As a dermatologist with over 20 years of experience, I have seen countless patients struggle with the frustrating and often embarrassing symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis. This common skin condition affects millions of people worldwide, causing redness, itching, and flaking on the scalp, face, and other oil-prone areas of the body. While the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis remains a mystery, recent research has shed light on a surprising connection between this inflammatory disease and vitamin deficiencies.
In this comprehensive article, we will dive deep into the link between seborrheic dermatitis and vitamins, exploring the latest scientific findings and practical tips for managing this challenging dermatological disorder. As a medical professional committed to providing accurate and trustworthy information, I will guide you through the complexities of this topic, empowering you with the knowledge and tools needed to take control of your skin health.
The Itchy Connection: How Seborrheic Dermatitis Affects Your Skin
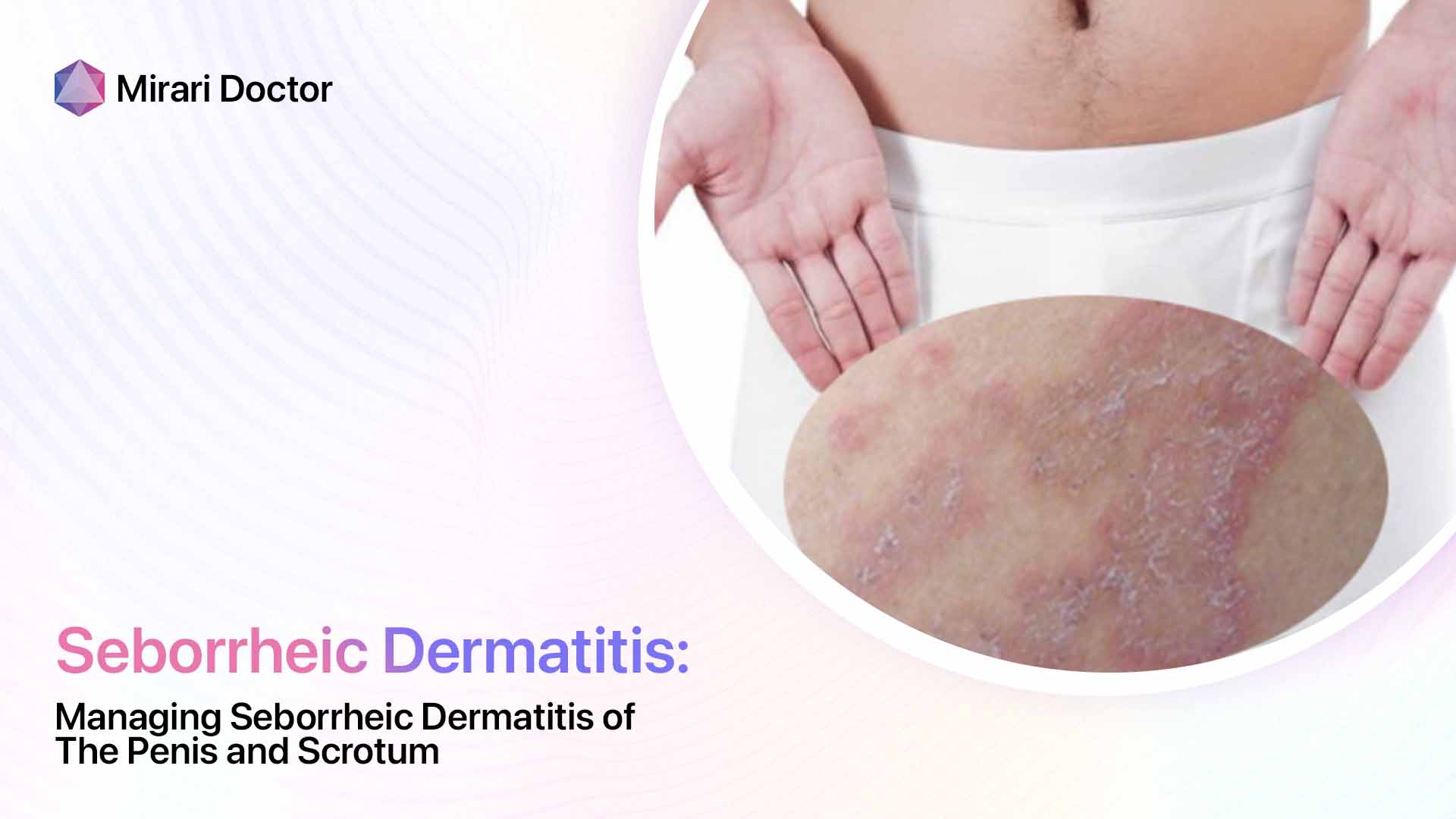
Before we delve into the role of vitamins in seborrheic dermatitis, let’s take a closer look at how this condition manifests on the skin. Seborrheic dermatitis, also known as seborrheic eczema, is characterized by several key symptoms that can vary in severity from person to person.
