Fibromyalgia, a chronic pain condition affecting millions worldwide, has long been a challenge for both patients and healthcare providers alike. With its complex array of symptoms and no known cure, those living with fibromyalgia often struggle to find effective relief. However, recent advancements in medical technology have brought new hope to the forefront, particularly in the form of cold plasma therapy. This innovative treatment modality, exemplified by the groundbreaking Mirari Cold Plasma device developed by General Vibronics, harnesses the power of nitric oxide (NO) to address the multifaceted nature of fibromyalgia[4]. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of fibromyalgia, exploring its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and the potential of cold plasma therapy as a revolutionary approach to managing this debilitating condition.
1. What is Fibromyalgia?
Definition and Overview
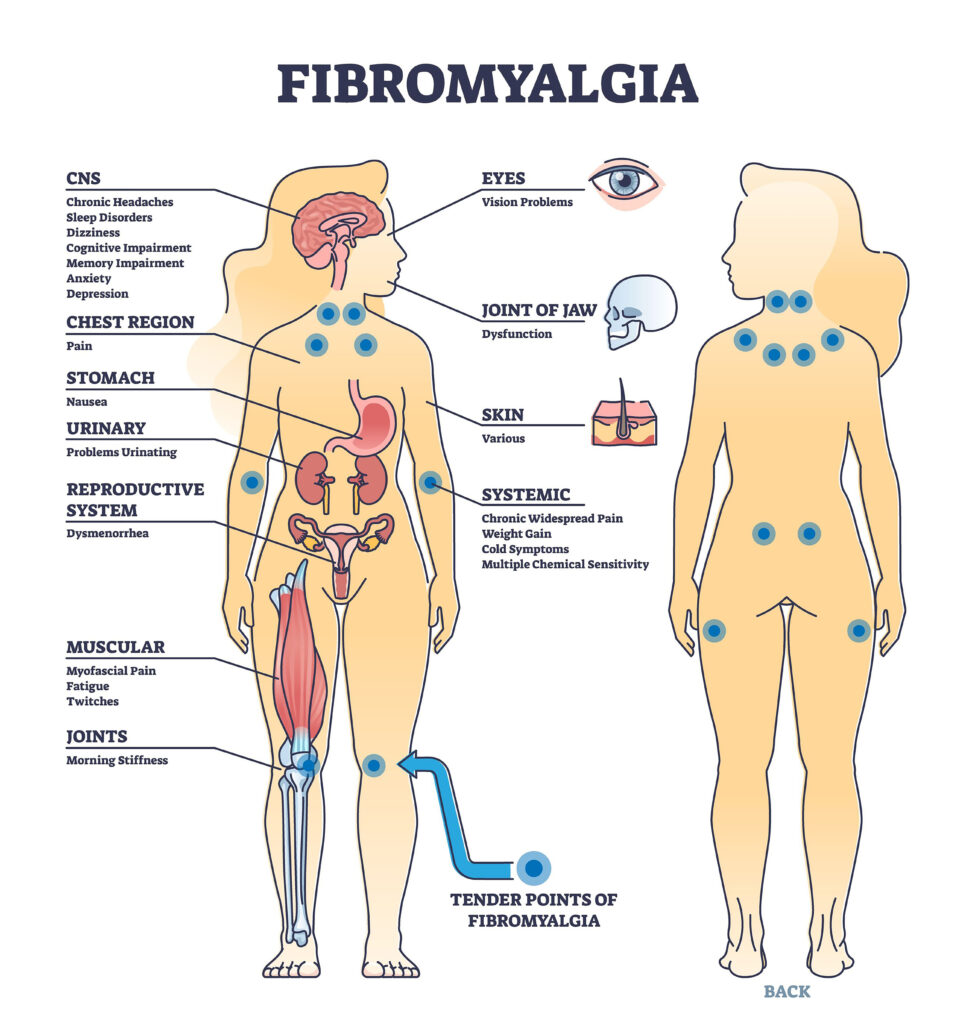
Fibromyalgia is a complex chronic pain disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, often accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbances, cognitive difficulties, and emotional distress[1][2]. It is estimated to affect 2-4% of the global population, with women being disproportionately impacted, outnumbering men by a ratio of approximately 7 to 1[1][2]. The condition can significantly diminish an individual’s quality of life, leading to decreased productivity, increased healthcare costs, and a profound impact on daily functioning[1].
