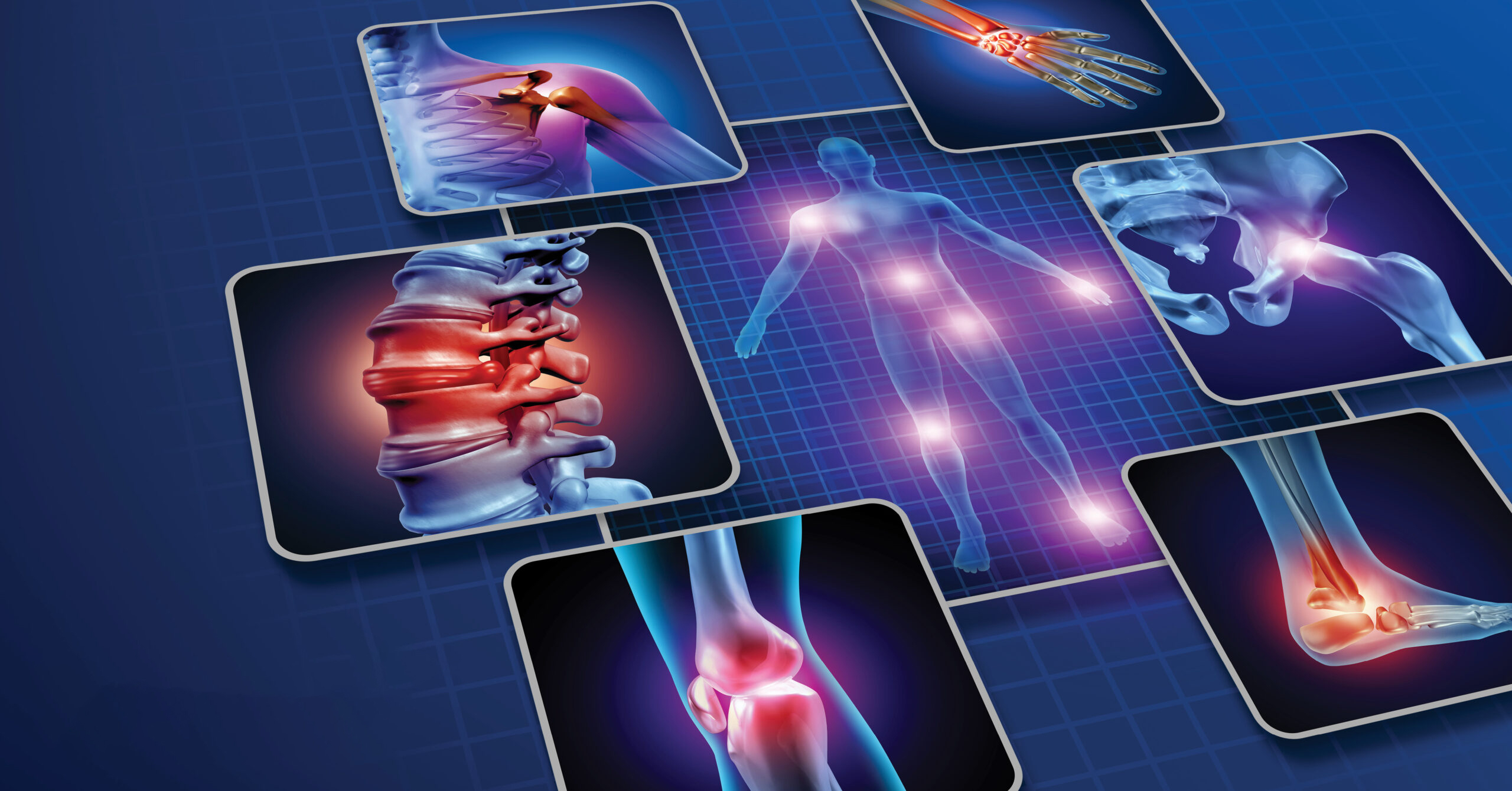
The location of acute chest pain varies based on the underlying cause[2]. Pain originates from any structure in the thoracic cavity.