Inflammation and Redness
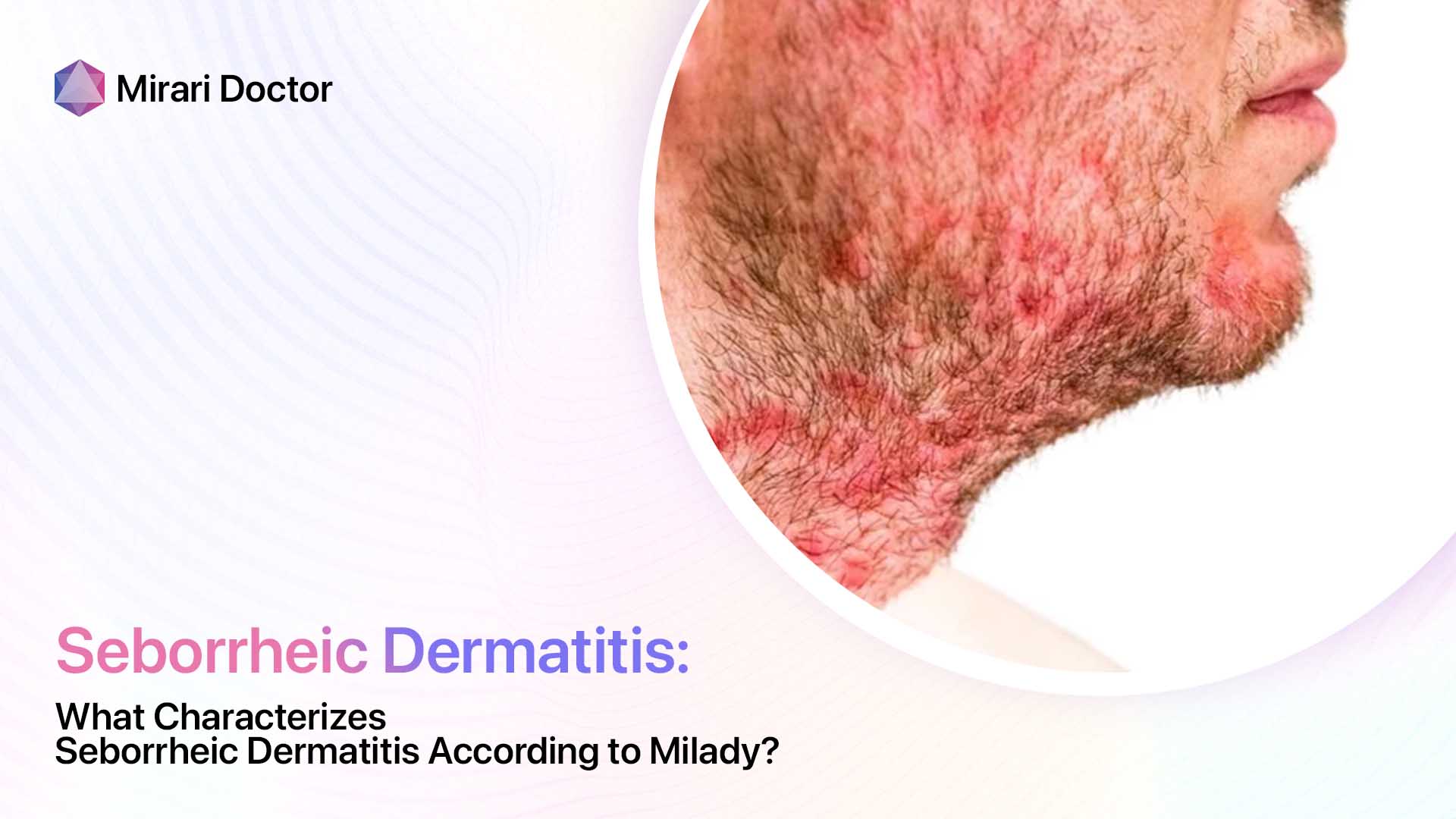
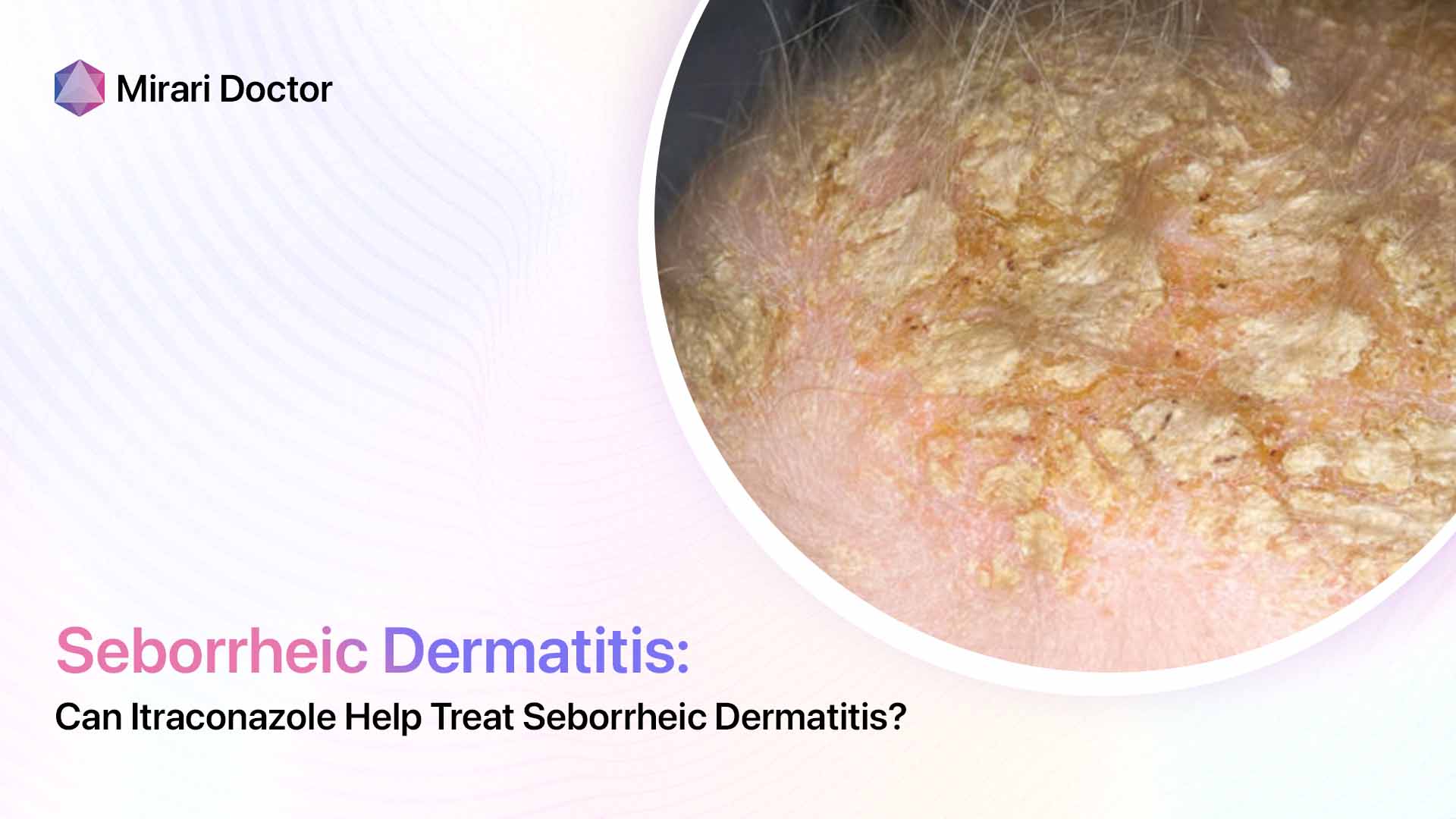
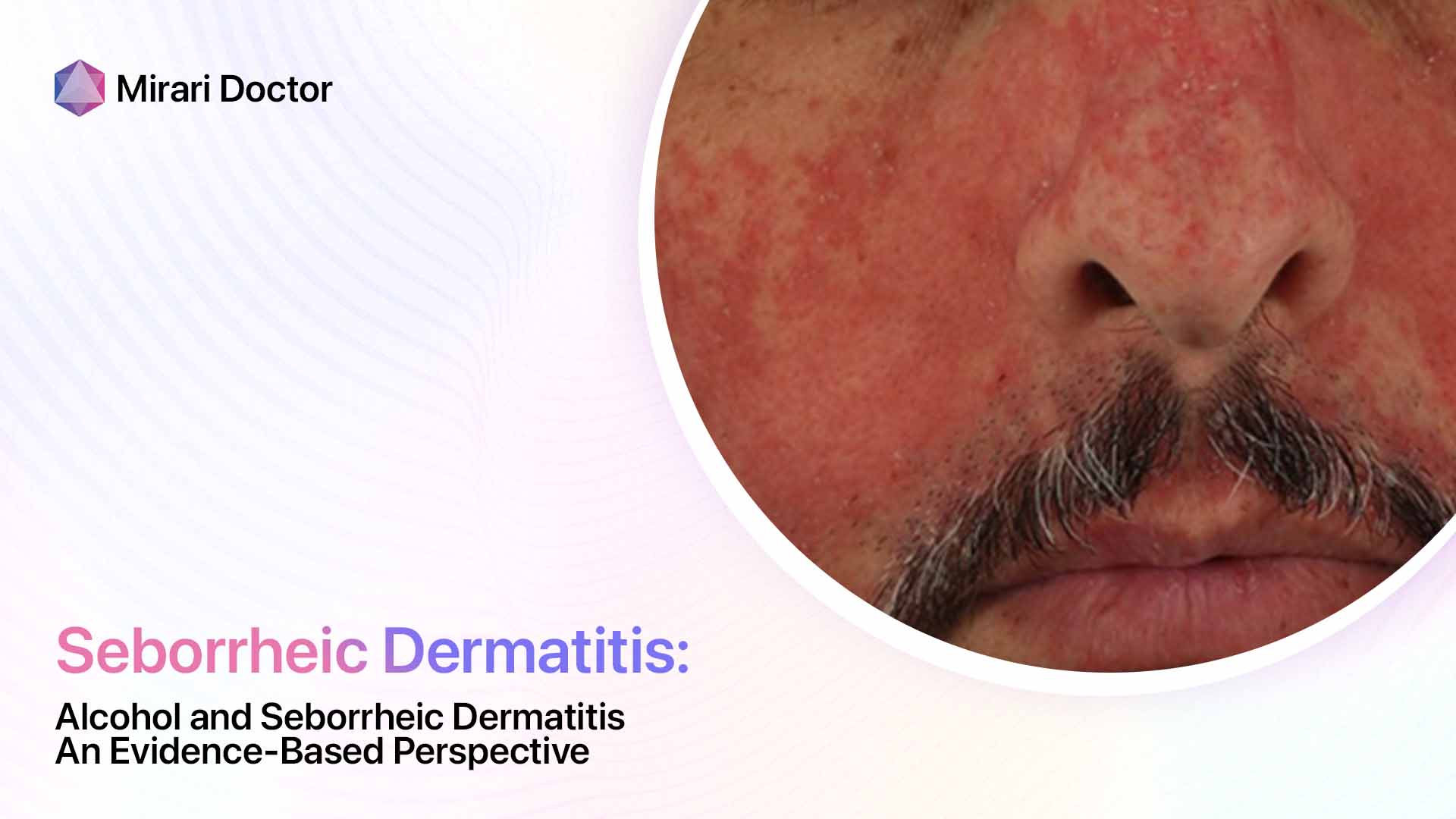
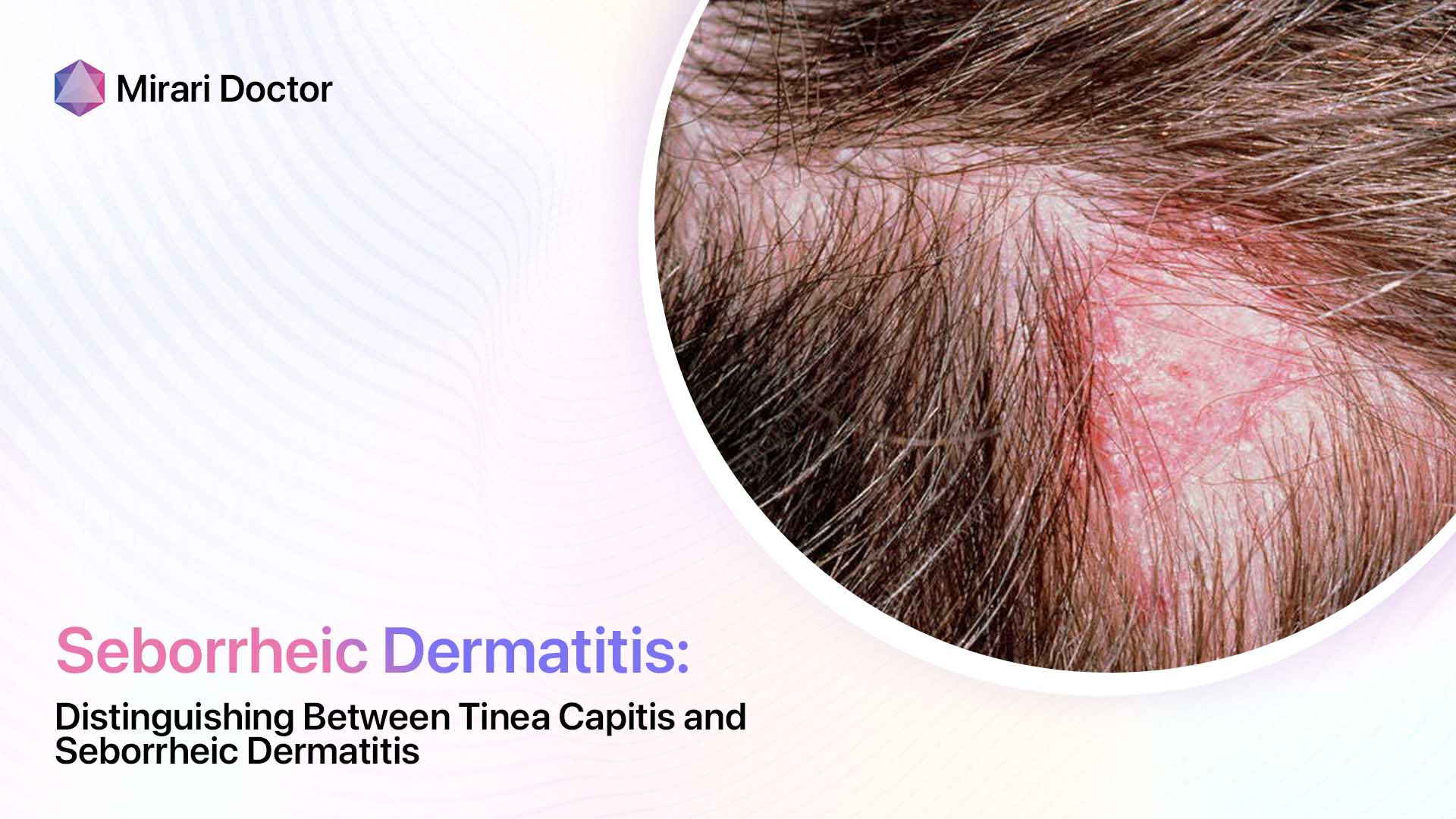
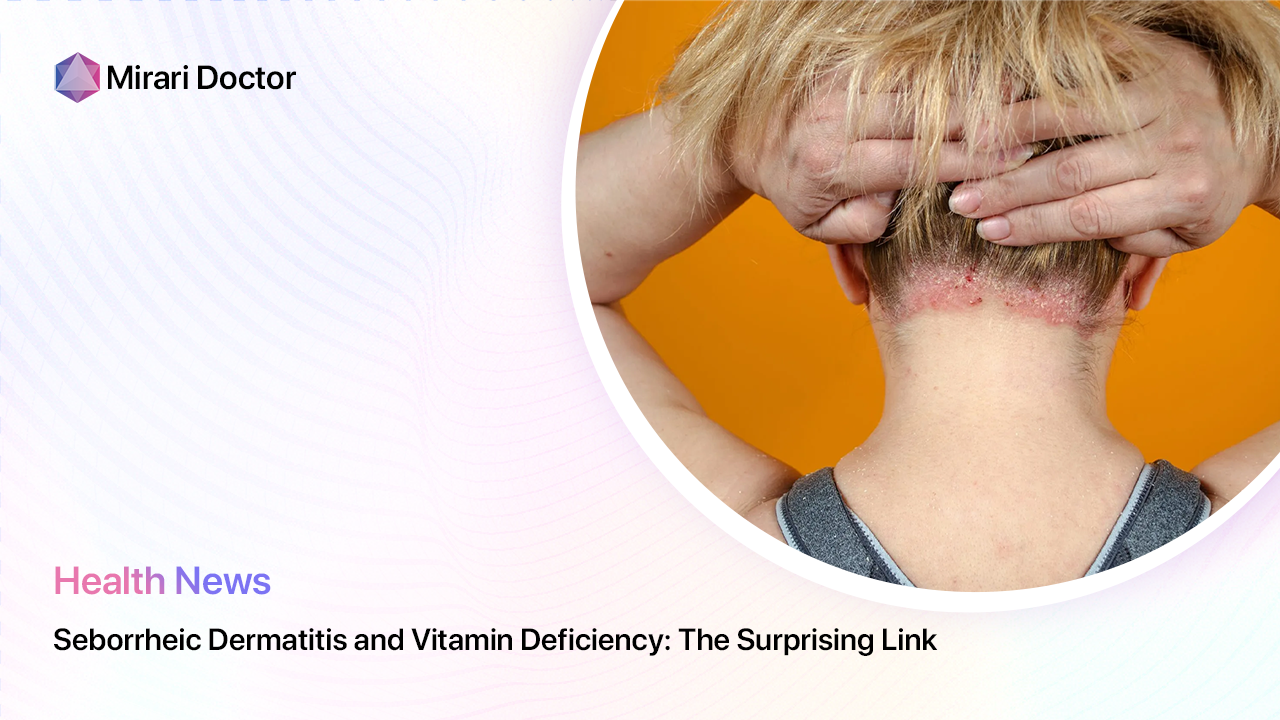
One of the hallmark signs of seborrheic dermatitis is inflammation, which causes the affected skin to appear red and irritated. This