Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It causes red, scaly, and itchy patches on the skin, particularly on the scalp, face, and chest. While there are several treatment options available, including topical antifungal creams and corticosteroids, some people may not respond well to these treatments or may experience side effects. In recent years, researchers have been exploring the potential of fluconazole, an oral antifungal medication, as a treatment for seborrheic dermatitis. In this article, we will take a closer look at seborrheic dermatitis, its causes and symptoms, and whether fluconazole can be an effective treatment option.
Understanding Seborrheic Dermatitis
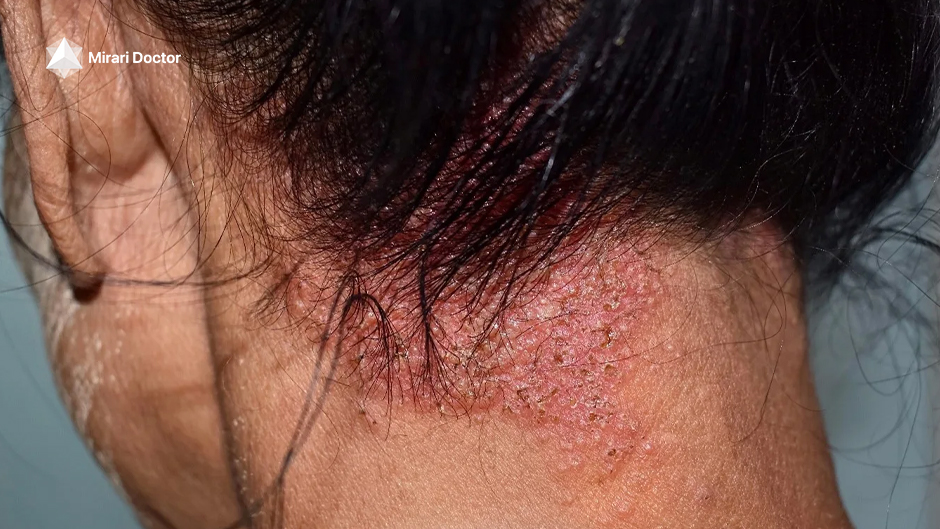
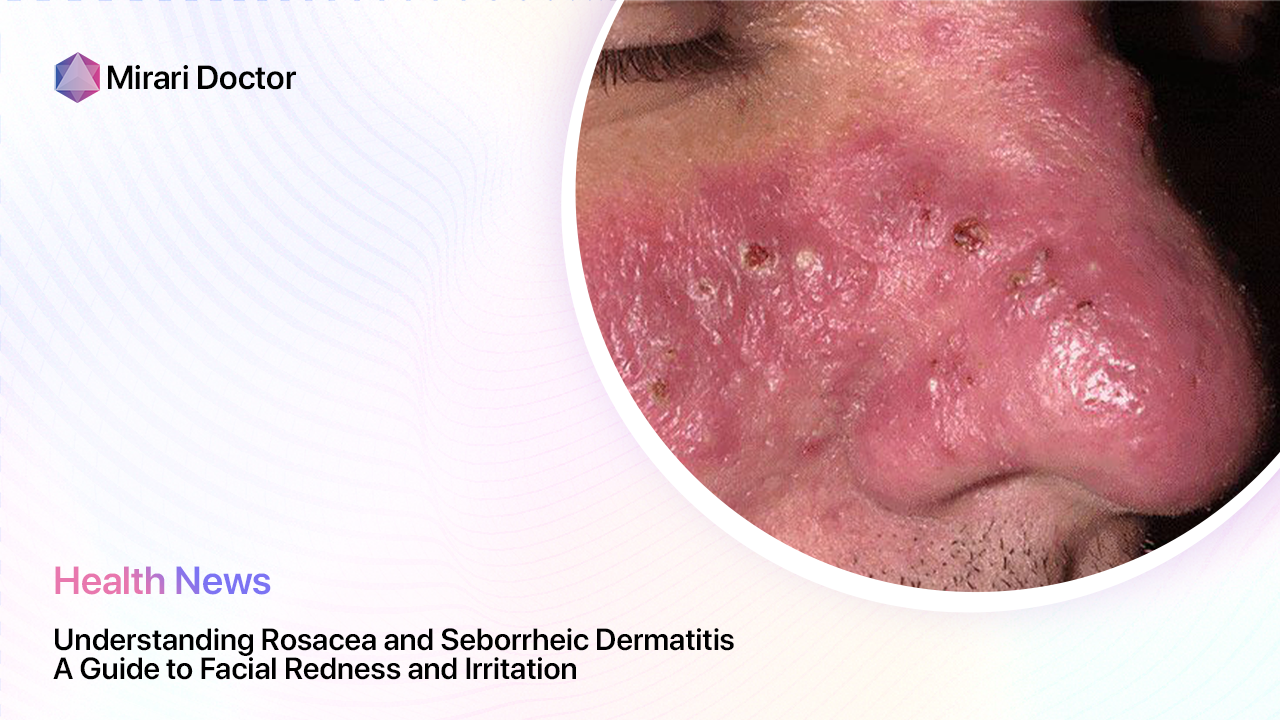
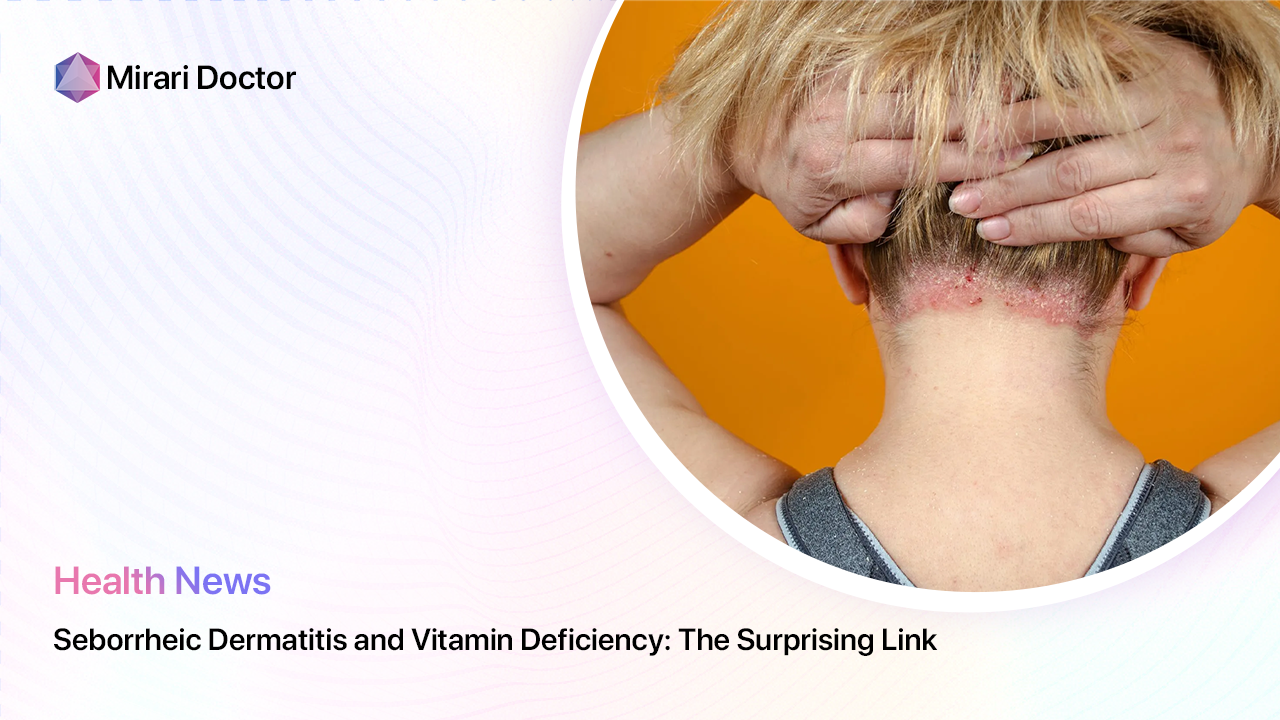
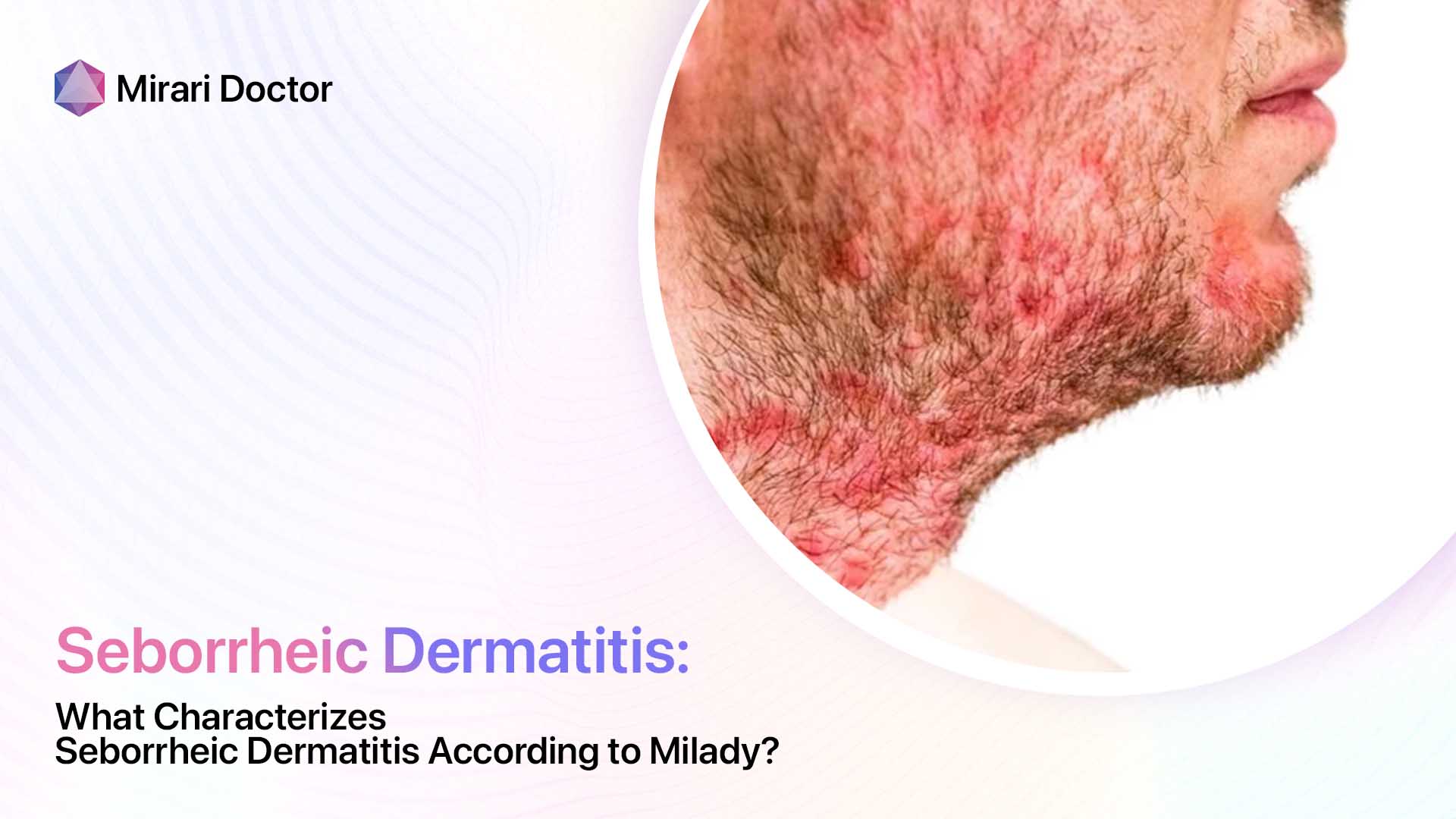
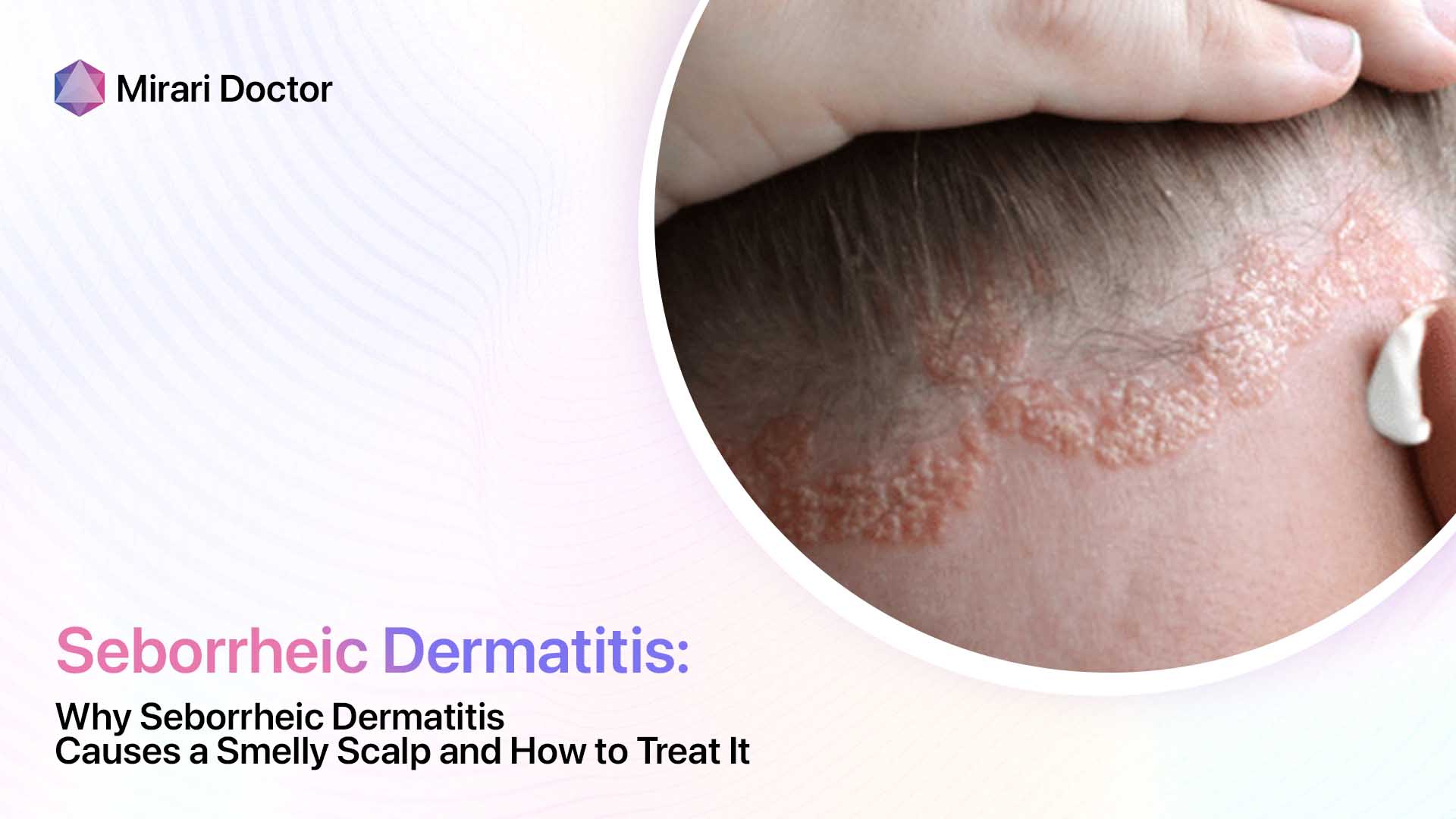
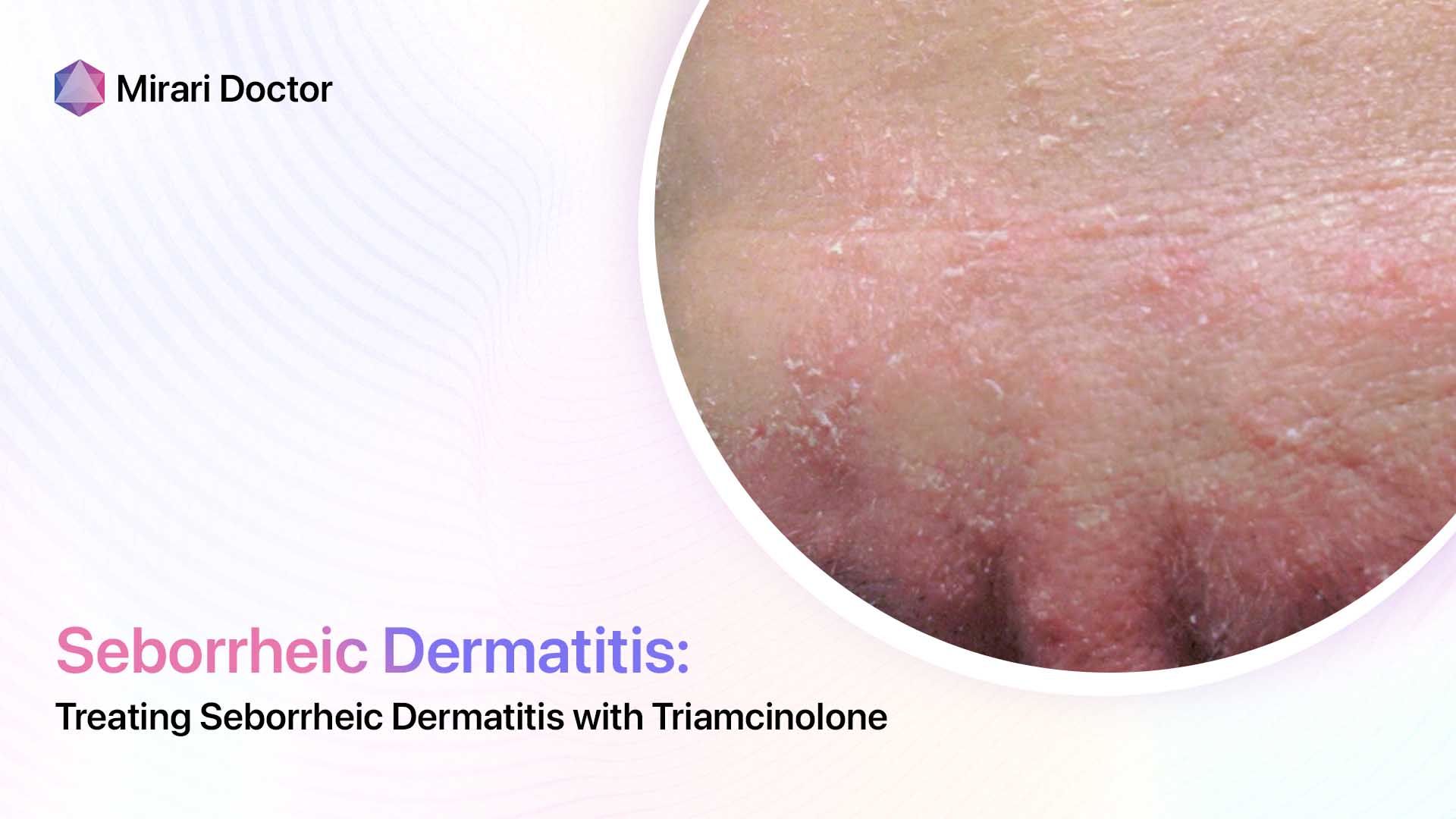