History and Discovery
The term “fibromyalgia” was first coined in 1976 by Dr. Muhammad Yunus, a pioneering rheumatologist who recognized the need for a more specific term to describe the condition[5]. However, descriptions of fibromyalgia-like symptoms can be traced back centuries, with references to widespread pain and fatigue appearing in medical literature as early as the 1800s[5]. It wasn’t until 1990 that the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) established the first diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia, which were subsequently revised in 2010 and 2016 to better capture the multidimensional nature of the condition[5].

Dr. Muhammad Yunus was the first person to coin the term ‘fibromyalgia’ in 1976
2. Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
 |
Chronic PainThe hallmark symptom of fibromyalgia is chronic, widespread pain that persists for at least three months[1][2]. This pain is often described as a constant, deep ache or burning sensation that can affect multiple areas of the body, including the muscles, joints, and soft tissues[1]. Many individuals with fibromyalgia also experience heightened sensitivity to pain (hyperalgesia) and may perceive normally non-painful stimuli as painful (allodynia)[1]. |
 |
FatigueFatigue is another defining characteristic of fibromyalgia, with many patients reporting persistent, debilitating exhaustion that is not alleviated by rest[1][2]. This fatigue can be both physical and mental, often described as a feeling of being “drained” or “exhausted to the core.” It can significantly interfere with daily activities, making even simple tasks feel overwhelming and challenging to accomplish[1]. |
|
|
Sleep DisturbancesSleep problems are common among individuals with fibromyalgia, with many experiencing difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up feeling unrefreshed[1][3]. These sleep disturbances can exacerbate other fibromyalgia symptoms, such as pain and fatigue, creating a vicious cycle that further impacts overall well-being[1]. Studies have shown that individuals with fibromyalgia often have altered sleep patterns, including reduced slow-wave sleep and increased arousal during the night[1]. |
|
|
Cognitive IssuesCognitive difficulties, often referred to as “fibro fog” or “brain fog,” are another prevalent symptom of fibromyalgia[1][2]. Patients may experience problems with memory, concentration, attention, and executive functioning, which can make it challenging to perform daily tasks, engage in conversations, or maintain productivity at work[1]. These cognitive issues can be frustrating and can contribute to increased stress and emotional distress[1]. |
3. Causes and Risk Factors
 |
Genetic FactorsWhile the exact causes of fibromyalgia remain unknown, research suggests that genetic factors may play a role in the development of the condition. Studies have shown that fibromyalgia tends to run in families, indicating a potential genetic predisposition[1]. However, the specific genes involved and the extent of their influence are still under investigation, and more research is needed to fully understand the genetic basis of fibromyalgia[6]. |
|
|
Environmental TriggersEnvironmental factors, such as physical or emotional stress, have been identified as potential triggers for the onset or exacerbation of fibromyalgia symptoms[7]. Traumatic events, including car accidents, surgery, or infections, have been associated with the development of fibromyalgia in some individuals[7]. Additionally, chronic stress, whether from personal, professional, or social sources, may contribute to the manifestation or worsening of fibromyalgia symptoms[7]. |
|
|
Psychological FactorsPsychological factors, such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), are commonly observed in individuals with fibromyalgia[8]. While the exact relationship between these psychological conditions and fibromyalgia is not fully understood, it is believed that they may interact in a bidirectional manner, with each potentially exacerbating the other[8]. Addressing mental health concerns is an essential aspect of comprehensive fibromyalgia management, as it can help improve overall well-being and coping abilities[8]. |
4. Diagnosis of Fibromyalgia
Criteria for Diagnosis
Diagnosing fibromyalgia can be challenging, as there is no single definitive test or biomarker for the condition. The current diagnostic criteria, established by the ACR in 2016, focus on the presence of widespread pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive symptoms, as well as the exclusion of other conditions that may present with similar symptoms[9]. Physicians will typically conduct a thorough medical history, physical examination, and may order various tests to rule out other potential causes of the patient’s symptoms[9].