redness can range from a subtle pink hue to a deep, angry-looking crimson, depending on the intensity of the inflammation. The inflammatory process is triggered by an overgrowth of a yeast-like fungus called Malassezia, which naturally lives on the skin but can proliferate in certain conditions.
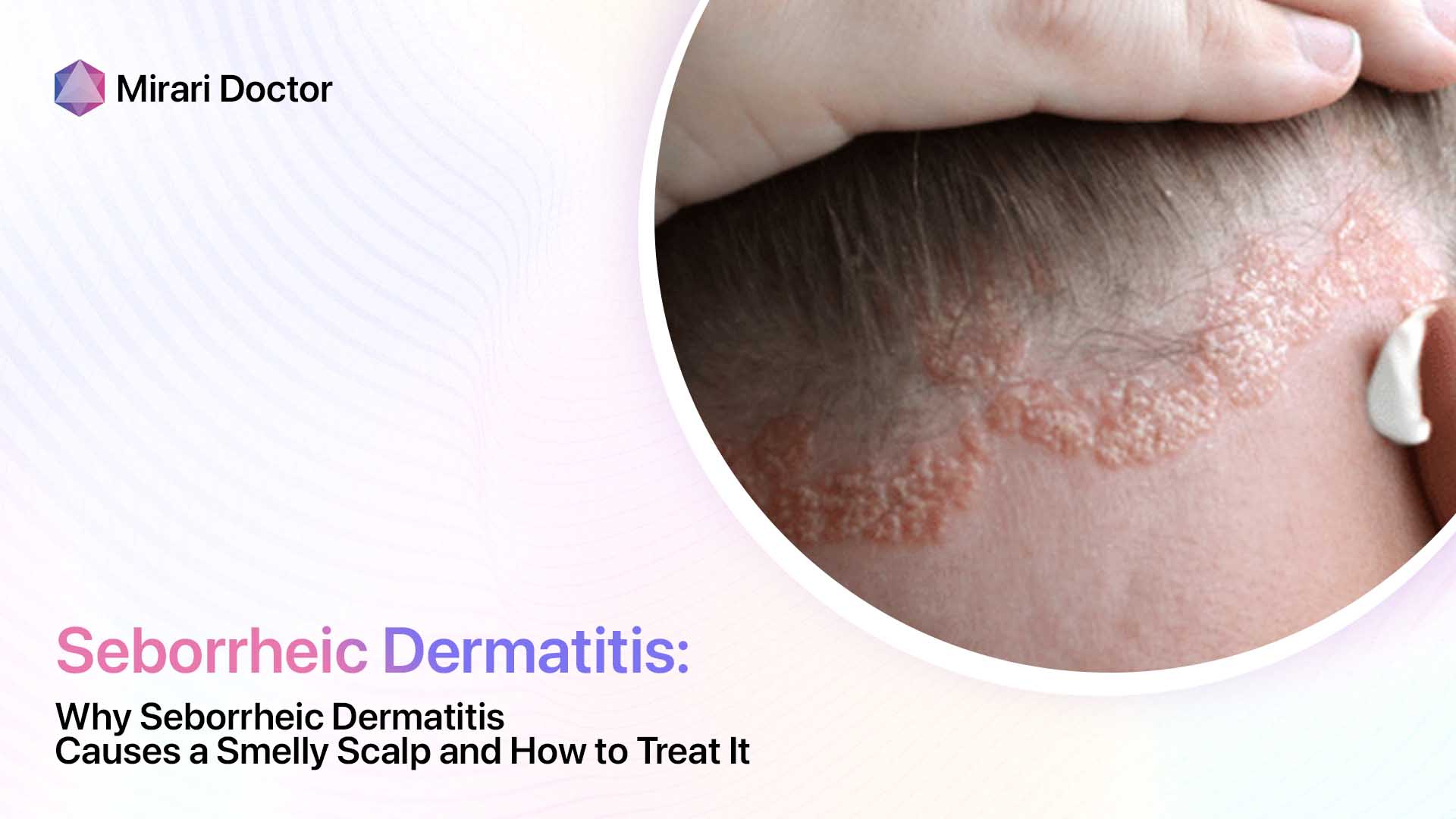
Flaking and Scaling
Another classic symptom of seborrheic dermatitis is the presence of flaky, scaly patches on the skin. These flakes, also known as dandruff when they appear on the scalp, can be white or yellowish in color and may be oily or dry to the touch. The scaling is a result of the skin’s rapid turnover rate, as the body tries to shed the irritated and inflamed cells.