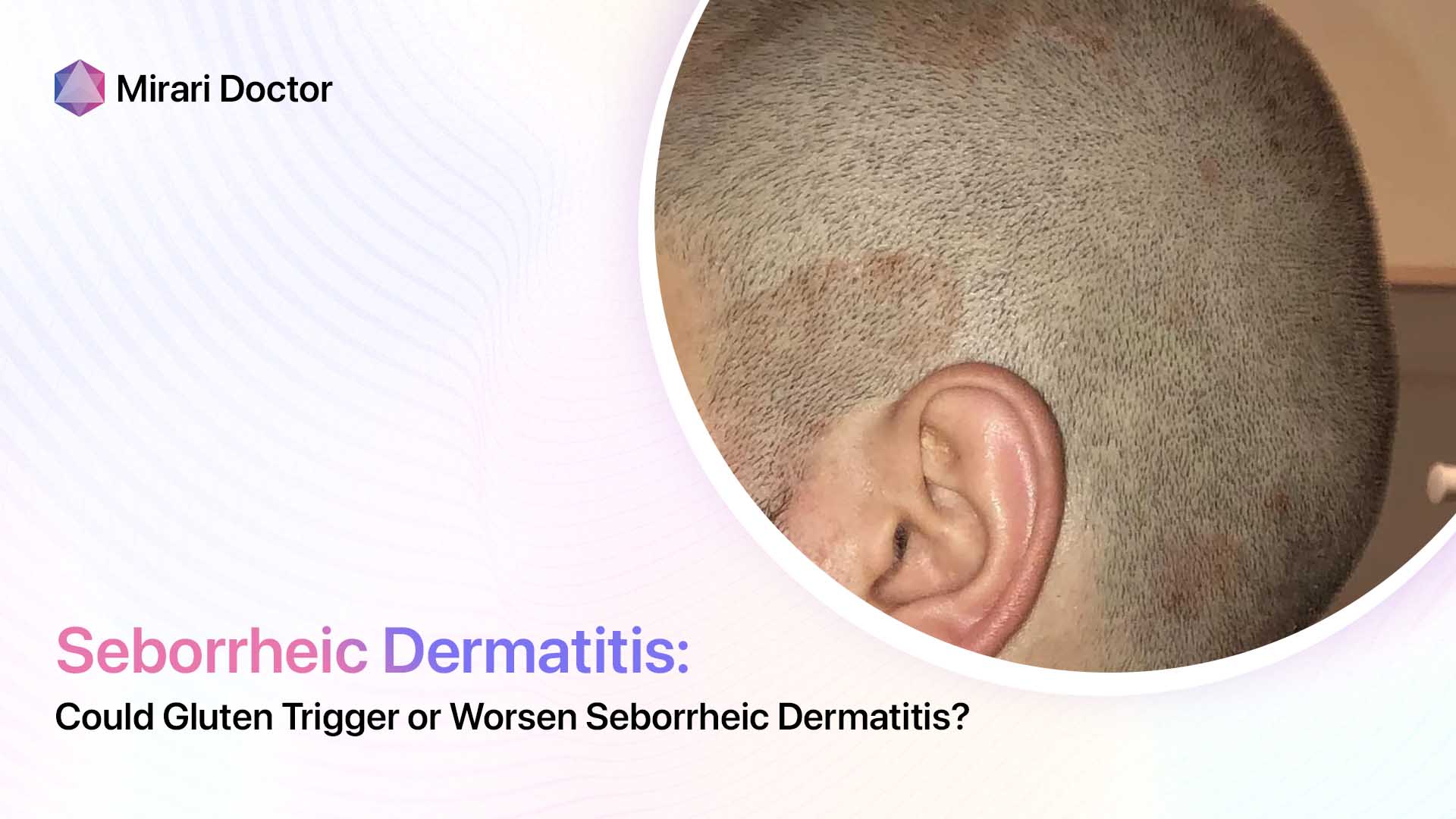
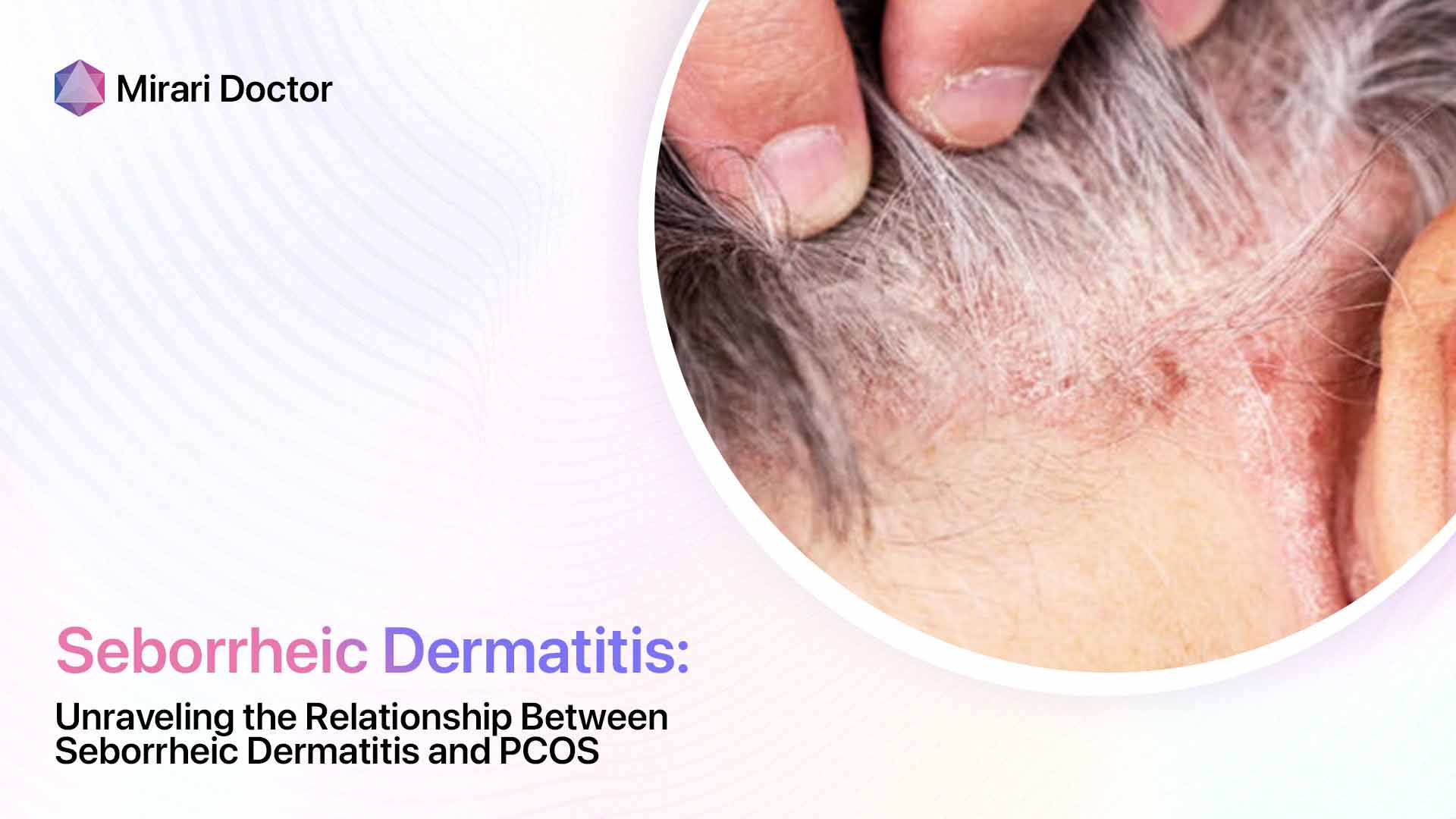
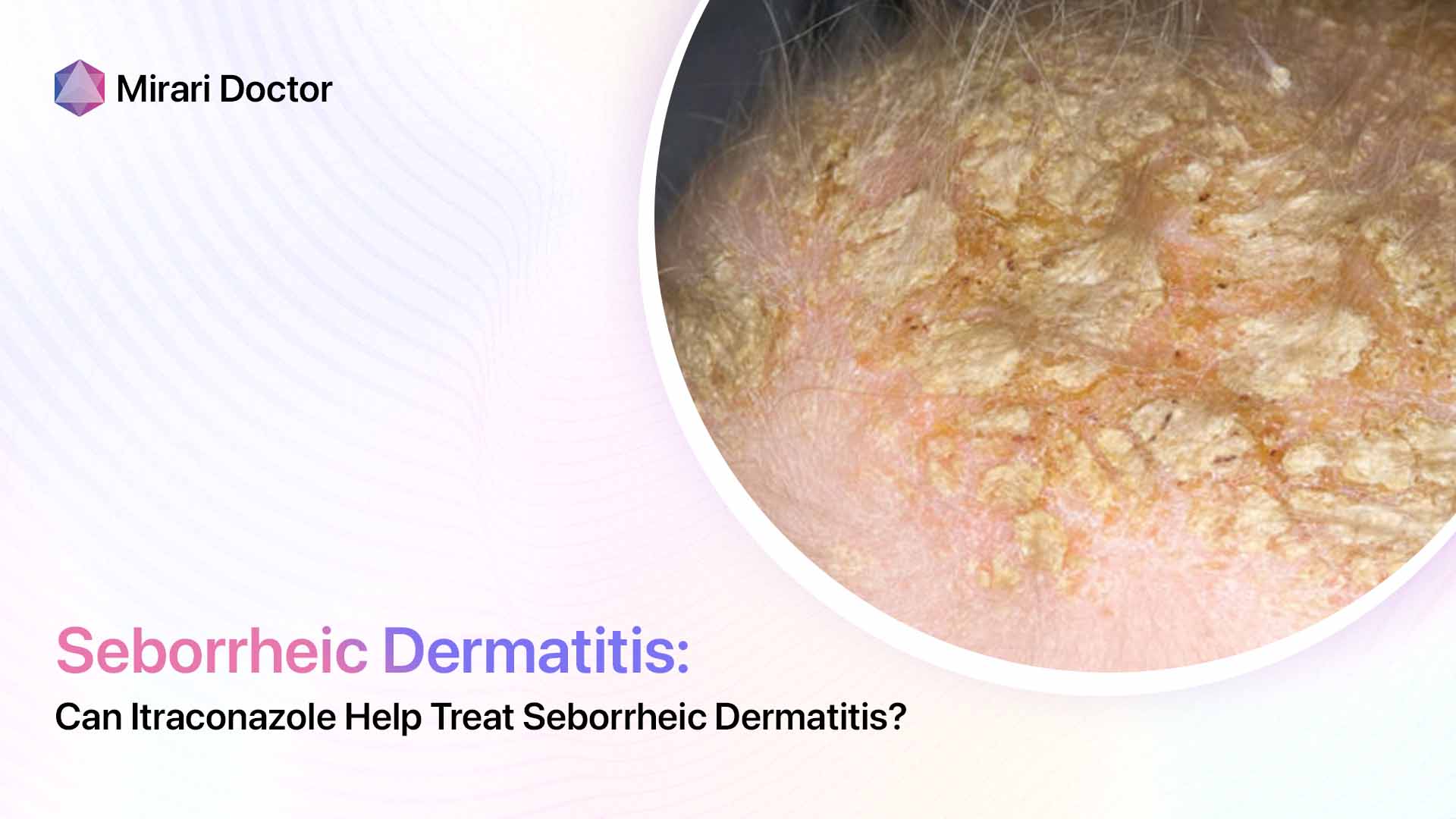
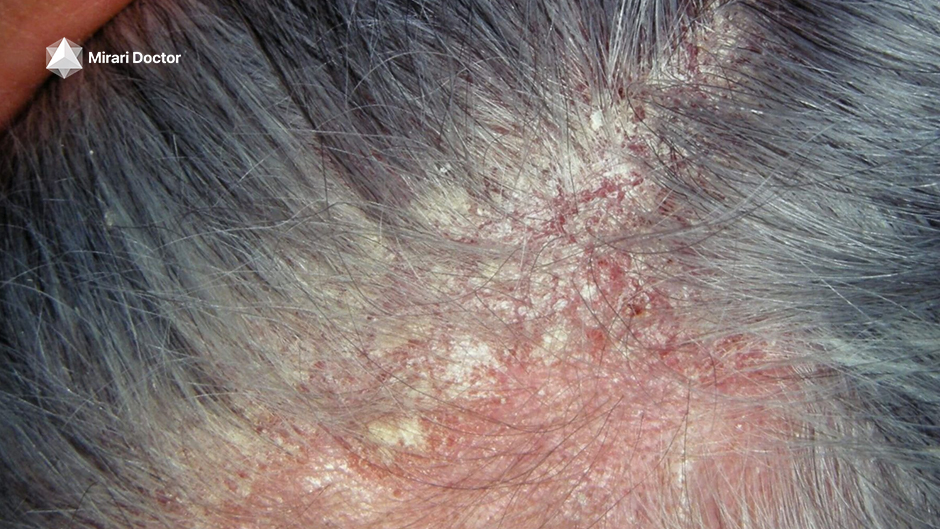
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects areas of the body with a high concentration of sebaceous (oil-producing) glands, such as the scalp, face, and chest. It is characterized by red, scaly, and sometimes greasy patches of skin that can cause itching and discomfort. While the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is not fully understood, it is thought to be related to an overgrowth of a type of yeast called Malassezia, which is commonly found on the skin.