Common Diagnostic Tests
While there is no specific test for fibromyalgia, healthcare providers may utilize various diagnostic tools to assess the presence and severity of symptoms, as well as to exclude other conditions[10]. These tests may include:
- Blood tests: To evaluate markers of inflammation, thyroid function, vitamin deficiencies, or other underlying health issues.
- Imaging studies: Such as X-rays or MRIs, to assess joint and soft tissue health and rule out conditions like arthritis or spinal disorders.
- Neurological exams: To evaluate cognitive function, reflexes, and sensory perception, helping to identify any underlying neurological conditions.
- Sleep studies: To assess the presence and severity of sleep disturbances, which are common in fibromyalgia.
Blood tests detect inflammation, thyroid issues, and vitamin deficiencies
5. Treatment Options
Medications
Medications are often used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for fibromyalgia, although there is no single drug that can cure the condition[11]. The most commonly prescribed medications for fibromyalgia include:
- Pain relievers: Such as acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or in some cases, opioids, to help manage pain symptoms[11].
- Antidepressants: Including tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) like amitriptyline, and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) like duloxetine, which can help alleviate pain, improve sleep, and address mood disturbances[11].
- Anticonvulsants: Such as pregabalin and gabapentin, which have been shown to reduce pain and improve sleep quality in some individuals with fibromyalgia[11].
Medications help manage fibromyalgia
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a crucial component of fibromyalgia management, as it can help improve strength, flexibility, and overall physical function[12]. A skilled physical therapist can develop an individualized exercise program that includes low-impact aerobic activities, stretching, and strength training exercises[12]. Aquatic therapy, or exercising in a warm water pool, may be particularly beneficial for individuals with fibromyalgia, as it provides a gentle, low-impact environment for movement and relaxation[12].
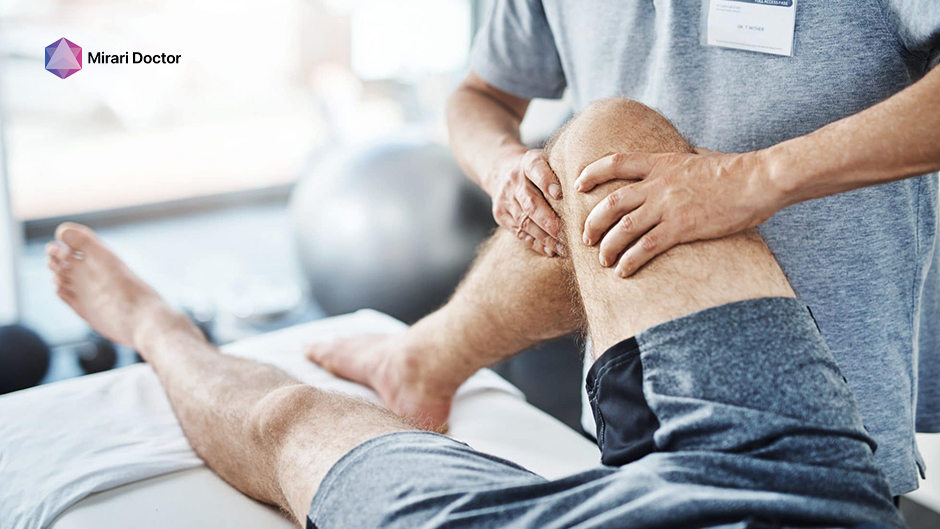
Physical therapy improves strength and flexibility in fibromyalgia
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing fibromyalgia symptoms and improving overall quality of life[13]. Some important lifestyle changes may include:
- Stress management: Incorporating techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
- Sleep hygiene: Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime to improve sleep quality.