Itching and Discomfort
For many people with seborrheic dermatitis, the itching and discomfort associated with the condition can be the most frustrating and challenging aspect to deal with. The itchiness can range from a mild annoyance to an intense, almost unbearable sensation that can interfere with daily activities and disrupt sleep. Some people may also experience a burning or stinging feeling in the affected areas.
Differentiating from Dandruff
It’s important to note that while dandruff is a form of seborrheic dermatitis that primarily affects the scalp, not all cases of dandruff are caused by this condition. Dandruff can also be a result of dry skin, sensitivity to hair care products, or other factors. However, if your dandruff is accompanied by redness, inflammation, and itching, it’s more likely to be a sign of seborrheic dermatitis.
Potential Impact on Self-Esteem
Living with seborrheic dermatitis can take a toll on a person’s self-esteem and confidence, as the visible symptoms can be difficult to hide and may attract unwanted attention or comments from others. As one patient shared with me, “Seborrheic dermatitis can be embarrassing and affect a person’s quality of life.” It’s crucial to remember that this condition is not a reflection of poor hygiene or personal cleanliness, and there are effective ways to manage the symptoms and regain control over your skin health.
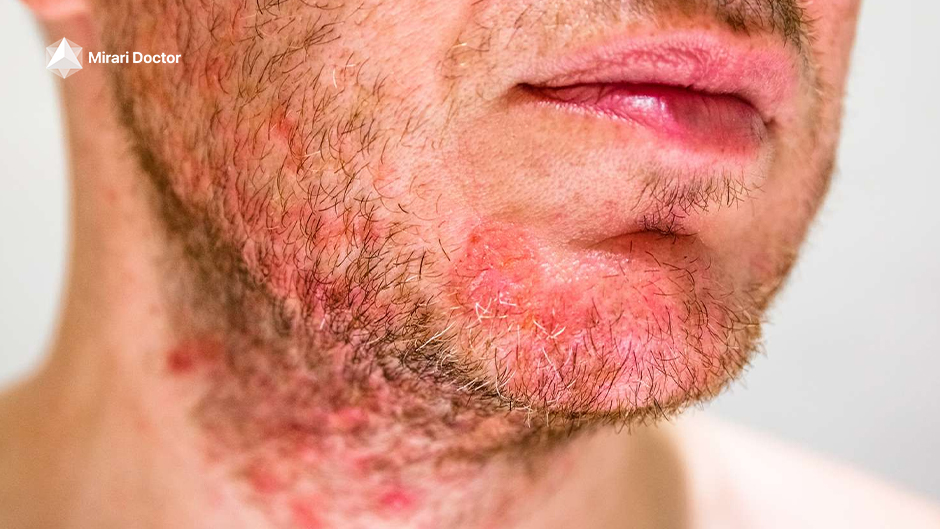
Can Vitamin Deficiencies Cause Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Now that we have a better understanding of how seborrheic dermatitis affects the skin, let’s explore the intriguing connection between this condition and vitamin deficiencies. While the exact causes of seborrheic dermatitis are still being researched, a growing body of evidence suggests that certain vitamin deficiencies may play a role in the development and severity of this skin condition.
Exploring the Link Between Vitamins and Skin Health
Vitamins are essential nutrients that play a vital role in maintaining overall health, including the health of our skin. They help to support the skin’s natural barrier function, promote cell turnover and regeneration, and protect against oxidative stress and inflammation. When our bodies are deficient in certain vitamins, it can lead to a range of skin problems, from dryness and dullness to more severe conditions like seborrheic dermatitis.
Specific Vitamins Potentially Involved
Several specific vitamins have been linked to seborrheic dermatitis, either through direct research or through their known effects on skin health. These include:
- Zinc: This mineral is crucial for skin repair and regeneration, and studies have found that people with seborrheic dermatitis often have lower levels of zinc compared to healthy individuals.
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin): Niacin deficiency, also known as pellagra, can cause a range of skin problems, including a type of dermatitis that resembles seborrheic dermatitis.
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): Like niacin, riboflavin is important for maintaining healthy skin, and deficiencies can lead to dermatitis and other skin issues.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): This vitamin plays a role in skin metabolism and the production of skin cells, and deficiencies have been linked to various skin conditions.
- Vitamin D: While the research on vitamin D and seborrheic dermatitis is limited, some studies suggest that people with this condition may have lower levels of vitamin D compared to healthy individuals.
It’s important to note that while vitamin deficiencies may contribute to the development or severity of seborrheic dermatitis, they are not the only factor involved. Genetics, immune function, and environmental triggers like stress and climate can also play a role.
Takeaway: While Some Vitamins May Play a Role, a Deficiency Isn’t Always the Cause
While the connection between vitamin deficiencies and seborrheic dermatitis is intriguing, it’s crucial to remember that not all cases of this condition are caused by a lack of specific nutrients. In many cases, seborrheic dermatitis can occur even in people with adequate vitamin levels, and addressing a deficiency may not always lead to a complete resolution of symptoms.
However, ensuring that you are getting enough of these key vitamins through a balanced diet and targeted supplementation (under the guidance of a healthcare provider) can be an important part of a holistic approach to managing seborrheic dermatitis and supporting overall skin health.