Symptoms and Appearance
The symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis can vary from person to person, but typically include:
- Red, scaly patches on the skin
- Itching and burning sensations
- Flaking or crusting of the skin
- Greasy or oily skin
- Dandruff (when it affects the scalp)
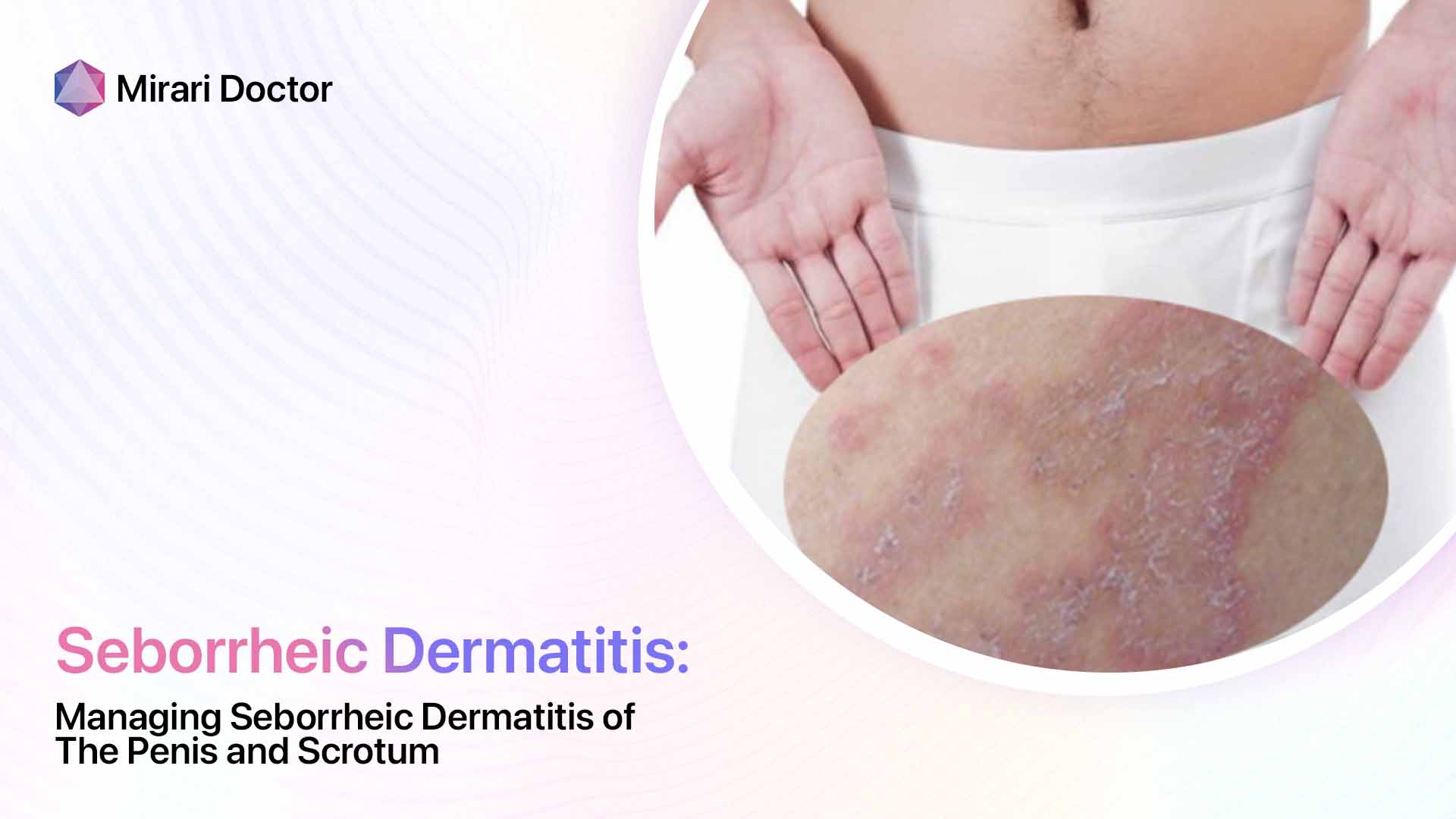
Seborrheic dermatitis can also affect other areas of the body, such as the ears, eyebrows, and eyelids. When it affects the scalp, it is known as seborrheic capitis, and when it affects the eyelids, it is called seborrheic blepharitis.
Causes and Triggers
While the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is not known, several factors are thought to contribute to its development, including:
- Malassezia yeast overgrowth: This type of yeast is commonly found on the skin, but in some people, it can grow excessively and trigger an inflammatory response.
- Hormonal changes: Seborrheic dermatitis is more common in infants and adults between the ages of 30 and 60, suggesting that hormonal changes may play a role.
- Weakened immune system: People with certain medical conditions, such as HIV/AIDS or Parkinson’s disease, may be more susceptible to developing seborrheic dermatitis.
- Stress: Emotional stress can exacerbate symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Cold and dry weather: Symptoms may worsen during the winter months when the air is dry and cold.
Traditional Treatments for Seborrheic Dermatitis
There are several treatment options available for seborrheic dermatitis, depending on the severity of the condition and the areas of the body affected. Some common treatments include:
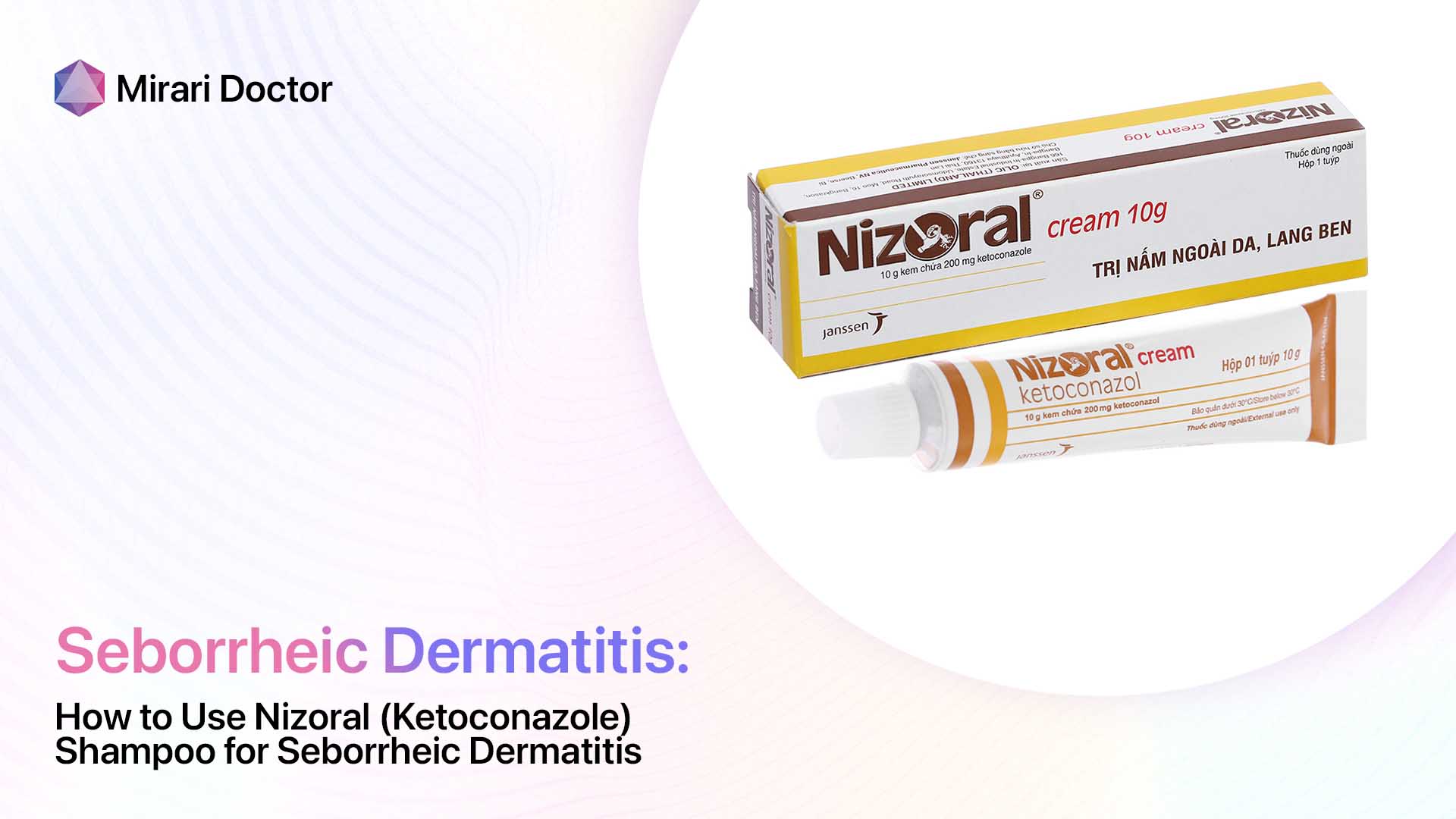
Topical Antifungal Creams
Topical antifungal creams, such as ketoconazole, are often used to treat seborrheic dermatitis. These creams work by reducing the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin and helping to control inflammation. They are typically applied to the affected areas once or twice a day for several weeks.
Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are another common treatment option for seborrheic dermatitis. These medications work by reducing inflammation and itching in the affected areas. They are typically used for short periods of time to avoid potential side effects, such as skin thinning and irritation.
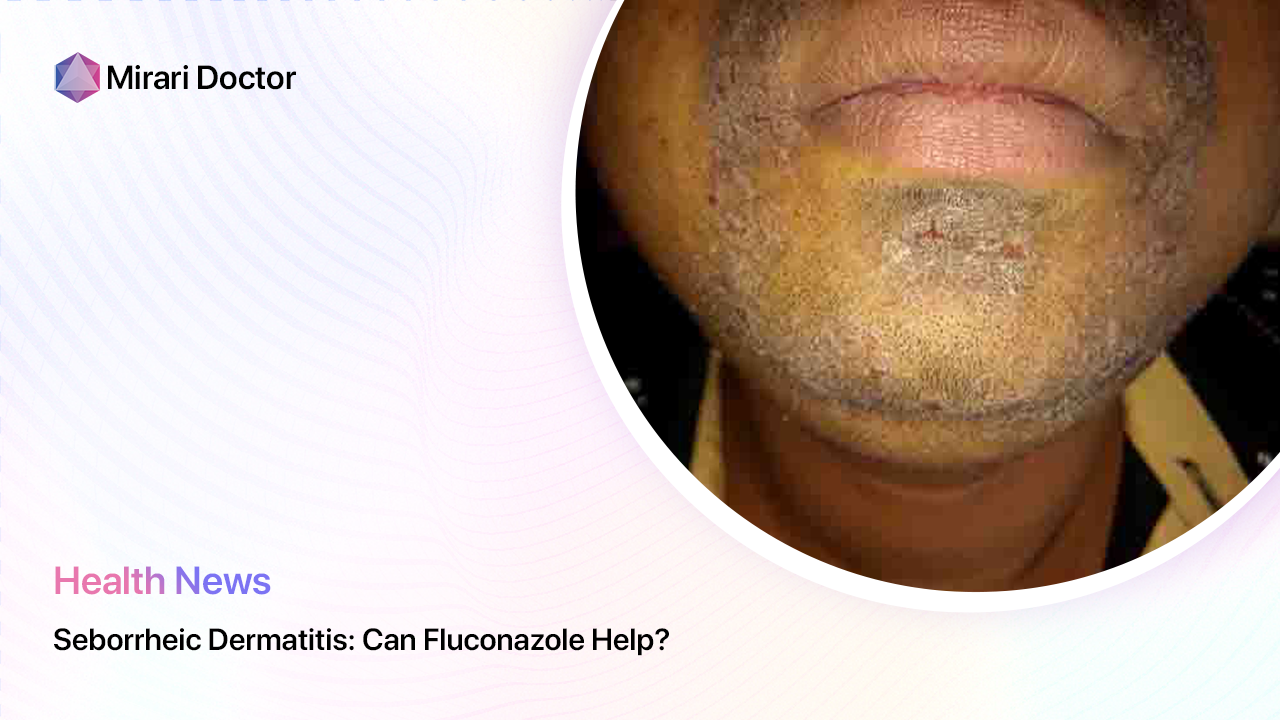
Fluconazole for Seborrheic Dermatitis: Exploring Its Potential
Fluconazole is an oral antifungal medication that has been used to treat various fungal infections, including yeast infections and thrush. In recent years, researchers have been exploring its potential as a treatment for seborrheic dermatitis.
How Might Fluconazole Work?
“While the exact mechanism isn’t fully understood, fluconazole may help by reducing inflammation and possibly controlling Malassezia yeast growth.”
Fluconazole works by inhibiting the growth of fungal cells, including Malassezia yeast. By reducing the overgrowth of this yeast on the skin, fluconazole may help to control the inflammatory response that leads to the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis. Additionally, fluconazole has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which may further contribute to its potential effectiveness in treating this condition.
Effectiveness of Fluconazole for Seborrheic Dermatitis
Several studies have investigated the effectiveness of fluconazole for treating seborrheic dermatitis, with mixed results.
Research and Evidence
A study published in the Journal of Dermatological Treatment found that oral fluconazole, taken once weekly for four weeks, was effective in reducing the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis in a group of 20 patients. The researchers noted that fluconazole was well-tolerated and did not cause any significant side effects.
Another study, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, compared the effectiveness of oral fluconazole with that of a topical antifungal cream (ketoconazole) in treating seborrheic dermatitis. The study found that both treatments were effective in reducing symptoms, but fluconazole was more effective in preventing relapse of the condition.
However, not all studies have shown clear benefits of fluconazole for seborrheic dermatitis. A systematic review published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology concluded that while fluconazole may be effective in some cases, more research is needed to establish its role in the treatment of this condition.
“Studies show some positive results, but more research is needed to confirm fluconazole’s effectiveness for seborrheic dermatitis compared to other treatments.”
Considering Fluconazole: Important Factors
If you are considering fluconazole as a treatment option for seborrheic dermatitis, there are several important factors to keep in mind.
When Might Fluconazole Be Used?
Fluconazole may be considered as a treatment option for seborrheic dermatitis in cases where topical treatments have not been effective, or when the condition is severe or widespread. It may also be considered for people who have a weakened immune system or other medical conditions that make them more susceptible to fungal infections.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
One potential benefit of fluconazole is that it is an oral medication, which means it can be more convenient to use than topical creams that need to be applied directly to the skin. Additionally, because it works systemically (throughout the body), it may be more effective in treating widespread or severe cases of seborrheic dermatitis.
However, fluconazole can also cause side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. It can also interact with certain medications, so it is important to discuss your medical history and any medications you are taking with your doctor before starting treatment.
Alternatives to Fluconazole
If fluconazole is not an appropriate treatment option for you, there are other alternatives that may be effective in managing seborrheic dermatitis. One such option is metronidazole, an antibiotic that has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help to control the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis.
Fluconazole and metronidazole are both potential treatment options for seborrheic dermatitis, but the choice of medication will depend on individual factors such as the severity of the condition, medical history, and potential side effects.