- Pacing activities: Learning to balance rest and activity, breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps to avoid overexertion and flare-ups.
- Nutrition: Maintaining a balanced, nutrient-rich diet and staying hydrated to support overall health and well-being[13].

Lifestyle changes aid in managing fibromyalgia symptoms
6. Cold Plasma Therapy
Introduction to Cold Plasma Technology
Cold plasma therapy, also known as non-thermal plasma or low-temperature plasma, is an emerging treatment modality that has shown promise in various medical applications, including wound healing, dermatology, and more recently, in the management of chronic pain conditions like fibromyalgia[4]. Cold plasma is generated by applying an electric field to a gas, causing the gas molecules to become ionized and creating a reactive mixture of electrons, ions, and other reactive species[4].
Cold plasma therapy is an emerging treatment for fibromyalgia and other medical conditions
Mechanism of Action in Fibromyalgia Treatment
The exact mechanisms by which cold plasma therapy may alleviate fibromyalgia symptoms are still under investigation, but current research suggests that it may exert its effects through multiple pathways[4]. One proposed mechanism involves the ability of cold plasma to stimulate the production of nitric oxide (NO), a signaling molecule that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including vasodilation, immune regulation, and pain modulation[4].
Mirari Cold Plasma, a groundbreaking technology developed by General Vibronics, harnesses the power of nitric oxide to address the complex pathophysiology of fibromyalgia[4]. By enhancing the body’s antioxidant defenses and modulating pain signaling pathways, Mirari Cold Plasma may help reduce oxidative stress, inflammation, and pain associated with fibromyalgia[4]. Additionally, the non-invasive and targeted delivery of cold plasma may promote tissue regeneration and repair, further contributing to its potential therapeutic effects[4].

Mirari Cold Plasma uses nitric oxide to reduce pain and promote healing in fibromyalgia
Potential Benefits and Limitations
Cold plasma therapy, particularly Mirari Cold Plasma, offers several potential benefits for individuals with fibromyalgia[4]:
- Non-invasive and targeted delivery: Cold plasma can be applied directly to the affected areas, allowing for localized treatment without the need for systemic medications or invasive procedures[4].
- Potential reduction in pain and inflammation: By modulating pain signaling pathways and reducing oxidative stress, cold plasma therapy may help alleviate the chronic pain and inflammation associated with fibromyalgia[4].
- Improvement in overall quality of life: By addressing the multifaceted symptoms of fibromyalgia, cold plasma therapy may contribute to improved daily functioning, sleep quality, and emotional well-being[4].
- Minimal side effects: Compared to traditional pharmacological treatments, cold plasma therapy has shown a favorable safety profile, with minimal reported side effects[4].
However, it is important to acknowledge that research on the use of cold plasma therapy for fibromyalgia is still in its early stages, and more clinical trials are needed to fully understand its efficacy, optimal treatment protocols, and long-term effects[4]. Additionally, access to cold plasma therapy may be limited, as it is not yet widely available in all healthcare settings[4].
7. Coping and Management Strategies
Stress Management Techniques
Stress management is a vital aspect of coping with fibromyalgia, as stress can exacerbate symptoms and negatively impact overall well-being[15]. Effective stress management techniques may include:
- Relaxation techniques: Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery can help reduce tension and promote a sense of calm[17].
- Mindfulness and meditation: Practicing mindfulness or engaging in regular meditation can help individuals focus on the present moment, reduce stress, and improve emotional regulation[17].
- Time management: Prioritizing tasks, setting realistic goals, and learning to say “no” when necessary can help reduce stress and prevent overexertion[17].