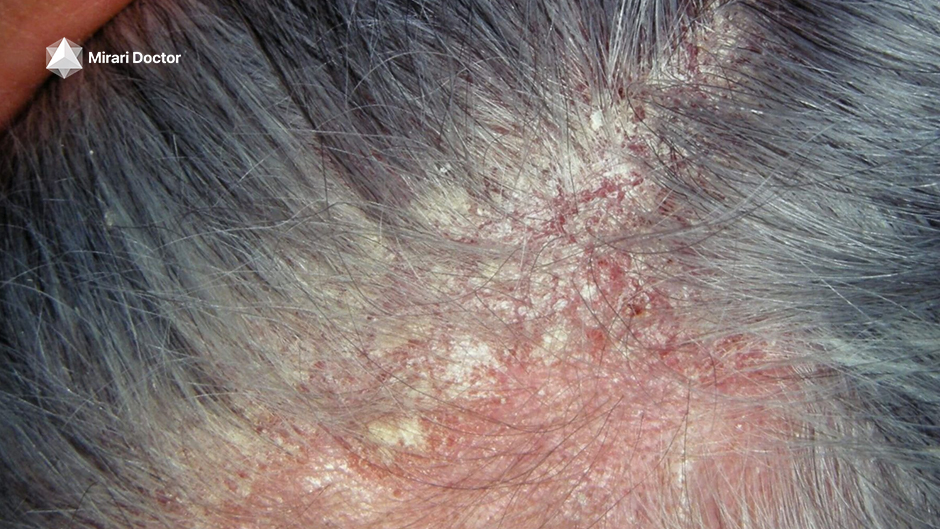
The Vitamin D Question: Can It Help Seborrheic Dermatitis?
One vitamin that has garnered particular attention in the context of seborrheic dermatitis is vitamin D. This essential nutrient, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin” because our bodies can produce it when our skin is exposed to sunlight, has been linked to a range of health benefits, from strengthening bones to boosting immune function.
Research on Vitamin D and Skin Conditions
Some studies have suggested that vitamin D may play a role in the development and severity of certain skin conditions, including atopic dermatitis (eczema) and psoriasis. However, the research on vitamin D and seborrheic dermatitis specifically is more limited and inconclusive.
A few small studies have found that people with seborrheic dermatitis may have lower levels of vitamin D compared to healthy individuals, and that supplementation with vitamin D may help to improve symptoms in some cases. However, larger and more robust studies are needed to confirm these findings and determine the optimal dosage and duration of treatment.
Importance of Consulting a Doctor for Vitamin D Testing
If you suspect that you may have a vitamin D deficiency, or if you are considering starting a vitamin D supplement to help manage your seborrheic dermatitis, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider first. Your doctor can order a simple blood test to check your vitamin D levels and determine if a deficiency is present.
It’s also important to note that while vitamin D is generally safe when taken in recommended doses, it is possible to take too much and experience adverse effects. Your doctor can help you determine the right dosage based on your individual needs and health status.

Diagnosing Seborrheic Dermatitis and Vitamin Deficiencies
If you are experiencing symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis or suspect that you may have a vitamin deficiency, the first step in getting the answers you need is to schedule an appointment with a qualified healthcare provider, such as a dermatologist or primary care physician. Your doctor can perform a thorough evaluation and help determine the underlying cause of your symptoms.
Importance of Consulting a Doctor
While it may be tempting to self-diagnose or try over-the-counter treatments for seborrheic dermatitis, it’s crucial to seek professional medical advice. Seborrheic dermatitis can mimic other skin conditions, such as psoriasis or atopic dermatitis, and an accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment.
Additionally, if a vitamin deficiency is suspected, it’s important to have your levels tested by a healthcare professional. Attempting to self-treat with vitamin supplements without proper guidance can be ineffective or even harmful, as some vitamins can be toxic in high doses.
Diagnostic Process
During your appointment, your doctor will likely perform the following:
- Physical examination: Your doctor will carefully examine your skin, noting the location, appearance, and severity of your symptoms. They may also check for signs of other skin conditions or underlying health issues.
- Medical history: Your doctor will ask about your personal and family medical history, including any previous skin problems, allergies, and medications you are taking. They may also inquire about your diet, lifestyle habits, and any recent changes or stressors in your life.
- Skin scraping or biopsy: In some cases, your doctor may take a small sample of skin cells or skin scrapings to examine under a microscope. This can help confirm the presence of Malassezia fungus or rule out other skin conditions.
- Blood tests: If a vitamin deficiency is suspected, your doctor may order blood tests to check your levels of specific nutrients, such as zinc, B vitamins, or vitamin D. These tests can help determine if a deficiency is contributing to your seborrheic dermatitis.
Based on the results of your evaluation, your doctor will provide a diagnosis and recommend an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your individual needs.
Soothing the Itch: Treatment Options for Seborrheic Dermatitis
Once seborrheic dermatitis has been diagnosed, the focus shifts to managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Treatment for seborrheic dermatitis typically involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle modifications.