Common descriptions include:
- Squeezing or pressure suggesting cardiac origin
- Sharp, stabbing, indicating possible lung issues
- Burning sensation suggesting acid reflux
- Crushing feeling often cardiac-related[4][8]
Major Causes of Acute Chest Pain
Heart-Related Causes
Cardiovascular causes represent the most serious acute chest pain triggers[4][8]. These conditions require immediate intervention.
Life-threatening cardiac causes:
- Heart attack (myocardial infarction)—blocked coronary artery
- Unstable angina—reduced blood flow to heart muscle
- Aortic dissection—tearing of main artery wall
- Pericarditis—inflammation around heart sac[4]
Acute coronary syndrome accounts for 31% of chest pain cases in emergency settings[20]. Symptoms include pressure, tightness, and pain spreading to shoulders, arms, back, neck, or jaw[8].
Pulmonary Causes
Lung-related conditions create serious acute chest pain requiring urgent care[4][6].
Critical pulmonary causes:
- Pulmonary embolism (2%)—blood clot in lung artery
- Pneumothorax—collapsed lung
- Pneumonia—lung infection with fever
- Pleurisy—inflamed lung lining[4][6][20]
Pulmonary embolism creates sudden sharp pain similar to a heart attack, worsening with exertion and breathing[6].
Gastrointestinal and Musculoskeletal Causes
Non-cardiac causes also create acute chest pain but generally pose less immediate danger[4][21].
Common non-cardiac causes:
- GERD/heartburn—acid reflux causing burning
- Costochondritis—inflamed rib cartilage
- Muscle strain—chest wall injury
- Panic attacks—anxiety-related symptoms[4][21]
| Cause Category | Symptoms | Emergency Level | Treatment Urgency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac | Pressure, radiating pain[8] | Highest | Immediate |
| Pulmonary | Sharp pain, breathing difficulty[6] | High | Urgent |
| Gastrointestinal | Burning, food-related[21] | Moderate | Prompt |
| Musculoskeletal | Movement-related pain[21] | Low | Routine |
Emergency Recognition and Response
When to Call 911 Immediately
Acute chest pain requires immediate emergency response when accompanied by specific warning signs[21][23].
Call 911 for these symptoms:
- Sudden severe chest pain not going away
- Pain spreading to left arm, neck, jaw, stomach, or back
- Chest pain with sweating, nausea, lightheadedness, shortness of breath
- Crushing pressure under breastbone
- Difficulty breathing, especially after inactivity[21][23]
Heart attack symptoms may include pressure, tightness, squeezing, or aching lasting more than 15 minutes[9]. Women often experience atypical symptoms like nausea, back pain, or jaw pain[9].
First Aid for Acute Chest Pain
Immediate first aid can save lives during acute chest pain episodes[9].
Emergency steps:
- Call 911 or emergency services immediately
- Take aspirin if recommended by medical professionals
- Use prescribed nitroglycerin if available
- Begin CPR if person becomes unconscious[9]
Do not drive yourself to the hospital during acute chest pain—have someone else drive or call an ambulance.[9][21]
Diagnostic Approach and Evaluation
Clinical Assessment Methods
Healthcare providers use systematic evaluation to diagnose acute chest pain causes[36][19].
Assessment components:
- 12-lead ECG performed immediately for all suspected cardiac cases
- Physical examination checking vital signs, heart sounds
- Detailed history, including onset, quality, radiation patterns
- Risk factor evaluation—age, family history, smoking[14][19]
Diagnostic tests include:
- Blood tests—troponins, D-dimer, complete blood count
- Chest X-ray—lung and heart imaging
- CT angiogram—detailed vessel visualization
- Echocardiogram—heart function assessment[5]
Risk Stratification Tools
Risk scores help physicians quickly identify the likelihood of adverse events[34]. These tools assist in fast decision-making for patient management.