Consulting a Dermatologist for Seborrheic Dermatitis
Importance of Diagnosis and Treatment Plan
If you suspect that you have seborrheic dermatitis, it is essential to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of skin, hair, and nail conditions. They have the expertise and experience to accurately identify seborrheic dermatitis and recommend the most appropriate treatment options based on your individual needs and medical history.
During your consultation, the dermatologist will examine your skin, scalp, and other affected areas, and ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any medications you are currently taking. They may also perform tests, such as a skin scraping or biopsy, to rule out other conditions that may mimic seborrheic dermatitis, such as fungal infections or psoriasis.
Once a diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis is confirmed, your dermatologist will develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. This may include topical medications, such as antifungal creams or corticosteroids, as well as lifestyle recommendations to help manage your symptoms and prevent flare-ups. In some cases, your dermatologist may prescribe oral medications, such as fluconazole or metronidazole, if your condition is severe or does not respond to topical treatments.
“A dermatologist can provide expert guidance on managing seborrheic dermatitis, including the appropriate use of medications like fluconazole or metronidazole.”
Regular follow-up appointments with your dermatologist are important to monitor your progress, adjust your treatment plan as needed, and address any concerns or side effects you may experience. Your dermatologist can also provide guidance on long-term management strategies to help keep your seborrheic dermatitis under control and improve your quality of life.
Living with Seborrheic Dermatitis: Management Tips
Daily Skincare Routine
Developing and maintaining a gentle, consistent skincare routine is crucial for managing seborrheic dermatitis and preventing flare-ups. Here are some tips to incorporate into your daily skincare regimen:
- Cleanse gently: Use a mild, fragrance-free cleanser to wash your face, scalp, and other affected areas twice daily. Avoid harsh scrubbing or hot water, which can irritate your skin and worsen symptoms.
- Moisturize regularly: Apply a light, non-greasy moisturizer to help keep your skin hydrated and reduce flaking and itching. Look for products that are specifically formulated for sensitive or seborrheic skin.
- Use medicated products as directed: If your dermatologist has prescribed topical medications, such as antifungal creams or corticosteroids, use them as directed and do not exceed the recommended frequency or duration of use.
- Protect your skin from the sun: Exposure to sunlight can sometimes exacerbate seborrheic dermatitis. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 when spending time outdoors, and wear protective clothing and hats.
- Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid personal triggers that may worsen your seborrheic dermatitis, such as certain hair products, cosmetics, or environmental factors like cold, dry weather.

Managing Stress and Triggers
Stress is a common trigger for seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups, so finding ways to manage stress is an important part of living with this condition. Some stress-management techniques that may be helpful include:
- Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga
- Engaging in regular exercise, which can help reduce stress and improve overall health
- Getting enough sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule
- Seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional
In addition to managing stress, it’s important to identify and avoid other potential triggers that may worsen your seborrheic dermatitis. Common triggers include:
- Harsh or irritating skincare products, such as those containing alcohol or fragrances
- Certain hair products, particularly those with oily or greasy formulations
- Cold, dry weather conditions
- Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty or menopause
- Certain medications, such as lithium or interferon
By working with your dermatologist and making lifestyle modifications to manage stress and avoid triggers, you can help keep your seborrheic dermatitis under control and improve your overall quality of life.

FAQs about Fluconazole and Seborrheic Dermatitis
Is fluconazole the best treatment for seborrheic dermatitis?
Fluconazole can be an effective treatment option for some people with seborrheic dermatitis, particularly those with moderate to severe cases that have not responded well to topical treatments. However, it may not be the best choice for everyone. The most appropriate treatment for seborrheic dermatitis depends on factors such as the severity of the condition, the location of affected areas, and individual medical history. A dermatologist can help determine whether fluconazole or other treatments, such as topical antifungals or corticosteroids, are the best options for your specific needs.
Can I get fluconazole over the counter for seborrheic dermatitis?
No, fluconazole is a prescription medication and is not available over the counter. It must be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider, such as a dermatologist, after a proper evaluation of your condition. Attempting to self-treat seborrheic dermatitis with fluconazole or other prescription medications without medical supervision can be dangerous and may worsen your symptoms or lead to adverse side effects.
What are the side effects of using fluconazole for seborrheic dermatitis?
Like all medications, fluconazole can cause side effects, although not everyone experiences them. Common side effects of fluconazole may include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Abdominal pain
- Rash
In rare cases, more serious side effects can occur, such as liver damage or allergic reactions. If you experience severe or persistent side effects while taking fluconazole, contact your dermatologist or seek medical attention immediately.
How long does it take for fluconazole to work for seborrheic dermatitis?
The time it takes for fluconazole to work for seborrheic dermatitis can vary from person to person. Some people may notice improvement in their symptoms within a few days of starting treatment, while others may require several weeks of consistent use before seeing significant results. Your dermatologist will provide guidance on how long to take fluconazole and when to expect improvements in your condition. It’s important to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed, even if your symptoms improve earlier, to prevent the recurrence of seborrheic dermatitis.
Are there natural remedies that can help with seborrheic dermatitis?
While there is limited scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of natural remedies for seborrheic dermatitis, some people find relief from certain home treatments. These may include:
- Applying aloe vera gel to soothe irritated skin
- Using tea tree oil shampoo to help control dandruff and scalp irritation
- Washing affected areas with a mild, non-irritating cleanser
- Avoiding triggers, such as harsh skincare products or environmental factors
It’s important to note that natural remedies may not work for everyone and can sometimes cause irritation or allergic reactions. Before trying any natural remedies, consult with your dermatologist to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your specific condition.
Key Takeaways
- Seborrheic dermatitis is a common, chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly, and itchy patches on the skin, particularly on the scalp, face, and chest.
- The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is unknown, but factors such as Malassezia yeast overgrowth, hormonal changes, and a weakened immune system may play a role.
- Traditional treatments for seborrheic dermatitis include topical antifungal creams, such as ketoconazole, and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Fluconazole, an oral antifungal medication, is being explored as a potential treatment option for seborrheic dermatitis, particularly in moderate to severe cases.
- While some studies have shown promising results, more research is needed to fully understand the **effectiveness of fluconazole in the management of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Consulting with a dermatologist is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan for seborrheic dermatitis, which may include fluconazole or other medications.
- Living with seborrheic dermatitis involves developing a gentle, consistent skincare routine, managing stress and triggers, and following your dermatologist’s recommendations for treatment and prevention.
- While fluconazole can be an effective treatment option for some people with seborrheic dermatitis, it is not the best choice for everyone and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition that can be challenging to manage, but with the right treatment approach and lifestyle modifications, it is possible to keep symptoms under control and improve your quality of life. If you suspect you have seborrheic dermatitis or are considering fluconazole as a treatment option, the most important step is to consult with a dermatologist who can provide personalized guidance and support. By working closely with your healthcare provider and staying committed to a consistent management plan, you can effectively navigate the challenges of living with seborrheic dermatitis and maintain healthy, comfortable skin.
Related articles
Made in USA