I often see children and teens suffering from two common but confusing scalp conditions: tinea capitis and seborrheic dermatitis. While both can cause annoying scalp symptoms like flaking, redness and itch, accurately differentiating the two is critical for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In this comprehensive guide, I will leverage my medical expertise to clarify the key differences between fungal tinea capitis infections and inflammatory seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups. I will also cover clinical presentation, causes, testing methods and treatment options to empower both patients and physicians with authoritative knowledge for optimal scalp health management.
Introduction to Scalp Inflammation
Scalp inflammation falls into two general categories:
- Infections – Fungal, bacterial or viral organisms attacking hair follicles
- Inflammatory Conditions – Immune-mediated reactions
Tinea capitis represents fungal infection-driven scalp inflammation, while seborrheic dermatitis involves an inflammatory immune response.
Let’s break down the key similarities first.
Commonalities Between Tinea Capitis and Seborrheic Dermatitis
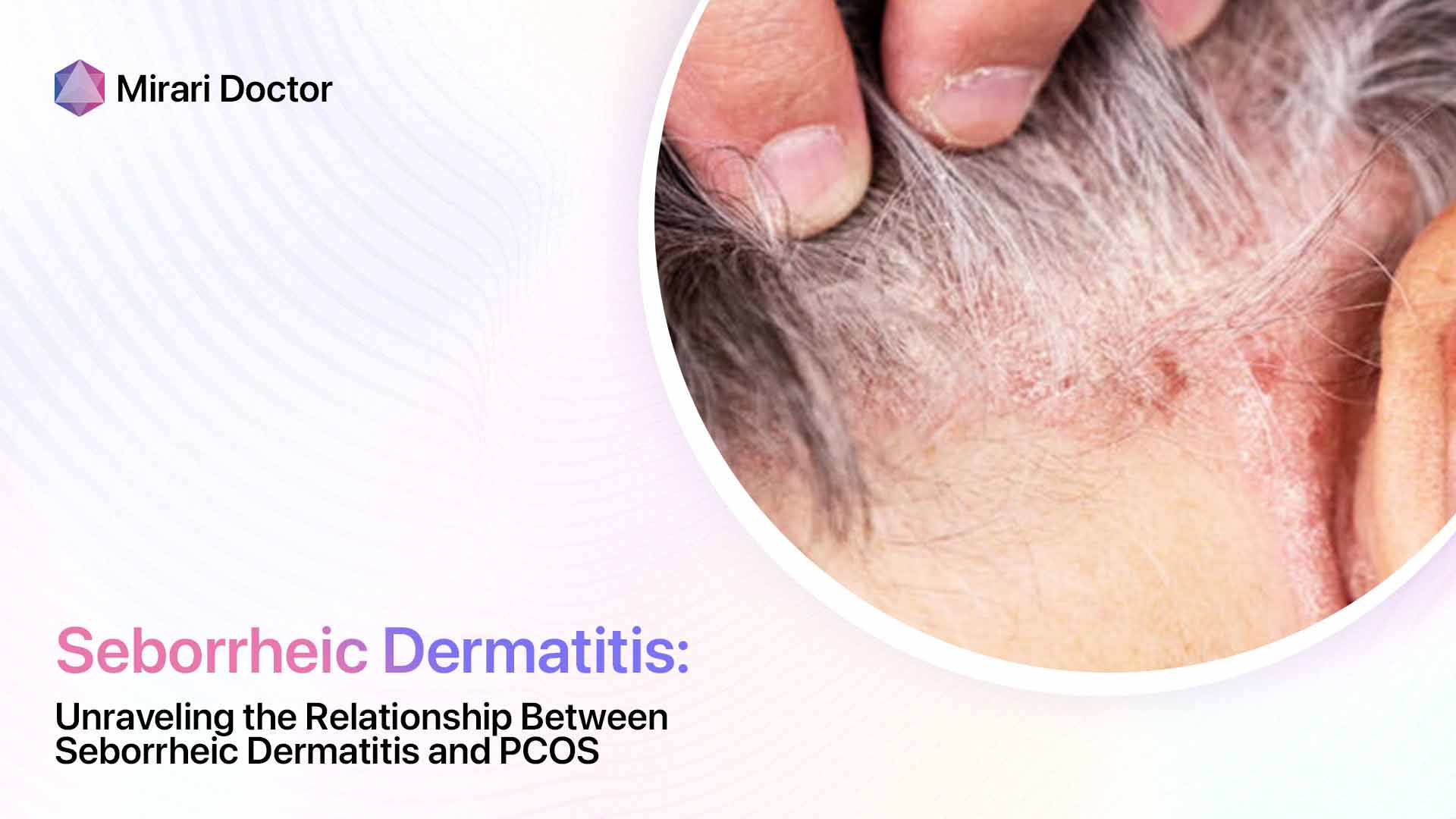
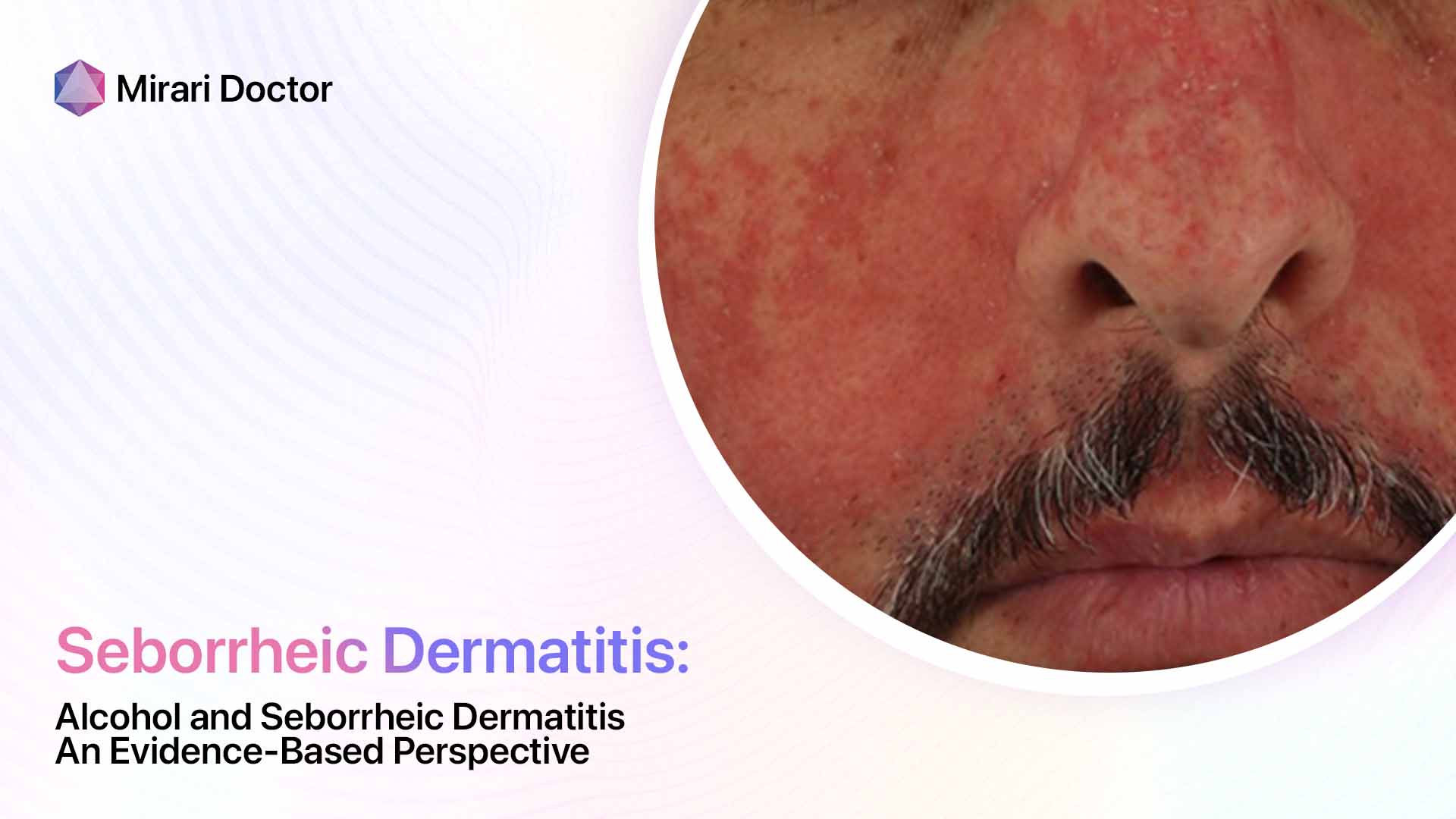
Overlapping Symptoms
- Scaly, flaky skin (dandruff-like)
- Red, irritated patches
- Itchy skin
- Temporary hair loss (in severe/chronic cases)
Due to these shared manifestations, tinea capitis is often initially misperceived as seborrheic dermatitis and vice versa, delaying intervention.
Prevalent Demographics
Both tinea capitis and seborrheic dermatitis tend to impact:
- Prepubescent children
- Teens
- Young adults
This further compounds diagnostic confusion in these high prevalence demographics.
Potential for Comorbidity
In some cases, patients actually suffer from both tinea capitis and seborrheic dermatitis concurrently. The conditions may synergistically provoke and exacerbate one another.
Careful testing is required to confirm if one or both scalp disorders are present for combo treatment.
Now let’s differentiate the key distinctions between the conditions.
Critical Differences Between Tinea Capitis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis
Etiology and Pathogenesis
Tinea capitis is caused by superficial fungal infection of hair shafts and follicles by dermatophytes, mainly:
- Trichophyton tonsurans
- Microsporum canis
- Microsporum audouinii
The fungi attack hairs, stimulating an inflammatory reaction.
Whereas seborrheic dermatitis develops fromSkinMalassezia yeasts triggering hyperactive sebaceous gland inflammation through mechanisms still being researched.