Evaluation priorities:
- Immediate life-threatening conditions – heart attack, aortic dissection
- High-risk presentations—acute coronary syndrome, pulmonary embolism
- Moderate-risk symptoms—pneumonia, pericarditis
- Low-risk causes – muscle strain, GERD[19][36]
Treatment Options and Management
Emergency Medical Interventions
Treatment approaches vary dramatically based on underlying cause and severity[12][17].
Cardiac treatments:
- Nitroglycerin—relaxes heart arteries
- Aspirin—prevents blood clots
- Thrombolytics—dissolves existing clots
- Angioplasty—opens blocked arteries[12]
Non-cardiac treatments:
- Antacids—for acid reflux
- Anti-anxiety medications—panic attack management
- Anti-inflammatory drugs—muscle strain relief
- Lung reinflation—collapsed lung treatment[17]
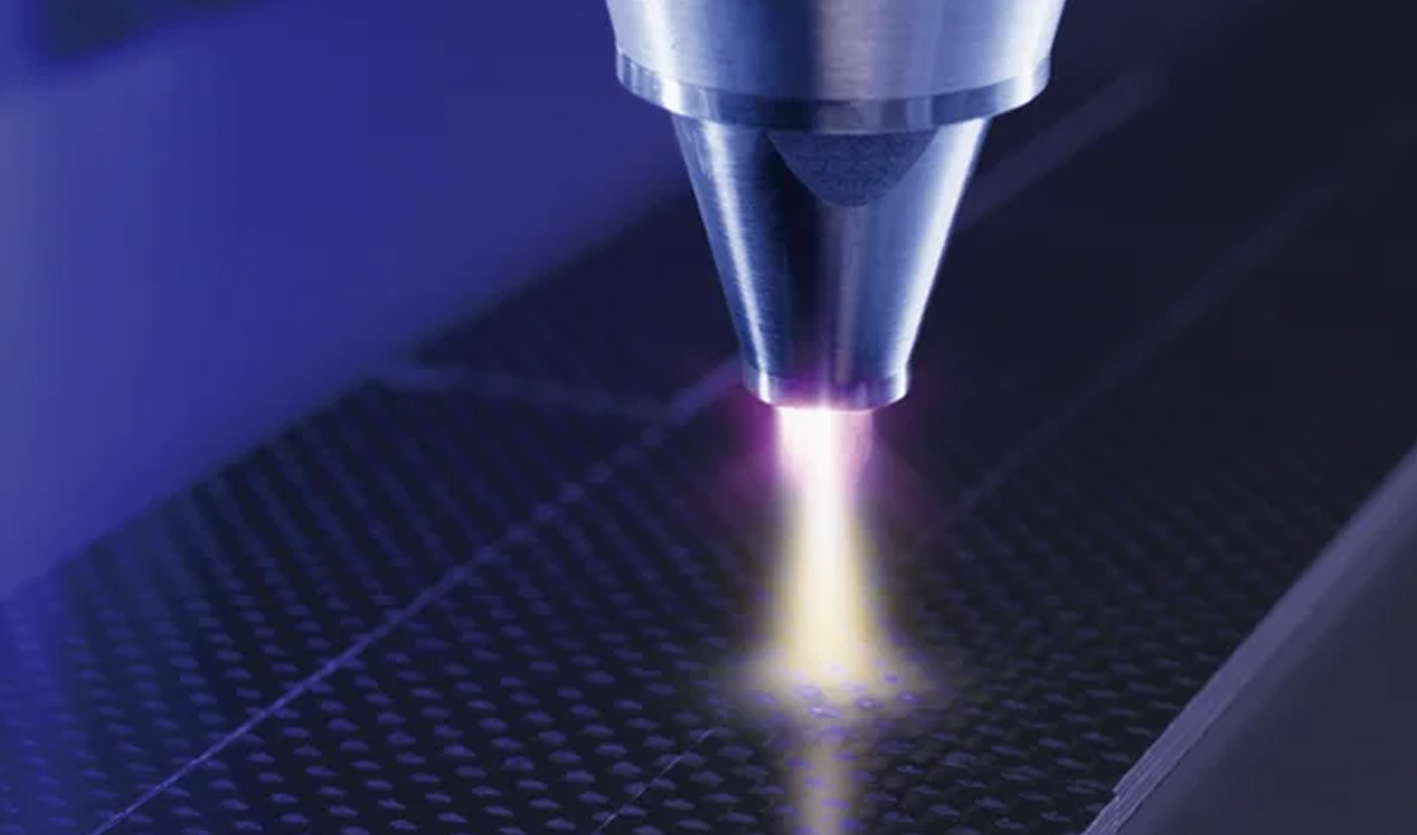
Revolutionary Cold Plasma Technology
The Mirari Cold Plasma System, developed by General Vibronics and commercialized through miraridoctor.com, offers breakthrough treatment for specific acute chest pain conditions. This FDA-cleared device provides targeted therapy for underlying tissue inflammation.
Clinical applications:
- Post-surgical chest pain management
- Inflammatory chest conditions treatment
- Enhanced tissue healing preventing complications
- A non-pharmacological approach avoiding drug interactions
Treatment benefits:
- Rapid pain reduction through neural modulation
- Anti-inflammatory effects reducing tissue swelling
- Accelerated healing promoting tissue repair
- Enhanced recovery minimizing hospitalization time
Urgent Care vs Emergency Room Decision
When Urgent Care Is Appropriate
Non-emergency chest pain can often be managed at urgent care facilities[31][32]. This provides faster, more affordable treatment.
Urgent care is suitable for:
- Mild to moderate pain not worsening
- Pressure or discomfort without severe symptoms
- Pain varying with movement suggesting muscle strain
- Burning sensation indicating possible heartburn[31][32]
Urgent care evaluation includes:
- Physical examination and symptom assessment
- EKG testing when indicated
- Blood work to rule out serious conditions
- Treatment recommendations for non-emergency causes[31]
Emergency Room Requirements
Emergency room treatment is mandatory for high-risk presentations[23][32].
ER indications:
- Sudden severe chest pain not resolving
- Pain radiating to arm, jaw, or back
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Nausea, dizziness, or sweating
- Loss of consciousness or confusion[23][31]
| Setting | Best For | Typical Wait Time | Cost Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emergency Room | Life-threatening symptoms[23] | Immediate for emergencies | Highest cost |
| Urgent Care | Non-emergency chest pain[31] | 15-30 minutes | Moderate cost |
| Primary Care | Follow-up care[24] | Scheduled appointments | Lowest cost |
| Chest Pain Units | Specialized evaluation[30] | Streamlined assessment | Variable |
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Lifestyle Modifications
Preventing acute chest pain focuses on reducing risk factors for serious underlying conditions[24].
Heart-healthy strategies:
- Regular exercise improving cardiovascular fitness
- Healthy diet low in saturated fats
- Smoking cessation reducing arterial damage
- Stress management preventing panic attacks
- Weight management reducing heart strain[4]
Monitoring approaches:
- Regular checkups for heart disease screening
- Blood pressure control preventing complications
- Cholesterol management reducing plaque buildup
- Diabetes control protecting blood vessels[24]
Home Management Strategies
Some chest pain can be safely managed at home with appropriate remedies[22].
Safe home treatments:
- Cold packs for muscle strain
- Hot drinks for gas-related discomfort
- Position changes – elevated head for reflux
- Relaxation techniques for anxiety-related pain[22]
Never attempt home treatment for suspected heart attacks or other emergency conditions[21].
FAQ: Essential Questions About Acute Chest Pain
What is acute chest pain?