Support Groups
Support groups can provide a valuable resource for individuals living with fibromyalgia, offering a safe space to share experiences, learn coping strategies, and connect with others who understand the challenges of the condition[16]. Participating in support groups, whether in-person or online, can help reduce feelings of isolation, improve self-efficacy, and promote a sense of empowerment[16]. Many organizations, such as the National Fibromyalgia Association, offer resources for finding local support groups or connecting with online communities[16].
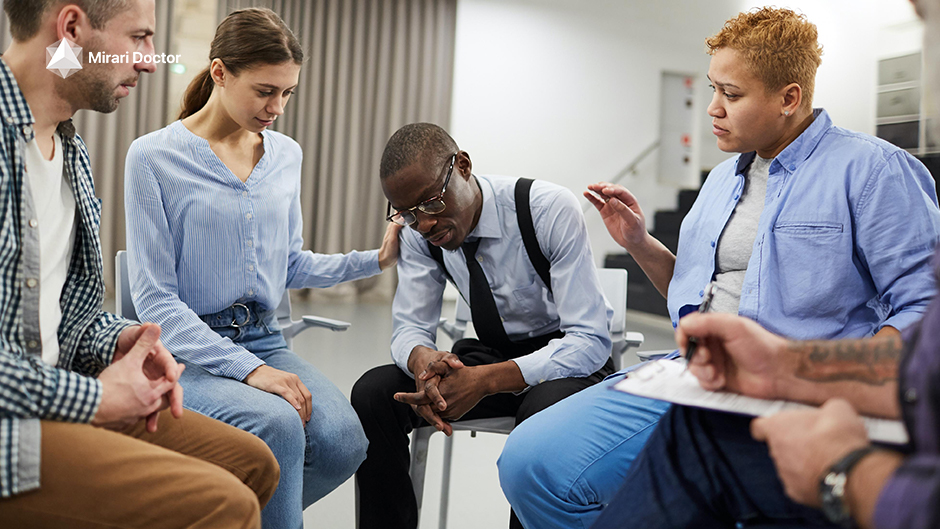

Support groups help fibromyalgia patients feel less isolated and more empowered
8. Alternative Therapies
Cold Plasma as a Complementary Therapy
In addition to conventional treatments, some individuals with fibromyalgia may benefit from incorporating alternative or complementary therapies into their management plan. Cold plasma therapy, such as Mirari Cold Plasma, may be used as a complementary treatment alongside other therapies to provide a more comprehensive approach to managing fibromyalgia symptoms[4].
Other alternative therapies that may be helpful for some individuals include:
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to promote healing and reduce pain[17].
- Massage therapy: Gentle massage techniques can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and promote relaxation[17].
- Chiropractic care: Chiropractors focus on the relationship between the body’s structure and function, using manual adjustments to alleviate pain and improve overall well-being[17].
- Herbal and nutritional supplements: Some individuals may find relief from fibromyalgia symptoms by incorporating certain herbs or nutritional supplements into their diet, such as magnesium, vitamin D, or omega-3 fatty acids. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen[17].
9. Living with Fibromyalgia
Daily Life Adaptations
Living with fibromyalgia often requires making adaptations to daily life to manage symptoms and maintain overall well-being. Some helpful adaptations may include:
- Pacing activities: Learning to balance rest and activity, breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps to avoid overexertion and flare-ups[17].
- Ergonomic modifications: Adjusting workspaces or using assistive devices to reduce physical strain and improve comfort[17].
- Prioritizing self-care: Making time for activities that promote relaxation, stress reduction, and emotional well-being, such as taking warm baths, reading, or engaging in hobbies[17].
- Maintaining a consistent routine: Establishing a regular schedule for sleep, meals, and activities can help improve symptom management and overall functioning[17].

Managing fibromyalgia requires adapting daily life for symptom control and well-being
Impact on Relationships
Fibromyalgia can have a significant impact on personal relationships, as the chronic pain, fatigue, and other symptoms can affect an individual’s ability to participate in social activities and maintain close connections with loved ones[17]. It is essential for individuals with fibromyalgia to communicate openly with their family and friends about their condition, their limitations, and their needs for support[17]. Educating loved ones about fibromyalgia can help foster understanding and empathy, strengthening relationships and promoting a supportive environment[17].