Topical Medications
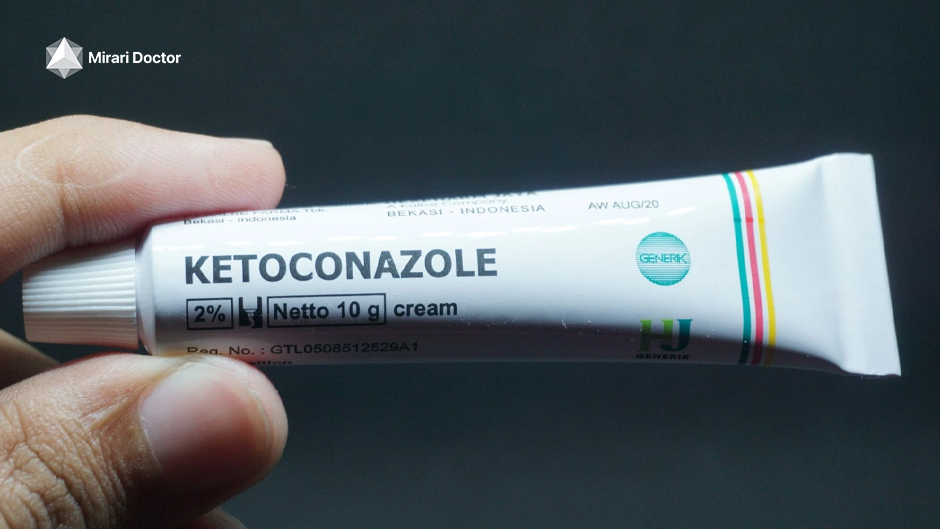
The mainstay of treatment for seborrheic dermatitis is topical medications, which are applied directly to the affected skin. These may include:
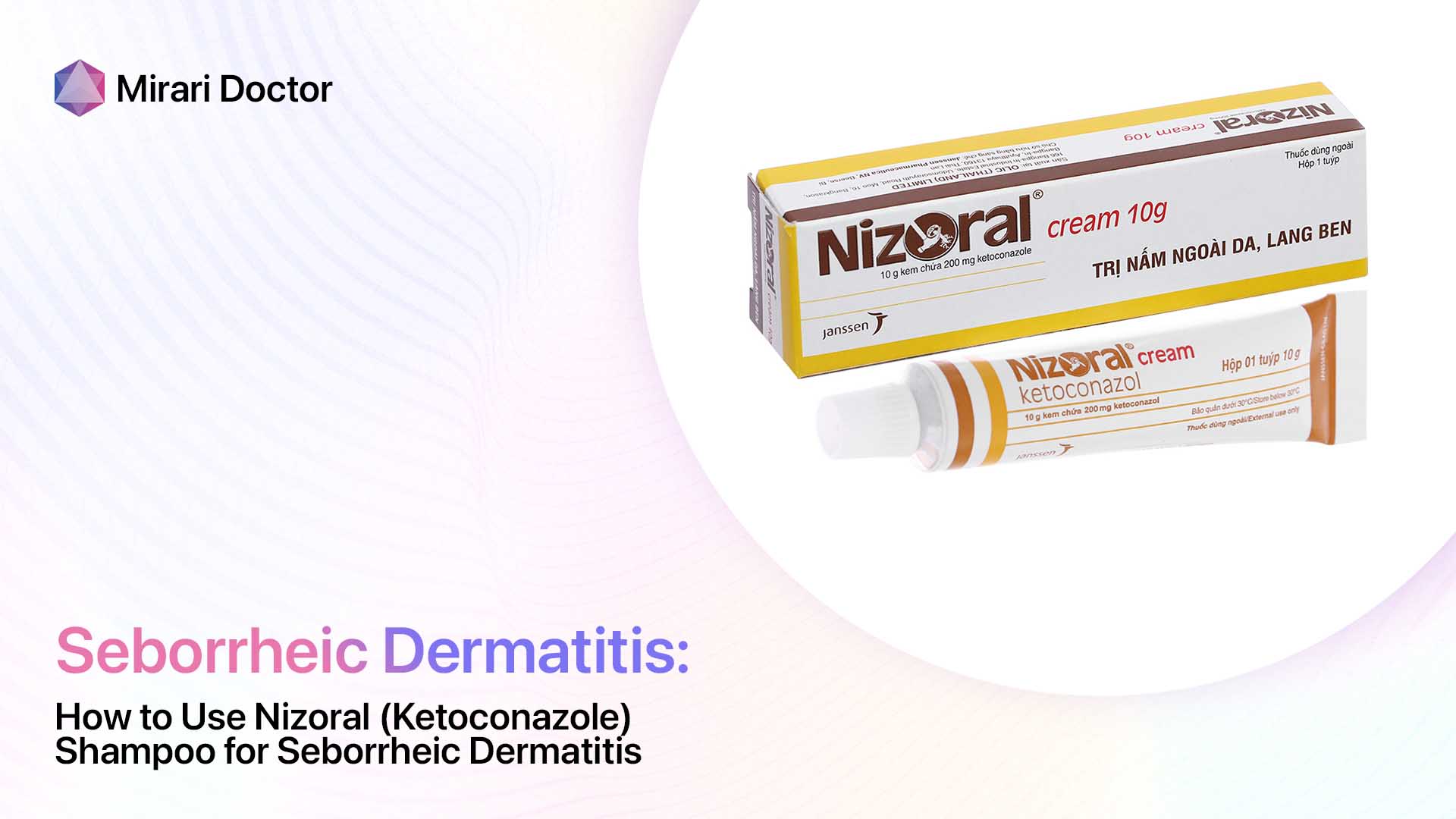
- Antifungal creams or shampoos: These products, such as ketoconazole or ciclopirox, help control the overgrowth of Malassezia fungus on the skin. They are typically used once or twice daily for several weeks, then as needed for maintenance.
- Corticosteroid creams or ointments: Topical corticosteroids, such as hydrocortisone or betamethasone, can help reduce inflammation, redness, and itching associated with seborrheic dermatitis. These are usually used for short periods during flare-ups, as long-term use can lead to side effects.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: These non-steroidal creams, such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, can help reduce inflammation and are sometimes used as an alternative to corticosteroids.
Your doctor will recommend the most appropriate topical treatment based on the severity and location of your seborrheic dermatitis.
Dietary Changes to Address Deficiencies
In addition to topical treatments, your doctor may recommend dietary changes to address any underlying vitamin deficiencies that may be contributing to your seborrheic dermatitis. This may involve increasing your intake of foods rich in specific nutrients or taking vitamin supplements under medical supervision.
It’s important to remember that while diet can play a role in skin health, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. Always consult with your doctor before making significant changes to your diet or starting any new supplements.
Finding the Right Foods: Including Zinc and B Vitamins in Your Diet
If your doctor has identified a deficiency in zinc or B vitamins as a potential factor in your seborrheic dermatitis, they may recommend incorporating more foods rich in these nutrients into your diet. Here are some examples:
- Zinc-rich foods: Oysters, beef, crab, pork, chicken, beans, nuts, and fortified cereals.
- Vitamin B3 (niacin) sources: Turkey, chicken, tuna, salmon, beef, peanuts, and legumes.
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) sources: Eggs, lean meats, milk, green vegetables, and fortified grains.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) sources: Poultry, fish, potatoes, chickpeas, bananas, and avocados.
Remember, a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods is key to supporting overall skin health. If you have difficulty obtaining enough of these nutrients through diet alone, your doctor may recommend supplements to help address deficiencies.
Preventing Flare-Ups: Managing Seborrheic Dermatitis Long-Term
While seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic condition that may require ongoing management, there are steps you can take to help prevent flare-ups and keep your symptoms under control. Scheduling an appointment with a dermatologist can provide you with personalized guidance on long-term management strategies.
Identifying Triggers
One important aspect of managing seborrheic dermatitis is identifying and avoiding potential triggers that can exacerbate your symptoms. Common triggers include:
- Stress: Emotional stress can weaken the immune system and increase inflammation, making seborrheic dermatitis worse. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as through exercise, meditation, or therapy, can help reduce flare-ups.
- Cold or dry weather: Low humidity and cold temperatures can dry out the skin, making it more prone to irritation and flaking. Using a humidifier and applying moisturizer regularly can help combat these effects.