Acute chest pain is new-onset or sudden change in pattern, intensity, or duration of chest pain that may signal life-threatening conditions like heart attack, pulmonary embolism, or aortic dissection[35][2]. It’s defined as a warning sign of diseases with imminent risk of death originating from any structure in the thoracic cavity[34][2]. Symptoms include sudden severe chest pain, pressure, tightness, burning sensations, and pain radiating to arms, neck, jaw, or back[8][23]. This emergency symptom requires rapid medical evaluation to prevent death.
Why do I have acute chest pain?
Acute chest pain causes include heart attack (31% of emergency cases), pulmonary embolism (2%), pneumothorax, aortic dissection, unstable angina, and pericarditis[20][4][8]. Non-cardiac causes include GERD, muscle strain, panic attacks, pneumonia, and costochondritis[4][21]. Heart-related causes represent the most serious triggers requiring immediate intervention, while lung conditions like pulmonary embolism create sudden sharp pain similar to heart attacks[6]. Proper medical evaluation determines the specific cause and urgency level.
When should I call 911 for acute chest pain?
Call 911 immediately for sudden severe chest pain that doesn’t go away, pain spreading to the left arm/neck/jaw/back, chest pain with sweating/nausea/lightheadedness/shortness of breath, crushing pressure under the breastbone, or difficulty breathing[21][23]. Heart attack symptoms include pressure, tightness, squeezing, or aching lasting more than 15 minutes[9]. Never drive yourself to the hospital during acute chest pain—have someone else drive or call an ambulance.[9][21] Women often experience atypical symptoms like nausea, back pain, or jaw pain[9].
Can I go to urgent care for acute chest pain?
You can go to urgent care for non-emergency chest pain, including mild to moderate pain not worsening, pressure or discomfort without severe symptoms, pain varying with movement suggesting muscle strain, or a burning sensation indicating possible heartburn[31][32]. However, you must go to the ER for sudden severe chest pain, pain radiating to the arm/jaw/back, shortness of breath, nausea/dizziness/sweating, or loss of consciousness[23][31]. Urgent care provides faster, more affordable treatment for non-emergency cases with 15-30 minute wait times[31].
What is not an immediate intervention for acute chest pain?
What is not an immediate intervention for acute chest pain includes waiting to see if pain goes away, attempting home remedies for a suspected heart attack, driving yourself to the hospital, delaying medical evaluation for severe symptoms, or taking random medications without medical guidance[21][9]. Immediate interventions should include calling 911, taking aspirin if recommended by medical professionals, using prescribed nitroglycerin if available, and beginning CPR if the person becomes unconscious[9]. Never ignore severe chest pain or attempt self-diagnosis for potentially life-threatening conditions.
What is acute chest pain? It represents a critical medical emergency requiring immediate recognition and appropriate response. Understanding symptom patterns, cause differentiation, and proper treatment pathways can save lives while preventing unnecessary complications. Modern approaches, including advanced technologies, offer enhanced outcomes for patients facing these potentially life-threatening conditions.