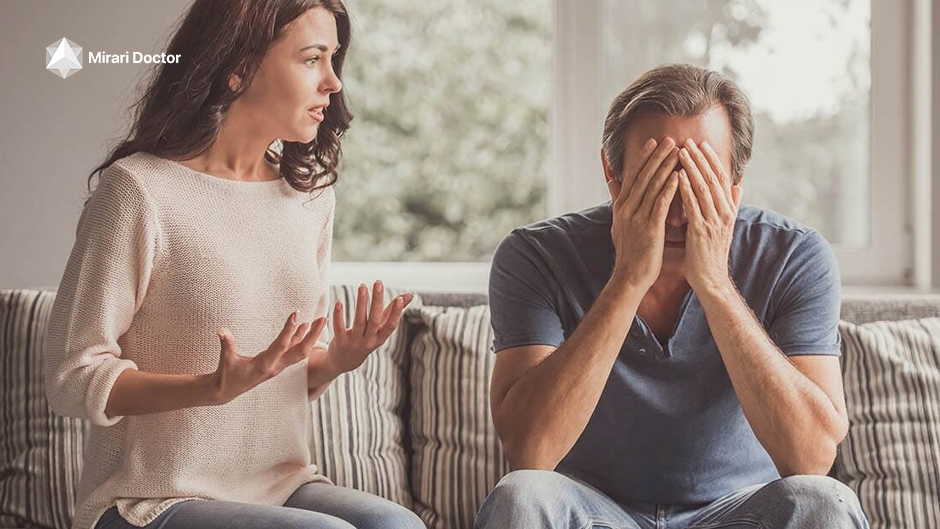

Fibromyalgia strains relationships; open communication and education are key for support
Employment Considerations
For many individuals with fibromyalgia, maintaining employment can be challenging due to the impact of symptoms on work performance and attendance[14]. Some strategies for managing fibromyalgia in the workplace include:
- Discussing accommodations with employers: Collaborating with supervisors or human resources to identify potential workplace accommodations, such as flexible scheduling, ergonomic modifications, or the ability to work from home when needed[14].
- Prioritizing tasks: Focusing on essential tasks and delegating or seeking assistance with less critical responsibilities to manage energy levels and minimize stress[14].
- Taking regular breaks: Incorporating short breaks throughout the workday to stretch, rest, or engage in relaxation techniques can help manage pain and fatigue[14].
- Maintaining open communication: Keeping supervisors and colleagues informed about the impact of fibromyalgia on work performance and the need for accommodations can help foster a supportive and understanding work environment[14].

Open communication about fibromyalgia helps create a supportive work environment
10. Current Research and Future Directions
Ongoing Studies
Research into the causes, mechanisms, and potential treatments for fibromyalgia is ongoing, with numerous studies exploring various aspects of the condition[4]. Some areas of active research include:
- Genetic and epigenetic factors: Investigating the role of specific genes and epigenetic modifications in the development and progression of fibromyalgia[4].
- Neuroimaging studies: Utilizing advanced imaging techniques to better understand brain function, pain processing, and the impact of various treatments on neural activity in individuals with fibromyalgia[4].
- Immune system involvement: Exploring the potential role of immune system dysfunction and inflammation in the pathophysiology of fibromyalgia[4].
- Novel treatment approaches: Evaluating the efficacy and safety of new pharmacological agents, non-pharmacological interventions, and combination therapies for managing fibromyalgia symptoms[4].

Genetic and epigenetic factors influence fibromyalgia development
Emerging Treatments
Advancements in Cold Plasma Technology for Fibromyalgia
As research into the use of cold plasma therapy for fibromyalgia continues, advancements in technology and treatment protocols are expected to emerge. Mirari Cold Plasma, developed by General Vibronics, represents a promising avenue for future fibromyalgia treatment, with its unique focus on harnessing the power of nitric oxide (NO) to address the complex pathophysiology of the condition[4].