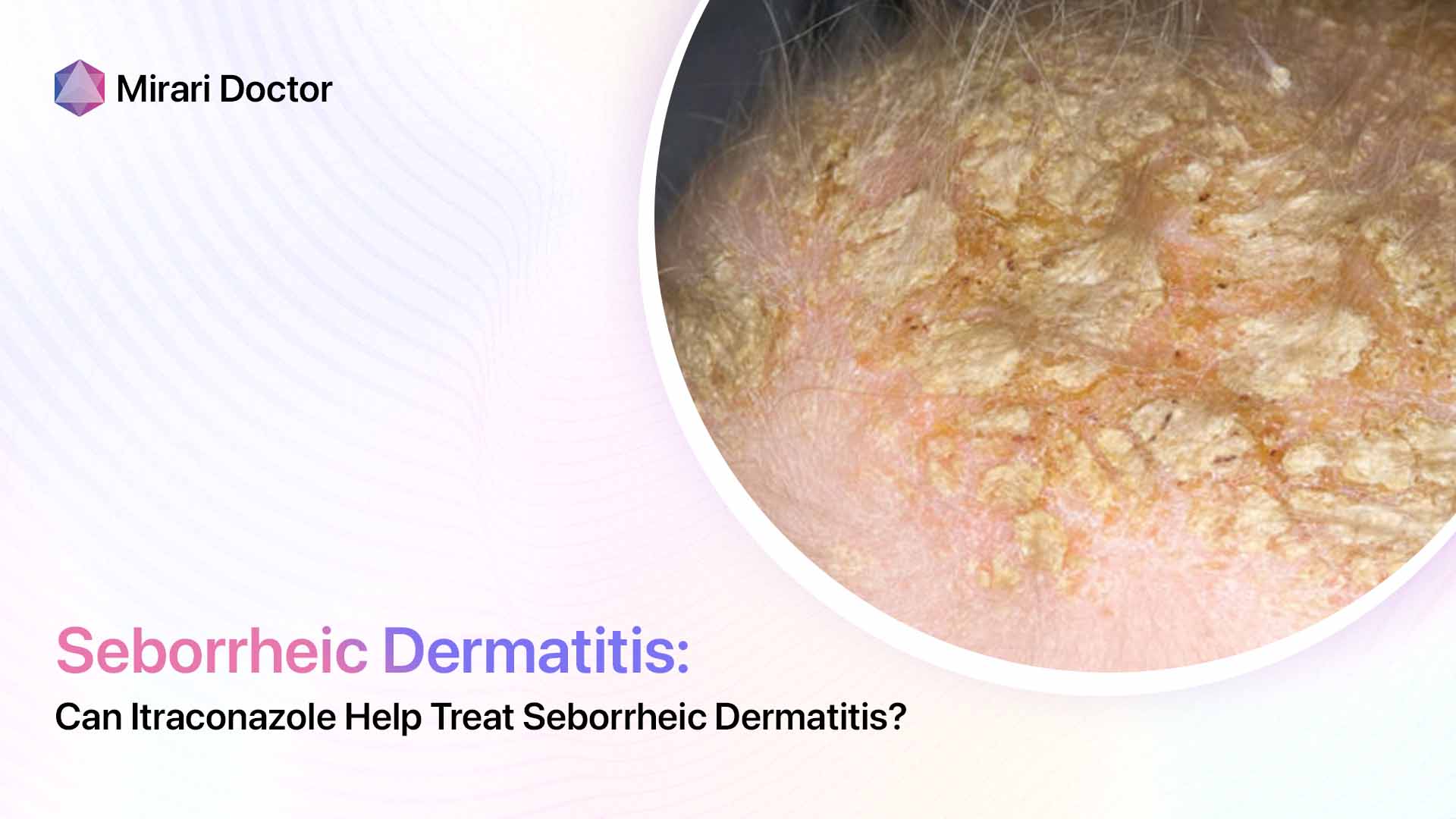
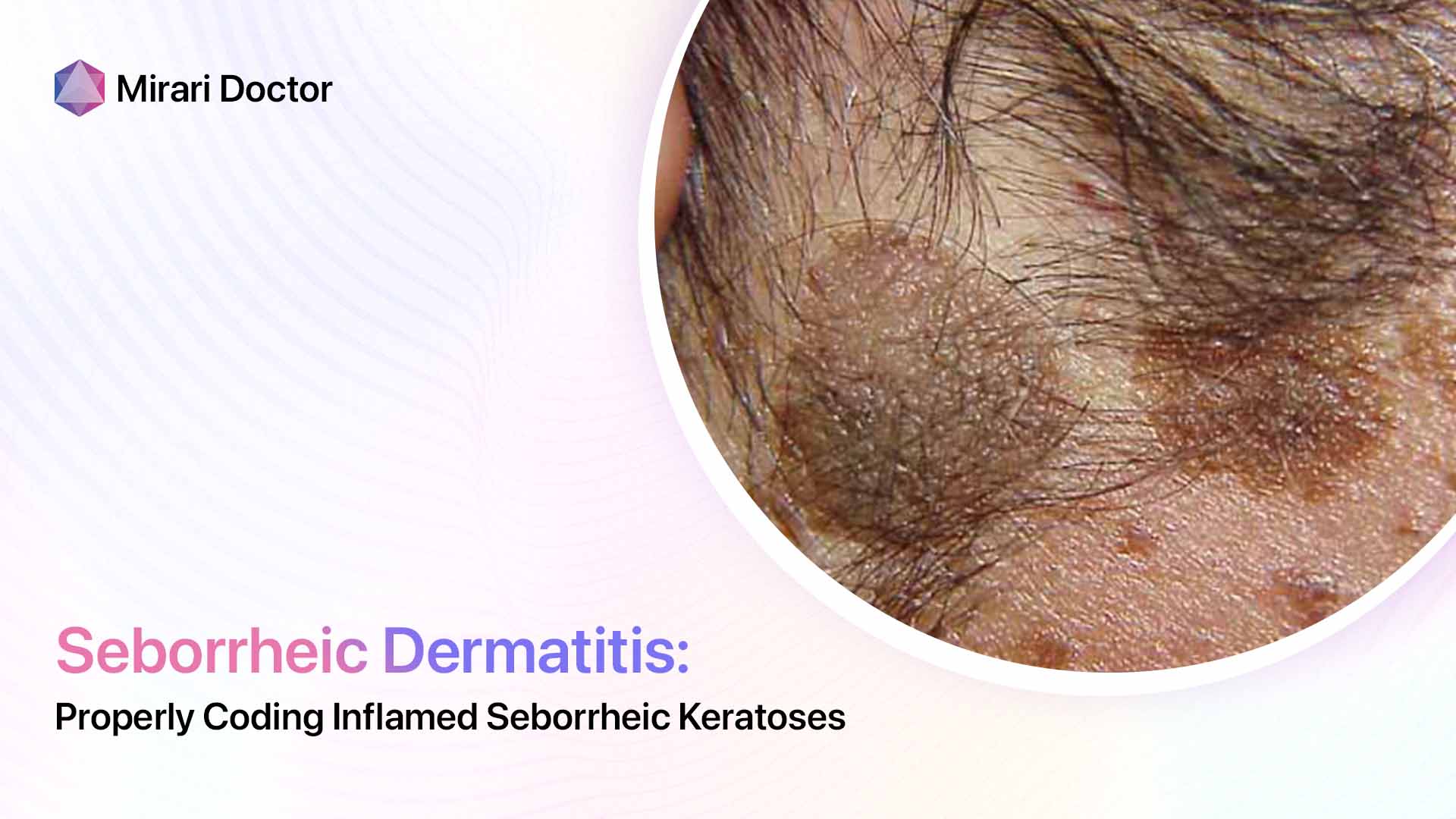
Clinical Presentation Variances
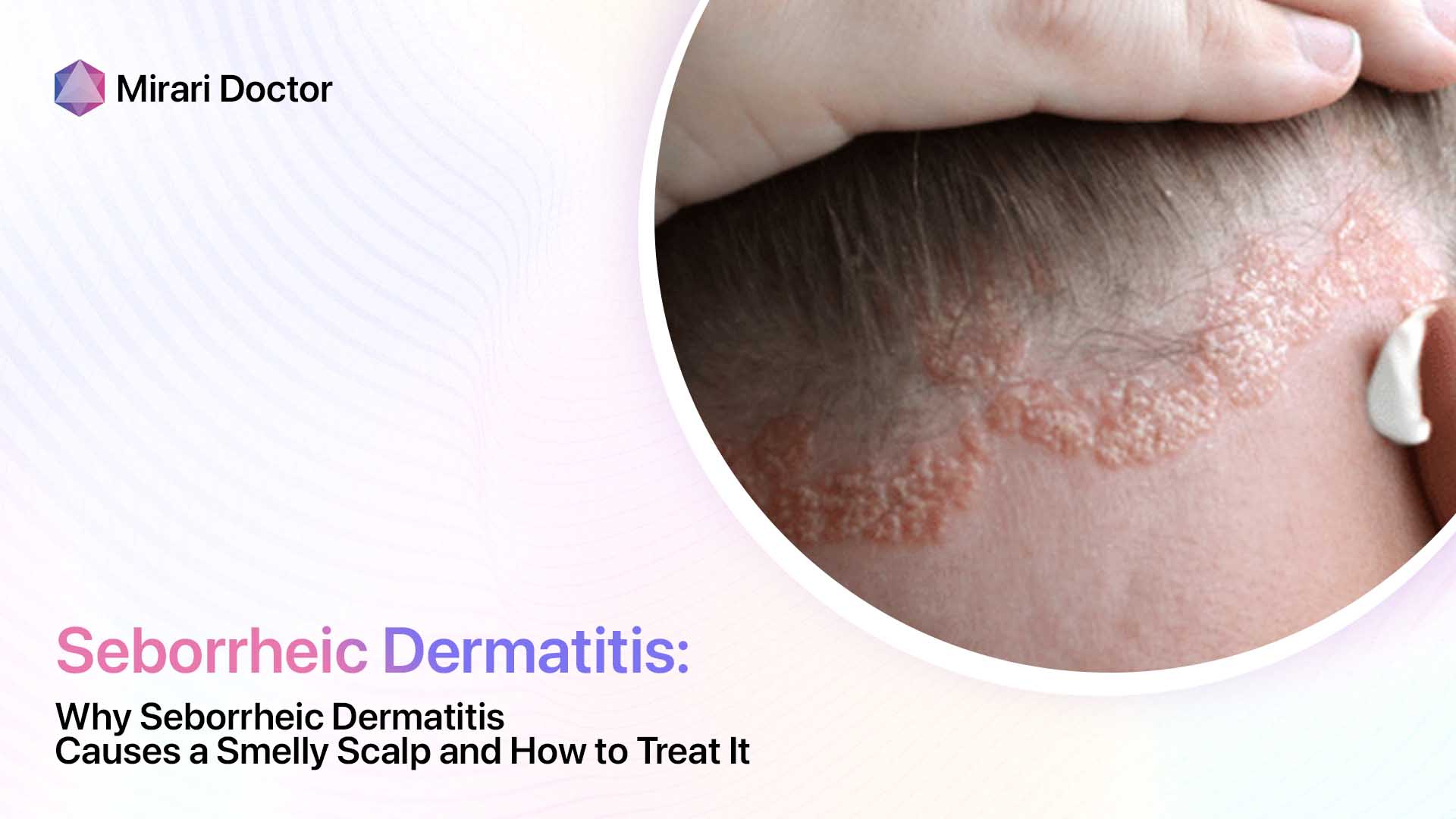
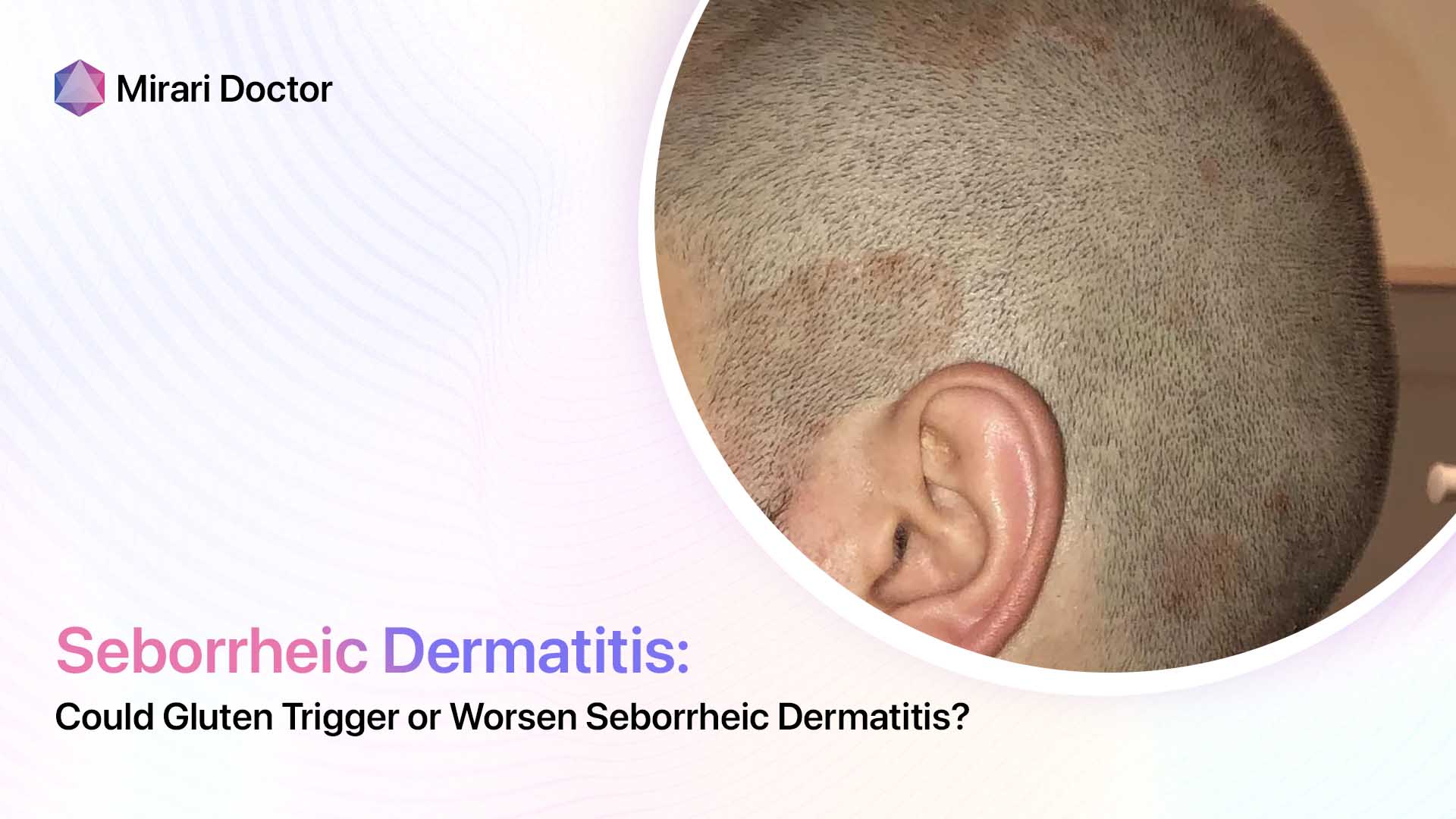
Tinea capitis infection manifests as:
- Well-demarcated hair loss patches
- Broken hairs visible
- Characteristic scaly plaques
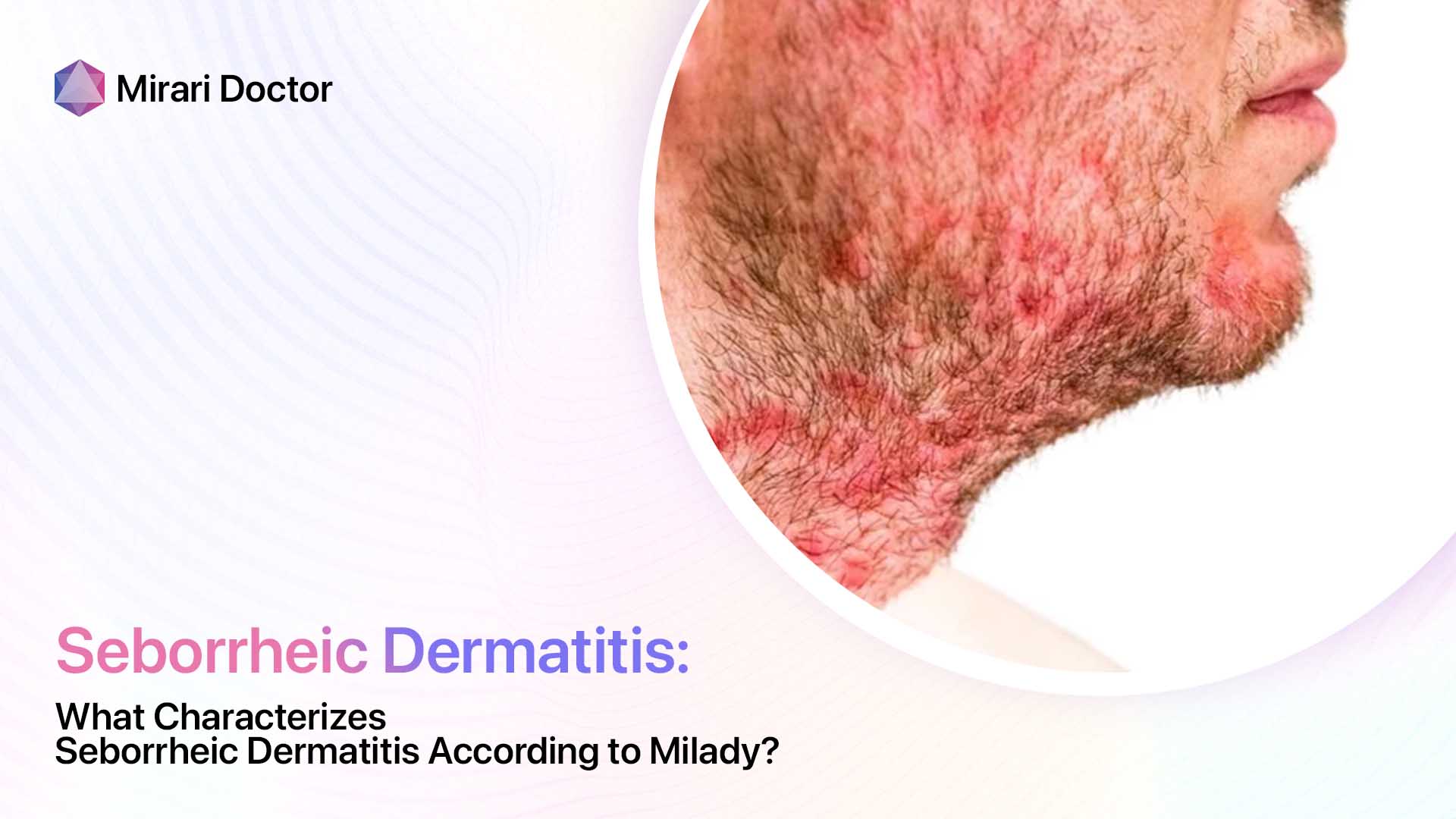
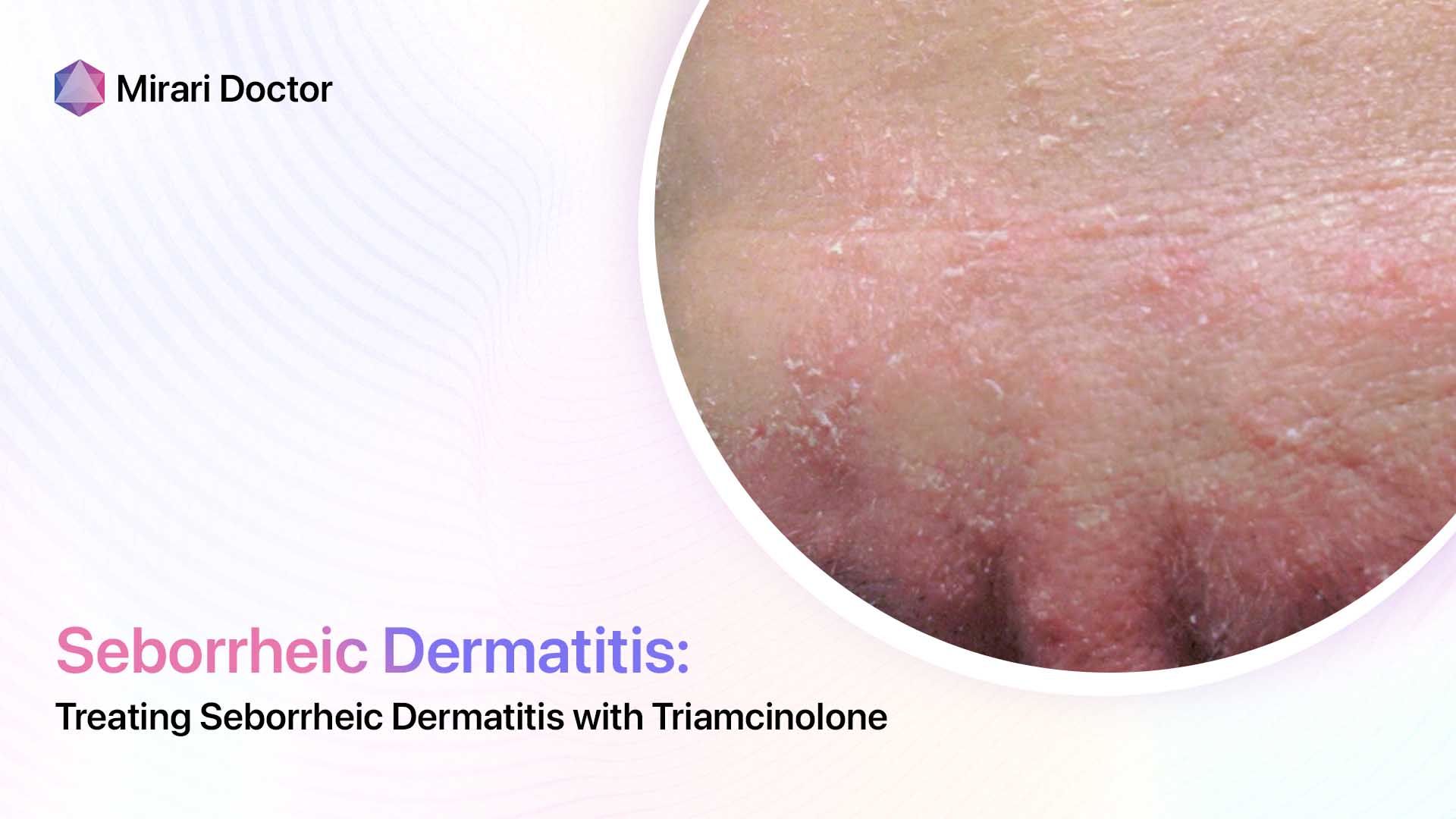
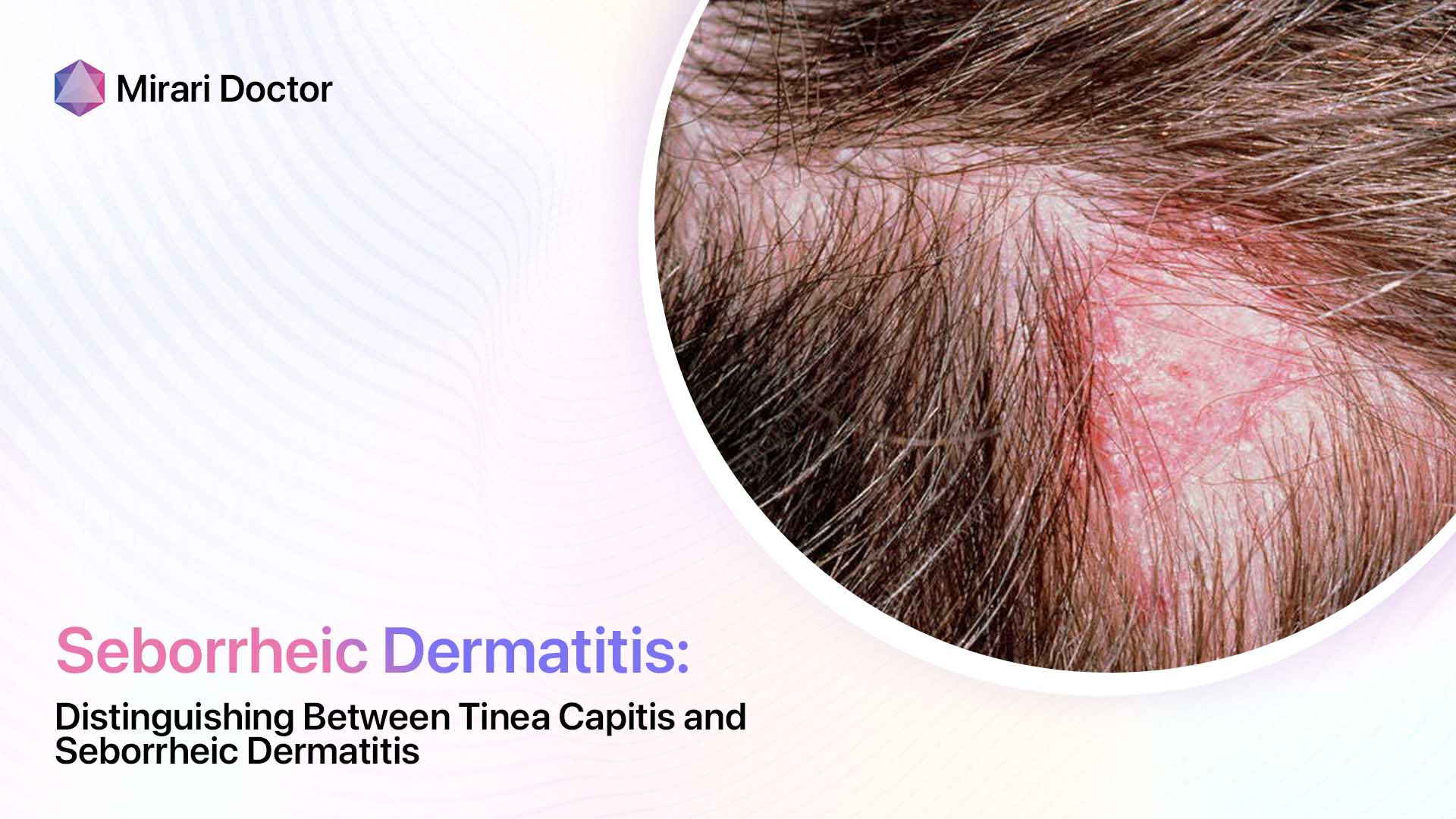
Seborrheic dermatitis flares involve:
- Poorly defined red, greasy areas
- No hair breakage
- Flexural distribution
So while both display scalp scaling, seborrheic dermatitis lacks defined balding patches and broken hairs indicative of tinea capitis fungal damage.
Testing and Diagnosis
Definitively diagnosing between tinea capitis vs seborrheic dermatitis involves:
- Microscopic exam and fungal culture of plucked hairs
- Skin scraping analysis
- Wood’s lamp inspection for fluorescence
These assessments can determine if pathogenic fungal elements are present signifying tinea capitis infection rather than solely inflammation.
Treatment Approaches
Medications used differs based on correctly identifying tinea capitis vs seborrheic dermatitis.