References
- Cleveland Clinic. (2025). Acute Chest Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23290-acute-chest-syndrome
- PubMed. (1997). Acute chest pain. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9313375/
- NCBI. (2025). Acute Chest Syndrome – StatPearls. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441872/
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Chest pain – Symptoms and causes. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chest-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20370838
- American Lung Association. (2024). Acute Chest Syndrome Symptoms and Diagnosis. Available at: https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/acute-chest-syndrome/symptoms-diagnosis
- Healthline. (2018). 30 Causes for Chest Pain and When to Seek Help. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/causes-of-chest-pain
- American Lung Association. (2025). Treating and Managing Acute Chest Syndrome. Available at: https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/acute-chest-syndrome/treatment
- Mayo Clinic. (2025). Acute coronary syndrome – Symptoms and causes. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/acute-coronary-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20352136
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Chest pain: First aid. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-chest-pain/basics/art-20056705
- WebMD. (2024). Acute Chest Syndrome in Adults with Sickle Cell Disease. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/acute-chest-syndrome
- Cleveland Clinic. (2025). Chest Pain: What It Feels Like, Causes & Treatment. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21209-chest-pain
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Chest pain – Diagnosis and treatment. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chest-pain/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20370842
- Pacific Cross Vietnam. (2025). Chest pain – Symptoms and causes. Available at: https://pacificcross.com.vn/chest-pain/
- BPAC. (2025). The immediate management of patients with acute chest pain. Available at: https://bpac.org.nz/2025/acs.aspx
- Open Respiratory Archives. (2020). Acute Chest Syndrome: An Unrecognized Progressive Condition. Available at: https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-open-respiratory-archives-11-articulo-acute-chest-syndrome-an-unrecognized-S2659663620300692
- Medical News Today. (2024). Chest pain: 27 causes, symptoms, and when to see a doctor. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321650
- Healthline. (2014). Chest Pain: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/chest-pain
- PMC. (2016). Acute chest pain fast track at the emergency department. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5144911/
- AAFP. (2020). Acute Chest Pain in Adults: Outpatient Evaluation. Available at: https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2020/1215/p721.html
- NCBI. (2022). Chest Pain – StatPearls. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470557/
- NHS. (2025). Chest pain. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/symptoms/chest-pain/
- Medical News Today. (2025). 10 home remedies for heart pain. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321133
- Wesley Medical Center. (2025). When to Visit the ER for Chest Pain. Available at: https://www.wesleymc.com/healthy-living/when-to-visit-the-er-for-chest-pain
- University of Chicago Medicine. (2021). What causes chest pain and when to consult a heart doctor. Available at: https://www.uchicagomedicine.org/forefront/heart-and-vascular-articles/2021/october/what-causes-chest-pain-and-when-to-consult-a-doctor
- PubMed. (1989). Management of acute chest pain syndrome. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2670088/
- NHLBI. (2023). Angina (Chest Pain) – Treatment. Available at: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/angina/treatment
- NJ Cardiovascular. (2009). When Do Chest Pains Warrant a Trip to the ER? Available at: https://www.njcardiovascular.com/blog/when-do-chest-pains-warrant-a-trip-to-the-er
- Nationwide Children’s. (2025). Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) and Acute Chest Syndrome (ACS). Available at: https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/sickle-cell-disease-and-acute-chest-syndrome
- The Cardiology Advisor. (2025). Chest Pain Differential Diagnosis. Available at: https://www.thecardiologyadvisor.com/ddi/chest-pain-differential-diagnosis/
- Science Direct. (2022). Care Models for Acute Chest Pain That Improve Outcomes. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0735109722047477
- Bayhealth Total Care. (2023). Can You Go to Urgent Care for Chest Pain? Available at: https://www.bayhealthtotalcare.org/blog/2023/june/can-you-go-to-urgent-care-for-chest-pain-/
- Priority Care Clinics. (2025). When to Visit Urgent Care for Chest Pain. Available at: https://prioritycareclinics.com/when-to-visit-urgent-care-for-chest-pain/
- Portland Urgent Care. (2025). Can I Go to Urgent Care for Chest Pain? Available at: https://www.portlandurgentcare.com/blog/can-i-go-to-urgent-care-for-chest-pain
- BVS. (2021). Chest Pain in the Emergency Room: Who is Left and Who Can Be Released? Available at: https://docs.bvsalud.org/biblioref/2021/08/970499/01_revistasocesp_v28_04_ingles.pdf
- AHA Journals. (2021). 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline. Available at: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
- PubMed. (2020). Acute Chest Pain in Adults: Outpatient Evaluation. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33320506/
- Medcare. (2024). Chest Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Diagnosis. Available at: https://www.medcare.ae/en/health-library/chest-pain-causes-symptoms-treatment-diagnosis.html
Related articles
Made in USA