- Harsh skincare products: Products containing alcohol, fragrances, or other irritants can aggravate seborrheic dermatitis. Choosing gentle, non-comedogenic, and fragrance-free products can help minimize irritation.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as lithium, interferon, and psoralen, can trigger or worsen seborrheic dermatitis. If you suspect a medication may be contributing to your symptoms, consult your doctor to discuss alternatives.
Keeping a symptom diary can help you identify your personal triggers and make lifestyle adjustments to avoid them.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
In addition to avoiding triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help support your skin health and reduce the frequency and severity of seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups. This includes:
- Eating a balanced diet: Consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including those rich in zinc and B vitamins, can help support skin health from the inside out.
- Managing stress: Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as exercise, hobbies, or spending time with loved ones, can help keep your immune system strong and your skin healthy.
- Practicing good skincare habits: Gently cleansing your skin, using moisturizer, and protecting your skin from the sun can help maintain the skin’s natural barrier and reduce irritation.
- Getting enough sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health, including skin health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to help your body repair and regenerate.
By incorporating these healthy habits into your daily routine, you can help manage your seborrheic dermatitis and improve your overall well-being.
Living with Seborrheic Dermatitis: Tips and Support
Living with a chronic skin condition like seborrheic dermatitis can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It’s important to remember that you are not alone and that there are resources available to help you cope with the impact of this condition on your daily life.
Finding Emotional Support
The visible symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis can sometimes lead to feelings of self-consciousness or embarrassment. It’s important to remember that this condition is not a reflection of your personal hygiene or self-care, and that many people struggle with similar issues.
Seeking support from loved ones, friends, or a therapist can help you manage the emotional impact of seborrheic dermatitis. Joining a support group, either in-person or online, can also provide a sense of community and allow you to connect with others who understand what you’re going through.
Managing Self-Consciousness
While it’s normal to feel self-conscious about the appearance of your skin, it’s important to remember that “There are ways to manage seborrheic dermatitis and feel confident in your skin.” Here are some tips for managing self-consciousness related to seborrheic dermatitis:
- Choosing gentle skincare products: Opt for non-comedogenic, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers that are less likely to irritate your skin. Look for products specifically formulated for sensitive or eczema-prone skin.
- Applying makeup strategically: If you choose to wear makeup, select non-comedogenic, mineral-based products that are less likely to aggravate your skin. Use a light touch when applying, and be sure to remove all makeup gently at the end of the day.
- Focusing on your overall appearance: While seborrheic dermatitis may be visible on your skin, remember that it does not define your overall appearance or worth. Dress in clothes that make you feel confident, style your hair in a way that makes you feel good, and focus on your positive attributes.
- Practicing self-compassion: Be kind to yourself and remember that everyone has challenges they are dealing with, even if they are not visible on the surface. Treat yourself with the same compassion and understanding you would extend to a good friend.
By incorporating these strategies and working closely with your dermatologist to manage your seborrheic dermatitis, you can build confidence and feel more comfortable in your skin.

FAQs
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious?
No, seborrheic dermatitis is not contagious. You cannot catch it from or spread it to another person through physical contact or by sharing personal items like towels or hairbrushes.
Can seborrheic dermatitis be cured?
Currently, there is no known cure for seborrheic dermatitis. However, with proper treatment and management strategies, the condition can be effectively controlled, and symptoms can be minimized. Many people are able to find a maintenance regimen that keeps their seborrheic dermatitis in check and allows them to maintain a good quality of life.
What are some natural remedies for seborrheic dermatitis?
Some people find relief from seborrheic dermatitis symptoms with natural remedies, although it’s important to note that these are not a substitute for medical treatment. Some potential natural remedies include:
- Tea tree oil: This essential oil has antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties that may help control Malassezia fungus and reduce inflammation. Always dilute tea tree oil in a carrier oil before applying to the skin.
- Aloe vera: The gel from this plant has soothing, moisturizing, and anti-inflammatory properties that may help calm irritated skin.
- Apple cider vinegar: Diluted apple cider vinegar may help balance the skin’s pH and reduce the growth of Malassezia fungus.
- Coconut oil: This natural oil has antimicrobial properties that may help control fungal growth, but be cautious as it may cause breakouts in some people.
Always patch test a small area of skin before applying any natural remedy more broadly, and discontinue use if irritation occurs. Consult with your dermatologist before trying any natural remedies to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your individual case.
How long does seborrheic dermatitis typically last?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic condition, which means it can last for a long time and may come and go with periods of flare-ups and remission. The duration of flare-ups can vary from person to person and may last anywhere from a few days to several weeks or months.
With proper treatment and management, most people are able to control their seborrheic dermatitis and minimize the frequency and severity of flare-ups. However, it’s important to understand that this is a long-term condition that may require ongoing attention and care.
Are there any underlying medical conditions linked to seborrheic dermatitis?
While seborrheic dermatitis can occur in otherwise healthy individuals, it has been associated with certain underlying medical conditions, including:
- Neurological conditions: Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and spinal cord injuries have been linked to an increased risk of seborrheic dermatitis.
- HIV/AIDS: People with weakened immune systems due to HIV/AIDS are more prone to developing seborrheic dermatitis.
- Psychiatric conditions: Stress, anxiety, and depression have been associated with seborrheic dermatitis, although the exact relationship is not fully understood.
- Metabolic disorders: Conditions like diabetes and obesity have been linked to a higher risk of seborrheic dermatitis.
If you have seborrheic dermatitis and are concerned about potential underlying health issues, consult with your doctor for a comprehensive evaluation.
Key Takeaways
- Seborrheic dermatitis is a common, chronic skin condition that causes redness, itching, and flaking on the scalp, face, and other oil-prone areas of the body.
- While the exact cause is unknown, factors like Malassezia fungus overgrowth, genetics, and immune system dysfunction may play a role.
- Recent research suggests a potential link between seborrheic dermatitis and vitamin deficiencies, particularly zinc and B vitamins.
- Consulting with a dermatologist is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and any underlying vitamin deficiencies.
- Treatment options for seborrheic dermatitis include topical antifungal agents, corticosteroids, and medicated shampoos, while vitamin deficiencies may be addressed through dietary changes and supplementation.
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in zinc and B vitamins, managing stress, and maintaining a gentle skincare routine can help control seborrheic dermatitis symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic condition that requires long-term management, but with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications, most people can effectively control their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
If you are struggling with seborrheic dermatitis or suspect you may have a vitamin deficiency, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with a qualified dermatologist. With the right diagnosis, treatment plan, and support, you can take control of your skin health and find relief from the frustration and discomfort of this challenging condition.
Related articles
Made in USA