Tinea capitis requires systemic oral antifungal medications like:
- Griseofulvin
- Terbinafine
- Itraconazole
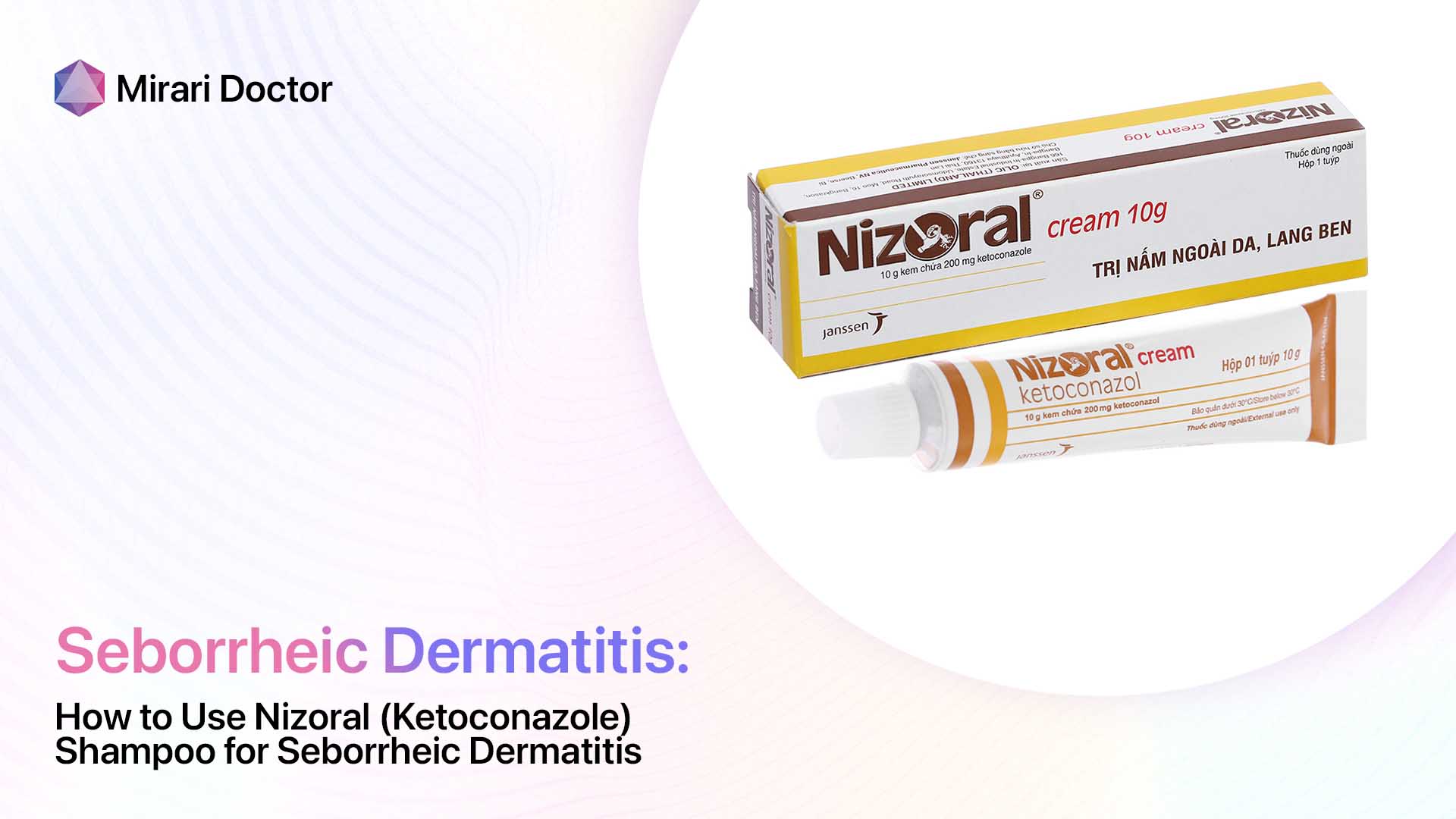
Whereas seborrheic dermatitis is often managed with topical:
- Medicated shampoos – Selenium sulfide, pyrithione zinc, ketoconazole
- Steroids – Hydrocortisone creams
So accurate diagnosis guides appropriate prescription of antifungal drugs for fungal infections vs topical anti-inflammatories for inflammatory flare-ups.
Let’s recap some key points in a comparison table:
| Factor | Tinea Capitis | Seborrheic Dermatitis |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Fungal infection | Inflammatory skin reaction |
| Areas Impacted | Well-defined patches | Poorly defined red, oily areas |
| Hair Loss | Broken hairs visible | No breakage, only shedding |
| Testing | Skin/hair exam shows fungi | Skin cultures negative for fungi |
| Treatment | Oral/topical antifungals | Topical steroids, medicated shampoos |
So while tinea capitis and seborrheic dermatitis share some common symptoms, properly distinguishing between their underlying fungal infection vs inflammatory immune causes is essential for appropriate diagnosis and management.
When to Seek Medical Care
If you or your child suffer from chronic, worsening or painful scalp issues, promptly consult a pediatric dermatologist. Early expert evaluation helps accurately differentiate and treat tinea capitis infections vs seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups for symptom relief and prevention of permanent hair loss.
Next, let’s explore some frequent questions about tinea capitis and seborrheic dermatitis comparisons.
FAQs
Can seborrheic dermatitis be mistaken for ringworm?
Yes, seborrheic dermatitis flares can mimic the scaly, red inflammation of ringworm (tinea capitis). Careful clinical inspection is required to check for hallmark tinea signs like defined balding patches and broken hairs. Microscopic skin testing can also confirm or rule out fungal infection.
What is the difference between dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis?
Dandruff represents mild flaking, while seborrheic dermatitis involves more severe, greasy scaling and redness caused by skin inflammation. But persistent dandruff can develop into seborrheic dermatitis if underlying causes like yeast or sebum imbalance are not addressed.
Can tinea capitis be mistaken for psoriasis?
Yes, the thick silvery-white scale buildup of scalp psoriasis outbreaks can resemble flaky tinea plaques before hair loss occurs. Skin scrapings or hair exams under a microscope can differentiate the psoriatic vs fungal skin changes.
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious?
No, seborrheic dermatitis is not considered contagious as it stems from internal skin inflammation rather than external pathogens. But secondary bacterial or fungal infections can sometimes develop and require antibiotics or antifungals.
How long does tinea capitis treatment take?
Oral antifungal treatment is usually given for 6-12 weeks until skin scrapings/hair follicle exams are clear. Maintenance antifungal shampoos may also be prescribed to prevent recurrence.
Conclusion and Takeaways
- Tinea capitis and seborrheic dermatitis both cause irritating scalp flaking, scaling and redness
- But tinea capitis involves infection with resulting hair breakage absent in the inflammation of seborrheic dermatitis
- Microscopic testing of skin and hair samples can definitively diagnose between fungal and inflammatory causes
- Accurate diagnosis then guides appropriate antifungal vs anti-inflammatory treatment
- Prompt diagnosis and management helps prevent scarring hair loss
I hope this detailed yet digestible guide to distinguishing between tinea capitis vs seborrheic dermatitis scalp conditions provides both informative and practical insights for those struggling with these often perplexing skin ailments. Please reach out with any other questions!
Related articles
Made in USA