Ongoing research aims to optimize treatment parameters, such as plasma composition, duration, and frequency of application, to maximize the therapeutic benefits of cold plasma therapy for individuals with fibromyalgia[4]. Additionally, studies are exploring the potential synergistic effects of combining cold plasma therapy with other established treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, and psychological interventions, to develop more comprehensive and effective management strategies[4].
Potential of Cold Plasma in Improving Quality of Life
The potential of cold plasma therapy, particularly Mirari Cold Plasma, to improve the quality of life for individuals with fibromyalgia is a key focus of current research[4]. By targeting the underlying mechanisms of pain, inflammation, and oxidative stress, cold plasma therapy may offer a novel approach to managing the complex symptoms of fibromyalgia and enhancing overall well-being[4].
As more evidence emerges from clinical trials and real-world applications, the role of cold plasma therapy in the comprehensive management of fibromyalgia will become clearer. Ultimately, the goal is to provide individuals with fibromyalgia a safe, effective, and accessible treatment option that can significantly improve their daily functioning, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life[4].
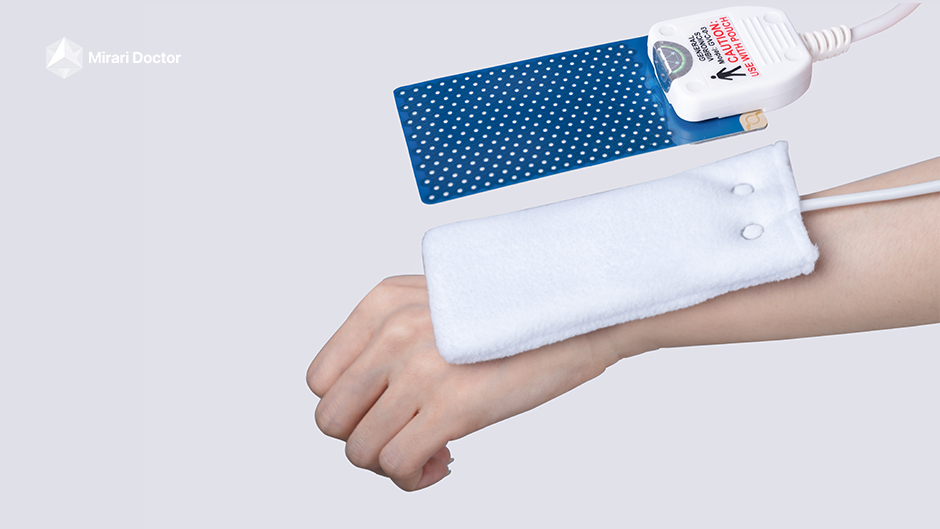
Mirari Cold Plasma may improve fibromyalgia by targeting pain and inflammation
11. Takeaways
- Fibromyalgia is a complex chronic pain disorder characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive difficulties[18].
- The exact causes of fibromyalgia are not fully understood, but genetic, environmental, and psychological factors may play a role in its development.
- Diagnosing fibromyalgia can be challenging, as there is no single definitive test; physicians rely on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and the exclusion of other conditions[19].
- Treatment options for fibromyalgia include medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and emerging therapies such as cold plasma[4].
- Mirari Cold Plasma, developed by General Vibronics, is a promising cold plasma therapy that harnesses the power of nitric oxide (NO) to address the complex pathophysiology of fibromyalgia[4].
- Coping strategies, such as stress management techniques, support groups, and alternative therapies, can help individuals with fibromyalgia manage their symptoms and improve overall quality of life[20].
- Ongoing research is exploring the causes, mechanisms, and potential treatments for fibromyalgia, with a focus on advancing cold plasma technology and optimizing its therapeutic potential[4].
12. FAQs
What are the main symptoms of fibromyalgia?
The main symptoms of fibromyalgia include chronic widespread pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive difficulties (often referred to as “fibro fog”)[18].
How is fibromyalgia diagnosed?
Fibromyalgia is diagnosed based on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and the exclusion of other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. There is no single definitive test for fibromyalgia[19].
What causes fibromyalgia?
The exact causes of fibromyalgia are not fully understood, but research suggests that genetic, environmental, and psychological factors may play a role in the development of the condition.
What treatments are available for fibromyalgia?
Treatment options for fibromyalgia include medications (pain relievers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants), physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and emerging therapies such as cold plasma (Mirari Cold Plasma)[4].
How can cold plasma therapy, like Mirari Cold Plasma, help with fibromyalgia?
Mirari Cold Plasma, developed by General Vibronics, harnesses the power of nitric oxide (NO) to address the complex pathophysiology of fibromyalgia. By modulating pain signaling pathways, reducing inflammation, and promoting tissue repair, cold plasma therapy may help alleviate the symptoms of fibromyalgia and improve overall quality of life[4].
13. References
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS). (n.d.). What is Fibromyalgia? – Symptoms & Treatment. Retrieved from https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/fibromyalgia
- Medscape. (n.d.). Fibromyalgia: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology. Retrieved from https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/329838-overview
- NHS. (n.d.). Fibromyalgia – NHS. Retrieved from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/fibromyalgia/
- Google Patents. (n.d.). US9440057B2 – Therapeutic applications of cold plasma. Retrieved from https://patents.google.com/patent/US9440057B2/en
- PubMed. (n.d.). History of fibromyalgia: past to present. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15361321/
- Clauw, D. J. (2014). Fibromyalgia: A clinical review. JAMA, 311(15), 1547-1555. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/1860480
- Wolfe, F., et al. (2010). The American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia and measurement of symptom severity. Arthritis Care & Research, 62(5), 600-610. Retrieved from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/acr.20140
- Arnold, L. M., et al. (2006). Comorbidity of fibromyalgia and psychiatric disorders. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 67(8), 1219-1225. Retrieved from https://www.psychiatrist.com/jcp/article/pages/2006/v67n08/v67n0810.aspx
- Wolfe, F., et al. (2016). 2016 Revisions to the 2010/2011 fibromyalgia diagnostic criteria. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 46(3), 319-329. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0049017216300285
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Fibromyalgia – Diagnosis and treatment. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/fibromyalgia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354785
- Goldenberg, D. L., et al. (2004). Management of fibromyalgia syndrome. JAMA, 292(19), 2388-2395. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/199231
- Busch, A. J., et al. (2008). Exercise for treating fibromyalgia syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (4). Retrieved from https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD003786.pub2/full
- Häuser, W., et al. (2010). Efficacy of multicomponent treatment in fibromyalgia syndrome: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Arthritis Care & Research, 62(3), 286-295. Retrieved from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/acr.20076
- WebMD. (n.d.). Fibromyalgia, Work, Disability, Benefits, Social Security, and More. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/fibromyalgia/fibromyalgia-work-and-disability
- Colorado Pain Care. (n.d.). The Role of Stress Management in Fibromyalgia Treatment. Retrieved from https://coloradopaincare.com/the-role-of-stress-management-in-fibromyalgia-treatment/
- Fibromyalgia Care Society of America. (n.d.). Services. Retrieved from https://www.fibro.org/services-1
- WebMD. (n.d.). 12 Tips for Coping With Fibromyalgia. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/fibromyalgia/ss/slideshow-fibro-coping-tips
- WebMD. (n.d.). Fibromyalgia: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/fibromyalgia/what-is-fibromyalgia
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Fibromyalgia – Symptoms & causes. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/fibromyalgia/symptoms-causes/syc-20354780
- NCBI. (n.d.). Fibromyalgia: Learn More – Complementary and alternative therapies. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK492996/
Related articles
Made in USA